Introjection defence mechanism is a psychological process in which an individual unconsciously takes on the beliefs, values, and attitudes of another person or group. This can be a positive or negative experience, depending on the nature of the introjected material.
Introjection can play a significant role in personality development, as it can help us to learn and adapt to our environment. However, it can also lead to problems if we introject negative or harmful beliefs.
In this presentation, we will explore the concept of introjection defence mechanism in more detail. We will discuss the different types of introjection, the origins of introjection, and the consequences of introjection. We will also provide some tips on how to identify and address introjection in our own lives.
Definition of Introjection Defence Mechanism

Introjection is a defence mechanism in which an individual unconsciously takes on the beliefs, values, and attitudes of another person or group. It is a process of internalizing external influences and making them part of one’s own personality.
Psychological Processes Involved in Introjection
Introjection involves several psychological processes, including:
- Identification:The individual identifies with another person or group and begins to adopt their characteristics.
- Internalization:The individual takes on the beliefs, values, and attitudes of the other person or group as their own.
- Assimilation:The introjected material is integrated into the individual’s existing personality structure.
Types of Introjection
Introjection is a defense mechanism that involves the unconscious incorporation of external objects or qualities into the self. This can manifest in different forms, with two primary types of introjection:
Positive Introjection
Positive introjection involves the internalization of desirable qualities or values from others. This can result in the development of a strong and healthy self-concept, as the individual adopts positive attributes from their environment.
Examples of positive introjection include:
- A child who internalizes their parents’ values of honesty and integrity.
- An employee who adopts the work ethic and dedication of their successful mentor.
Negative Introjection
Negative introjection involves the internalization of negative qualities or criticisms from others. This can lead to a diminished self-concept and feelings of inadequacy, as the individual internalizes negative messages about themselves.
Examples of negative introjection include:
- A student who internalizes their teacher’s criticism of their intelligence.
- A woman who internalizes her partner’s negative comments about her appearance.
Origins of Introjection

Introjection, the defense mechanism by which people take in the values and behaviors of others, often originates in childhood experiences. These experiences can include:
- Parental Relationships:Children who have parents who are highly critical or demanding may develop introjection as a way to avoid punishment or gain approval. They may internalize their parents’ values and beliefs, even if they do not agree with them, in order to maintain a sense of belonging and acceptance.
Consequences of Introjection
Introjection can have both positive and negative consequences on mental health. On the negative side, introjection can lead to:
- Low self-esteem
- Self-criticism
- Guilt
- Shame
- Depression
- Anxiety
On the positive side, introjection can help people to:
- Internalize positive values and beliefs
- Develop a strong sense of identity
- Form healthy relationships
- Cope with difficult life experiences
Introjection can manifest in daily life in a variety of ways. For example, someone who has introjected the belief that they are not good enough may constantly criticize themselves and avoid taking risks. Someone who has introjected the belief that they are responsible for the happiness of others may feel guilty when they cannot meet the needs of others.
The Psychological Mechanisms that Underlie Introjection
Introjection is a complex psychological process that is not fully understood. However, it is thought to involve the following mechanisms:
- Identification: The person identifies with another person or group and takes on their values and beliefs.
- Internalization: The person incorporates the values and beliefs of the other person or group into their own self-concept.
- Assimilation: The person integrates the values and beliefs of the other person or group into their own existing beliefs and values.
The Role of Introjection in the Development of Personality Disorders
Introjection is thought to play a role in the development of several personality disorders, including:
- Borderline personality disorder
- Narcissistic personality disorder
- Dependent personality disorder
- Obsessive-compulsive personality disorder
In these disorders, introjection can lead to the development of maladaptive coping mechanisms and unhealthy relationships.
Potential Therapeutic Interventions for Addressing Introjection, Introjection defence mechanism
There are a number of therapeutic interventions that can be used to address introjection. These interventions include:
- Cognitive-behavioral therapy
- Psychodynamic therapy
- Humanistic therapy
These therapies can help people to identify and challenge their negative introjections and to develop more positive and healthy beliefs about themselves and others.
Diagnosis of Introjection: Introjection Defence Mechanism
Introjection is a defense mechanism that involves taking in the beliefs, values, and attitudes of others, often unconsciously. It is a complex and multifaceted defense mechanism that can have a significant impact on an individual’s personality and behavior. Diagnosis of introjection can be challenging, as it often occurs in conjunction with other defense mechanisms and may not be readily apparent in an individual’s presentation.
