Army promotions represent a crucial aspect of military service, serving as a pathway for soldiers to advance their careers and contribute more significantly to the armed forces. This intricate system, encompassing various promotion types, processes, and eligibility criteria, plays a vital role in shaping the structure, leadership, and overall effectiveness of the army.
Understanding the complexities of army promotions is essential for aspiring soldiers who seek to climb the ranks and achieve their full potential. This guide aims to demystify the promotion system, providing comprehensive information on the different types of promotions, the application process, eligibility requirements, benefits, challenges, and the impact of promotions on unit performance and military readiness. By navigating the nuances of this system, soldiers can gain valuable insights and strategies to enhance their chances of advancement.
2. Promotion Process
The army’s promotion process is a complex and often opaque system, designed to recognize merit and potential while ensuring the right individuals are placed in leadership roles. This process, however, has been subject to criticism for its lack of transparency and its potential for bias.
2.1. Application Process
The application process for army promotion typically involves submitting a detailed application form, along with supporting documentation that demonstrates the applicant’s qualifications.
- The application form usually requires the applicant to provide information about their education, training, experience, performance evaluations, awards and decorations, and any other relevant information that showcases their suitability for promotion. This information is then reviewed by a promotion board.
- There are strict timelines for submitting applications, and late submissions are typically not accepted. Missing deadlines can be a significant obstacle to promotion, as it can be interpreted as a lack of seriousness or commitment.
- The applicant must also submit supporting documentation, such as performance evaluations, training records, and letters of recommendation. These documents are crucial in providing evidence of the applicant’s abilities and potential. The quality and completeness of this documentation can heavily influence the outcome of the promotion process.
2.2. Review and Selection Process, Army promotions
The promotion process involves a rigorous review and selection process conducted by a promotion board or committee.
- Promotion boards typically consist of senior officers, who are tasked with evaluating the applications and recommending candidates for promotion. The board members are usually selected based on their rank, experience, and expertise in the specific area of the applicant’s specialty.
- The board members use a variety of criteria to evaluate the applications, including the applicant’s performance record, leadership skills, potential for advancement, and overall suitability for the higher rank. These criteria are often weighted differently, with some factors being considered more important than others.
- The board members then rank the candidates based on their evaluation, and the top-ranked candidates are recommended for promotion. This ranking system can be subjective, and there have been allegations of bias and favoritism in the promotion process.
2.3. Notification and Appeal Process
Once the promotion board has completed its review, the decision is communicated to the candidates.
- Candidates are typically notified of the promotion board’s decision in writing, and the notification may include information about the reasons for the decision. This notification is usually sent within a specific timeframe, and any delays can be cause for concern.
- Candidates who are not selected for promotion have the right to appeal the decision. The appeal process typically involves submitting a written request for reconsideration, outlining the reasons for the appeal. Appeals are often reviewed by a higher-level board or committee, and the decision of this board is usually final.
- The grounds for appeal can vary, but they typically include allegations of bias, errors in evaluation, or other procedural irregularities. The appeal process is a critical safeguard against unfair or arbitrary promotion decisions, but it can be a lengthy and complex process.
2.4. Role of Performance Evaluations and Training Records
Performance evaluations and training records play a crucial role in the army’s promotion process.
- Performance evaluations are used to assess an individual’s performance over a specific period, usually a year. These evaluations are typically conducted by the individual’s supervisor and can be used to highlight strengths, weaknesses, and areas for improvement.
- Training records document an individual’s participation in various training programs, courses, and exercises. These records provide evidence of an individual’s professional development and their ability to acquire new skills and knowledge.
- Both performance evaluations and training records are carefully reviewed by the promotion board, and they can be used to support or refute the applicant’s claims about their qualifications and potential for promotion.
2.5. Guide for Soldiers Seeking Promotion to the Rank of Sergeant
Aspiring to the rank of Sergeant is a significant step in an army career, demanding dedication and commitment.
- Promotion to Sergeant typically requires a certain amount of time in service, a clean disciplinary record, and a strong performance evaluation. The specific requirements can vary depending on the branch of the army and the specific unit.
- Soldiers should begin preparing for promotion early, by focusing on improving their performance, seeking out training opportunities, and building strong relationships with their superiors.