There are a number of criteria that can be used to diagnose introjection as a defense mechanism. These include:
- A history of being exposed to traumatic or stressful events
- Difficulty identifying and expressing one’s own thoughts and feelings
- A tendency to adopt the beliefs and values of others, even when they conflict with one’s own
- Difficulty making decisions or taking action without seeking the approval of others
- A lack of self-esteem and a tendency to feel inferior to others
It is important to note that these criteria are not exhaustive and that not all individuals who meet these criteria will necessarily have introjection as a defense mechanism. Additionally, introjection can occur in varying degrees of severity, and it may be more or less apparent in different situations.
Challenges in Diagnosing Introjection
There are a number of challenges associated with diagnosing introjection. These include:
- Introjection can be difficult to distinguish from other defense mechanisms, such as identification and internalization
- Introjection may not be readily apparent in an individual’s presentation, especially if it is unconscious
- Individuals who use introjection as a defense mechanism may be reluctant to admit to it, as it can be seen as a sign of weakness
Differentiating Introjection from Other Similar Defense Mechanisms
Introjection can be differentiated from other similar defense mechanisms by considering the following factors:
- Identificationinvolves taking on the characteristics of another person, often consciously and voluntarily, in order to feel closer to them or to gain their approval. Introjection, on the other hand, is more unconscious and involves taking in the beliefs and values of others, often without realizing it.
- Internalizationinvolves taking in the values and beliefs of others, but in a more conscious and deliberate way than introjection. Internalization is often seen as a positive process, as it allows individuals to adopt healthy and adaptive values and beliefs. Introjection, on the other hand, can be more problematic, as it can lead to individuals adopting unhealthy or maladaptive beliefs and values.
Using Structured Interviews to Assess for Introjection
Structured interviews can be used to assess for introjection by asking individuals questions about their beliefs, values, and attitudes. These questions can be designed to explore whether individuals have taken on the beliefs and values of others, even when they conflict with their own.
Introjection defence mechanism is a process where an individual unconsciously takes on the beliefs, values, and attitudes of others. This can be a positive or negative experience, depending on the nature of the introjected material. For example, a child who is raised in a loving and supportive environment may introject positive values such as empathy and compassion.
However, a child who is raised in a neglectful or abusive environment may introject negative values such as self-hatred and worthlessness. In some cases, introjection can lead to the development of mental health problems such as anxiety and depression. Tower defence x codes are a type of video game in which the player must defend their base from waves of enemies.
The player can build towers to attack the enemies, and each tower has its own unique abilities. Introjection defence mechanism can be used to help players develop strategies for defending their base. For example, a player who has introjected the value of teamwork may be more likely to build towers that work well together.
For example, an interviewer might ask an individual about their beliefs about success and failure. If the individual’s beliefs about success and failure are very similar to those of their parents or other authority figures, this may be an indication that introjection has occurred.
Using Projective Tests to Assess for Introjection
Projective tests can also be used to assess for introjection. Projective tests are indirect measures of personality that allow individuals to express their thoughts and feelings in a less conscious way. For example, the Thematic Apperception Test (TAT) is a projective test that presents individuals with a series of ambiguous images and asks them to tell a story about each image.
The stories that individuals tell can be analyzed to identify themes and patterns that may indicate introjection.
Using Behavioral Observations to Assess for Introjection
Behavioral observations can also be used to assess for introjection. Behavioral observations involve observing an individual’s behavior in different situations. For example, an observer might note whether an individual is more likely to agree with others, even when they disagree with them, or whether they are more likely to seek the approval of others before making decisions.
Using Self-Report Measures to Assess for Introjection
Self-report measures can also be used to assess for introjection. Self-report measures are questionnaires or inventories that ask individuals to report on their own beliefs, values, and attitudes. For example, the Introjection Scale is a self-report measure that assesses the extent to which individuals introject the beliefs and values of others.