- When preparing for an interview with a promotion board, soldiers should be prepared to discuss their experience, skills, and leadership qualities. They should also be able to articulate their vision for the future and their commitment to serving the army.
- Soldiers seeking promotion to Sergeant should familiarize themselves with the specific requirements for the rank, the application process, and the appeal process. They should also seek guidance from their superiors and mentors who can provide valuable advice and support.
Promotion Benefits
Promotion in the army is not just about a change in rank or a pay raise. It signifies a significant step forward in a soldier’s career, unlocking a wealth of opportunities and advantages that can shape their future. The benefits extend far beyond financial gains, impacting a soldier’s professional development, leadership skills, and overall career trajectory.
Career Advancement and Future Opportunities
Promotion in the army opens doors to a wider range of career paths and opportunities. A higher rank often grants access to specialized training programs, leadership roles, and assignments that can significantly enhance a soldier’s skillset and expertise. This, in turn, increases their marketability within the military and in the civilian sector.
- Increased Responsibility: Promotions often come with increased responsibility, allowing soldiers to take on more challenging and impactful roles. This experience builds their confidence and leadership skills, preparing them for future leadership positions.
- Enhanced Skills and Knowledge: Higher-ranking positions often require specialized training and knowledge, which can be obtained through promotion-related programs. This allows soldiers to expand their skillset and become more versatile and valuable assets to the military.
- Greater Influence: Promotions often grant soldiers a greater voice and influence within the military hierarchy. This allows them to contribute more effectively to decision-making processes and advocate for the needs of their units and fellow soldiers.
Leadership Development and Professional Growth
Promotion in the army is inherently linked to leadership development. As soldiers progress through the ranks, they are entrusted with greater responsibility, requiring them to hone their leadership skills and inspire their teams.
“Leadership is not about rank, but about influence. It’s about the ability to inspire and motivate others to achieve a common goal.”
- Mentorship and Coaching: Higher-ranking officers often act as mentors and coaches for junior soldiers, providing guidance and support in their professional development. This fosters a culture of learning and growth within the military.
- Strategic Thinking: Promotion often requires soldiers to develop strategic thinking skills, allowing them to analyze situations, make informed decisions, and plan for the future. This is crucial for effective leadership and success in the military.
- Problem-Solving and Decision-Making: As soldiers rise through the ranks, they are increasingly responsible for problem-solving and decision-making in complex and challenging situations. This builds their critical thinking and decision-making abilities, essential for leadership roles.
Impact of Promotions on Unit Performance

Promotions are a vital component of any military organization, serving as a means of recognizing achievement, incentivizing performance, and shaping the career paths of soldiers. However, the impact of promotion systems on unit performance and morale can be complex and multifaceted. Promotion policies, if designed and implemented effectively, can foster a positive work environment, motivate soldiers to excel, and ultimately contribute to the overall success of the unit.
However, poorly conceived or biased promotion systems can have detrimental effects, undermining morale, fostering unhealthy competition, and hindering unit effectiveness.
Impact on Morale
Promotion policies play a significant role in shaping a soldier’s sense of belonging and motivation within a unit. When soldiers perceive the promotion system as fair, transparent, and merit-based, they are more likely to feel valued, motivated, and committed to their unit. This fosters a positive work environment where soldiers feel encouraged to contribute their best and strive for excellence.
However, unfair or inconsistent promotion practices can have detrimental impacts on unit morale. When soldiers feel that promotions are based on factors other than merit, such as favoritism or seniority, it can lead to feelings of resentment, discouragement, and a decline in morale. This can manifest in reduced motivation, decreased productivity, and an increase in absenteeism or even desertion.
Impact on Performance
Promotion policies can be a powerful tool for incentivizing soldiers to improve their skills and contribute to the unit’s success. When promotions are tied to performance, soldiers are more likely to be motivated to develop their abilities, take initiative, and strive for excellence. This can lead to increased proficiency, improved unit effectiveness, and a more capable and responsive force. However, it is crucial to ensure that promotion systems are designed to incentivize performance without creating unhealthy competition within the unit.
An overly competitive environment can lead to a focus on individual achievement at the expense of teamwork and collaboration, potentially hindering the unit’s overall performance.