Writing a Case Formulation that Includes a Diagnosis of Introjection
When writing a case formulation that includes a diagnosis of introjection, it is important to consider the following factors:
- The individual’s history of trauma or stress
- The individual’s difficulty identifying and expressing their own thoughts and feelings
- The individual’s tendency to adopt the beliefs and values of others, even when they conflict with their own
- The individual’s difficulty making decisions or taking action without seeking the approval of others
- The individual’s lack of self-esteem and tendency to feel inferior to others
Treating Introjection Using Psychotherapy
Introjection can be treated using psychotherapy. Psychotherapy can help individuals to identify and challenge the beliefs and values that they have introjected from others. It can also help individuals to develop a stronger sense of self and to become more confident in their own thoughts and feelings.
Preventing Introjection from Developing in the First Place
There are a number of things that can be done to prevent introjection from developing in the first place. These include:
- Providing children with a safe and supportive environment
- Encouraging children to express their own thoughts and feelings
- Helping children to develop a strong sense of self-esteem
- Teaching children how to make decisions and take action without seeking the approval of others
Treatment of Introjection
Introjection is a defense mechanism that involves taking in the beliefs, values, and behaviors of others as if they were one’s own. This can lead to a number of problems, including difficulty developing a sense of self, problems with relationships, and difficulty coping with stress.
There are a number of different therapeutic approaches that can be used to treat introjection. These approaches include:
Psychodynamic Therapy
Psychodynamic therapy focuses on helping individuals understand the unconscious motivations behind their behavior. In the context of introjection, psychodynamic therapy can help individuals identify the people and experiences that have led them to internalize certain beliefs and values. Once these unconscious motivations are understood, individuals can begin to challenge them and develop a more authentic sense of self.
Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy
Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) focuses on helping individuals change their thoughts and behaviors. In the context of introjection, CBT can help individuals identify the negative thoughts and beliefs that they have internalized. Once these negative thoughts and beliefs are identified, individuals can begin to challenge them and develop more positive and realistic thoughts and beliefs.
Humanistic Therapy
Humanistic therapy focuses on helping individuals achieve their full potential. In the context of introjection, humanistic therapy can help individuals develop a stronger sense of self-acceptance and self-worth. Once individuals have a stronger sense of self-acceptance and self-worth, they are less likely to internalize the negative beliefs and values of others.
Mindfulness-Based Therapy
Mindfulness-based therapy (MBT) focuses on helping individuals develop mindfulness skills. Mindfulness skills can help individuals become more aware of their thoughts and feelings. This increased awareness can help individuals identify the negative thoughts and beliefs that they have internalized. Once these negative thoughts and beliefs are identified, individuals can begin to challenge them and develop more positive and realistic thoughts and beliefs.
The effectiveness of different treatment methods for introjection depends on a number of factors, including the patient population, the treatment setting, and the therapist experience. However, there is some evidence to suggest that CBT and MBT may be particularly effective in treating introjection.
Some specific examples of therapeutic interventions that have been shown to be effective in treating introjection include:
- Cognitive restructuring:This intervention helps individuals identify and challenge the negative thoughts and beliefs that they have internalized.
- Exposure therapy:This intervention helps individuals gradually face the situations that they fear or avoid.
- Mindfulness meditation:This intervention helps individuals develop mindfulness skills, which can help them become more aware of their thoughts and feelings.
The following table summarizes the different treatment approaches for introjection, their effectiveness, and the factors that influence their effectiveness:
| Treatment Approach | Effectiveness | Factors Influencing Effectiveness |
|---|---|---|
| Psychodynamic Therapy | Moderate | Patient population, treatment setting, therapist experience |
| Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy | High | Patient population, treatment setting, therapist experience |
| Humanistic Therapy | Moderate | Patient population, treatment setting, therapist experience |
| Mindfulness-Based Therapy | High | Patient population, treatment setting, therapist experience |
In summary, there are a number of different therapeutic approaches that can be used to treat introjection. The effectiveness of different treatment methods depends on a number of factors, including the patient population, the treatment setting, and the therapist experience.
However, there is some evidence to suggest that CBT and MBT may be particularly effective in treating introjection.
Case Studies
Introjection can be observed in various individuals, leading to distinct treatment plans and outcomes. This section presents case studies to illustrate the complexities and nuances of introjection.
Introjection often manifests in individuals who have experienced trauma, abuse, or neglect. These experiences can lead to the internalization of negative beliefs and values, which can have significant consequences for the individual’s well-being.
Treatment Plans
Treatment plans for individuals experiencing introjection typically involve a combination of psychotherapy and medication. Psychotherapy can help individuals to identify and challenge the negative beliefs and values that they have internalized. Medication can be used to manage symptoms of anxiety and depression that may be associated with introjection.
Outcomes
The outcomes of treatment for introjection can vary depending on the individual’s circumstances and the severity of their symptoms. However, with appropriate treatment, individuals can experience significant improvements in their mental health and well-being.
Cultural Considerations
Cultural factors play a significant role in shaping the development, expression, and treatment of introjection. Different cultures have unique beliefs, values, and practices that influence how individuals internalize and process external experiences.
In some cultures, introjection may be considered a positive or adaptive mechanism, while in others, it may be seen as a sign of weakness or vulnerability. The cultural context can also influence the types of introjects that are adopted, as well as the consequences and treatment options available.
Role of Culture in the Treatment of Introjection
Culture plays a vital role in the treatment of introjection. Culturally sensitive interventions that take into account the beliefs, values, and practices of the individual can be more effective in addressing the underlying causes and consequences of introjection.
For example, in cultures where introjection is seen as a positive mechanism, therapy may focus on helping individuals to identify and integrate healthy introjects, while in cultures where introjection is seen as a negative mechanism, therapy may focus on helping individuals to challenge and reject unhealthy introjects.
Table: Cultural Factors Influencing Introjection
| Cultural Factor | Influence on Introjection |
|---|---|
| Beliefs about the self | Influence the types of introjects that are adopted and the consequences of introjection. |
| Values | Shape the cultural norms and expectations that influence the development and expression of introjection. |
| Practices | Can reinforce or challenge introjection, depending on the specific cultural context. |
Specific Examples of Cultural Impact on Introjection Treatment
- In some Asian cultures, introjection is seen as a way to maintain harmony and social order. In these cultures, therapy may focus on helping individuals to identify and integrate healthy introjects that promote social cohesion.
- In some Western cultures, introjection is seen as a sign of weakness or vulnerability. In these cultures, therapy may focus on helping individuals to challenge and reject unhealthy introjects that hinder personal growth and autonomy.
Ethical Implications of Cultural Considerations
Cultural considerations in the treatment of introjection raise important ethical implications. Therapists must be aware of their own cultural biases and the potential for cultural misunderstandings.
It is essential to respect cultural diversity and to tailor interventions to the specific needs and values of the individual. This includes using culturally sensitive language, considering the cultural context of the presenting problem, and involving family and community members in the treatment process when appropriate.
Compare and contrast introjection with other defence mechanisms, such as projection, displacement, and rationalization.
Introjection, projection, displacement, and rationalization are all defence mechanisms that individuals use to cope with anxiety and other uncomfortable emotions. However, there are some key similarities and differences between these defence mechanisms.
Purpose
The purpose of all defence mechanisms is to protect the individual from anxiety. However, each defence mechanism has a different way of doing this.
- Introjection: The individual takes on the beliefs and values of others, even if they are not their own.
- Projection: The individual attributes their own unacceptable thoughts and feelings to others.
- Displacement: The individual redirects their unacceptable thoughts and feelings to a less threatening target.
- Rationalization: The individual creates a logical explanation for their unacceptable thoughts and feelings.
Manifestations
The manifestations of defence mechanisms can vary depending on the individual. However, there are some common manifestations of each defence mechanism.
- Introjection: The individual may appear to be conforming to the expectations of others, even if they do not agree with those expectations.
- Projection: The individual may accuse others of having the same unacceptable thoughts and feelings that they have.
- Displacement: The individual may express their unacceptable thoughts and feelings in a way that is not directly threatening to themselves or others.
- Rationalization: The individual may create elaborate explanations for their unacceptable thoughts and feelings.
Impact on the individual’s psychological well-being
The impact of defence mechanisms on the individual’s psychological well-being can vary depending on the individual and the situation. However, some general statements can be made about the impact of each defence mechanism.
- Introjection: Introjection can help the individual to feel more connected to others and to feel more accepted. However, it can also lead to the individual feeling like they are not being true to themselves.
- Projection: Projection can help the individual to avoid feeling guilty or ashamed about their unacceptable thoughts and feelings. However, it can also lead to the individual having difficulty forming close relationships.
- Displacement: Displacement can help the individual to express their unacceptable thoughts and feelings in a way that is not directly threatening to themselves or others. However, it can also lead to the individual feeling like they are not being honest with themselves or others.