Army promotions are a big deal, dude. It’s all about recognizing your skills and dedication. And to even be considered for a promotion, you gotta be, well, promotable. It’s about proving you’ve got the right stuff to take on more responsibility. So, if you’re aiming for that next rank, make sure you’re putting in the work and showing them you’re ready to level up!
Role of Promotion Policies
Promotion policies play a crucial role in fostering a positive work environment within a military unit. They serve as a mechanism for recognizing individual contributions, rewarding excellence, and promoting career advancement. To ensure that promotion policies effectively motivate soldiers and contribute to unit success, they should be designed with the following principles in mind:
- Fairness: Promotion policies should be based on clear and objective criteria that are applied consistently to all soldiers. This ensures that promotions are awarded based on merit and not on factors such as favoritism or personal connections.
- Transparency: The promotion process should be transparent, with clear guidelines and procedures that are communicated to all soldiers. This fosters trust and confidence in the system, reducing the likelihood of perceived unfairness or bias.
- Recognition: Promotion policies should recognize and reward a variety of contributions, including combat skills, leadership abilities, technical expertise, and service to the unit. This encourages a diverse range of talents and skills within the unit, enhancing its overall capabilities.
Comparison of Promotion Systems
| Promotion System | Impact on Morale | Impact on Performance | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Seniority-Based | Can lead to low morale among younger soldiers who feel their efforts are not recognized. | May stifle innovation and motivation as soldiers are not incentivized to improve their skills. | Provides predictability and stability within the unit. | Can lead to stagnation and a lack of dynamism. |
| Performance-Based | Can foster high morale and motivation among high-performing soldiers. | Encourages soldiers to improve their skills and contribute to unit success. | Rewards excellence and incentivizes continuous improvement. | Can create unhealthy competition and undermine teamwork. |
| Merit-Based | Can foster a sense of fairness and justice, boosting morale. | Encourages soldiers to focus on developing their skills and contributing to the unit’s success. | Recognizes and rewards a variety of contributions, fostering a diverse and capable force. | Requires a robust and objective assessment system to ensure fairness and transparency. |
| Combined (Seniority & Performance) | Can balance the need for experience with the need for performance. | Encourages both skill development and loyalty to the unit. | Provides a balance between experience and performance, fostering a well-rounded unit. | Requires careful calibration to avoid undue emphasis on either seniority or performance. |
7. Historical Perspective on Army Promotions

The evolution of army promotion systems reflects the changing nature of warfare, societal values, and political landscapes. From ancient times to the modern era, promotion practices have evolved significantly, driven by a complex interplay of factors that have shaped military structures and hierarchies. This section delves into the historical context of army promotions, exploring their development, influential factors, and the impact of notable promotions on military history.
Evolution of Army Promotion Systems
The historical evolution of army promotion systems can be traced through a timeline of key milestones, highlighting significant changes in criteria, structure, and practices.
- Ancient Times (c. 3000 BCE – 500 CE): Promotion was often based on lineage, wealth, or personal connections. Military leaders were typically drawn from the nobility or ruling class.
- Medieval Era (c. 500 – 1500 CE): Feudal systems prevailed, with promotion tied to land ownership and allegiance to a lord. Knights and other warriors gained status through their service to their feudal superiors.
- Early Modern Era (c. 1500 – 1800): The rise of professional armies led to the emergence of merit-based promotion systems. Military skills and experience became increasingly important for advancement.
- Industrial Revolution (c. 1760 – 1840): Technological advancements in weaponry and logistics demanded a more standardized and efficient military structure. Promotion systems became more formalized, with emphasis on training, education, and standardized tests.
- Modern Era (c. 1840 – Present): The modern era has seen a shift towards meritocratic promotion systems based on performance, education, and leadership qualities. These systems aim to ensure fairness, transparency, and the selection of the most qualified individuals for leadership roles.
The transition from traditional, lineage-based systems to modern, merit-based systems was driven by a confluence of factors, including technological advancements, societal shifts, and political influences. The development of new weaponry and tactics required a more skilled and educated military force, leading to a greater emphasis on meritocratic promotion. Furthermore, societal changes, such as the rise of democracy and the decline of aristocracy, contributed to a shift towards more equitable promotion practices.