- Rationalization: Rationalization can help the individual to feel more in control of their unacceptable thoughts and feelings. However, it can also lead to the individual having difficulty accepting reality.
– Provide a detailed definition of introjection.

Introjection is a defense mechanism in which an individual takes in or incorporates aspects of another person into their own personality. This can include both positive and negative qualities, and can be conscious or unconscious.
Introjection is often seen as a way of coping with difficult emotions or experiences. By taking in aspects of another person, the individual can feel less alone or overwhelmed. Introjection can also be a way of idealizing or devaluing another person, as the individual may introject only the positive or negative aspects of that person.
Types of Introjection
There are many different types of introjection, including:
- Positive introjection: This occurs when an individual takes in positive aspects of another person, such as their kindness, intelligence, or strength.
- Negative introjection: This occurs when an individual takes in negative aspects of another person, such as their anger, hatred, or jealousy.
- Conscious introjection: This occurs when an individual is aware of the process of introjection and is able to control it.
- Unconscious introjection: This occurs when an individual is not aware of the process of introjection and is unable to control it.
Introjection in Film

Introjection is a defense mechanism that involves taking on the characteristics, beliefs, or values of another person. In film, introjection can be used to convey psychological themes and to explore the complexities of human relationships.
One example of introjection in film is the character of Forrest Gump. Forrest is a simple-minded man who is often taken advantage of by others. However, he is also a kind and compassionate person who always tries to see the best in people.
Over the course of the film, Forrest introjects the values of his mother, who taught him to always be kind and to never give up on his dreams.
Another example of introjection in film is the character of Anakin Skywalker in the Star Wars prequels. Anakin is a young Jedi who is tempted by the dark side of the Force. He eventually succumbs to the dark side and becomes Darth Vader.
However, even as Darth Vader, Anakin still retains some of his former goodness. He eventually redeems himself by sacrificing his life to save his son, Luke.
Introjection can be a powerful tool for conveying psychological themes in film. It can be used to explore the complexities of human relationships, the struggle between good and evil, and the power of redemption.
The Use of Introjection to Convey Psychological Themes
Introjection can be used to convey a variety of psychological themes in film, including:
- The complexities of human relationships
- The struggle between good and evil
- The power of redemption
By exploring these themes through the lens of introjection, filmmakers can create powerful and moving stories that resonate with audiences on a deep level.
Introjection in Art
Introjection, a psychological defense mechanism, finds expression in art in various ways. By embodying external qualities, ideas, or people into the self, artists can explore complex psychological themes and create works that resonate with viewers on a deeply personal level.The psychological significance of introjection in art lies in its ability to provide a means of self-exploration and expression.
Through introjection, artists can grapple with their own identities, motivations, and relationships, and communicate these experiences to others. By embodying external elements, artists can explore the boundaries of the self, challenge societal norms, and create works that provoke thought and evoke emotion.
Introjection of Cultural Values
Artists often introject cultural values, beliefs, and norms into their work. This can manifest in the choice of subject matter, the use of symbolism, or the overall style and tone of the piece. By embodying these external elements, artists can comment on the impact of culture on the individual, explore social issues, and create works that reflect the collective experiences of a particular group.
Introjection defence mechanism is a psychological process whereby individuals unconsciously adopt the values, beliefs, and behaviors of others. In the context of military operations, this mechanism can manifest in the adoption of advanced weaponry, such as the daniel defence delta 5 , to enhance self-protection and assert dominance.
Through introjection, individuals internalize external attributes, bolstering their sense of self-worth and competence. This process can influence decision-making, leading to increased risk-taking and a reliance on external validation.
Conclusion
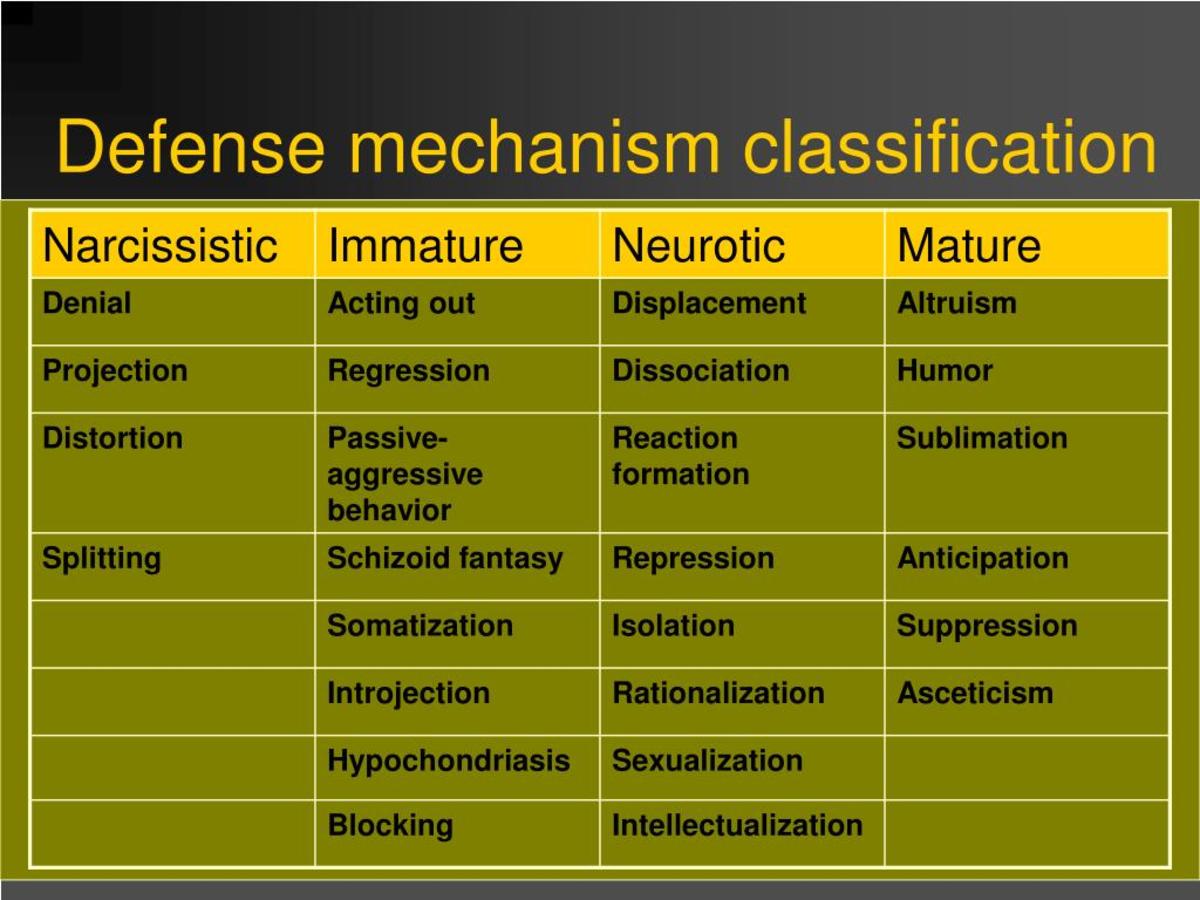
Introjection is a complex and multifaceted defense mechanism that can have a significant impact on mental health and well-being. It is important to be aware of the potential consequences of introjection and to seek professional help if necessary.
Individuals who struggle with introjection may benefit from therapy that focuses on developing healthier coping mechanisms and improving self-esteem. With the right support, individuals can learn to manage their emotions in a healthy way and to develop a more positive sense of self.
Answers to Common Questions
What is introjection defence mechanism?
Introjection defence mechanism is a psychological process in which an individual unconsciously takes on the beliefs, values, and attitudes of another person or group.
What are the different types of introjection?
There are two main types of introjection: positive introjection and negative introjection. Positive introjection occurs when we take on the positive qualities of another person or group. Negative introjection occurs when we take on the negative qualities of another person or group.
What are the origins of introjection?
Introjection is thought to originate in childhood, when we learn to identify with our parents and other caregivers. We may introject their beliefs, values, and attitudes in order to feel loved and accepted.
What are the consequences of introjection?
Introjection can have both positive and negative consequences. Positive introjection can help us to learn and adapt to our environment. Negative introjection can lead to problems if we introject negative or harmful beliefs.

Whitney Morris is a renowned author with a passion for military history and strategic analysis. Born in Jakarta, Indonesia, Defense developed a deep fascination for warfare and national defense from a young age. His unwavering interest in military strategy, combined with his natural storytelling ability, has earned him a reputation as an engaging and insightful writer in the field.