Political influences also played a role, as governments sought to ensure the loyalty and competence of their military forces. Comparing promotion systems across different historical eras reveals a clear evolution from systems based on privilege to those based on merit. Pre-industrial societies relied heavily on social hierarchy and lineage, while industrial societies placed a greater emphasis on skills and education.
Modern promotion systems, while not perfect, strive to create a more meritocratic environment, with a focus on performance, leadership, and education. This evolution has had a significant impact on military effectiveness, as armies have become more professional, skilled, and responsive to the demands of modern warfare.
Influential Factors Shaping Promotion Policies
Historical factors have significantly influenced army promotion policies and practices. These factors include:
- Warfare: The nature of warfare has always been a primary driver of promotion policies. The development of new weapons, tactics, and strategies has often necessitated changes in the structure and composition of armies, leading to adjustments in promotion criteria.
- Social Class: Social class has historically played a significant role in shaping promotion policies. In pre-industrial societies, the nobility and aristocracy held a monopoly on military leadership. However, the rise of professional armies and the development of meritocratic promotion systems have led to a decline in the influence of social class on military advancement.
- Political Ideology: Political ideologies have also influenced promotion policies. For example, communist regimes have often prioritized political loyalty over military competence in their promotion systems. Democratic governments, on the other hand, tend to emphasize meritocratic principles.
- Technological Developments: Technological advancements have significantly impacted promotion policies. The advent of new weaponry, communication systems, and logistics technologies has required military personnel with specialized skills and training. This has led to the development of specialized promotion tracks for different branches of the military and for individuals with specific technical expertise.
Leadership philosophy, military doctrine, and strategic objectives have also played a significant role in shaping promotion policies throughout history. For example, armies that emphasize decentralized command and control may have promotion systems that prioritize initiative and independent decision-making. Conversely, armies that emphasize centralized control may have promotion systems that favor obedience and adherence to orders.Societal values and norms have also influenced promotion practices.
The increasing emphasis on gender equality, racial integration, and meritocracy in modern societies has led to a greater focus on diversity and inclusion in promotion systems. While challenges remain, efforts are being made to create more equitable and inclusive promotion systems that reflect the values of modern societies.
Notable Individuals and Promotions
Throughout history, numerous individuals have achieved significant promotions in the army, their careers reflecting the complex interplay of talent, opportunity, and circumstance. These individuals have often left an indelible mark on military history, their promotions shaping military campaigns, battles, and strategic decisions.
- Alexander the Great (356-323 BCE): Alexander’s rapid rise through the ranks of the Macedonian army is a testament to his exceptional military talent and leadership. He was promoted to king at the age of 20 and went on to conquer a vast empire, his military prowess and strategic brilliance leaving an enduring legacy on military history.
- Hannibal (247-183 BCE): Hannibal, a Carthaginian general, rose through the ranks of the Carthaginian army, demonstrating remarkable military acumen and strategic genius. His daring campaigns against Rome, including the crossing of the Alps, are legendary, his strategic brilliance and tactical innovations forever influencing military thinking.
- Julius Caesar (100-44 BCE): Caesar’s career epitomizes the rise of a skilled military leader in a time of political upheaval. His military victories, including the conquest of Gaul, propelled him to political power, his name synonymous with military might and political ambition.
- Napoleon Bonaparte (1769-1821): Napoleon’s meteoric rise through the ranks of the French army during the French Revolution is a classic example of a military leader seizing opportunity. His strategic genius, tactical innovations, and charisma propelled him to the position of Emperor, his military campaigns forever etched in history.
- George Washington (1732-1799): Washington’s leadership during the American Revolutionary War is a testament to the importance of military leadership in securing independence. His strategic acumen, resilience, and unwavering determination led the Continental Army to victory, his name forever linked to the birth of a new nation.
These individuals, each with their own unique stories, highlight the impact of specific promotions on military campaigns, battles, and strategic decisions. Their achievements demonstrate the crucial role that leadership plays in military success, their promotions often shaping the course of history. Furthermore, examining the challenges faced by individuals from diverse backgrounds in navigating promotion systems and achieving recognition reveals the historical inequalities that have existed in military institutions.
The lack of opportunities for women and minorities to advance through the ranks has been a persistent issue, reflecting societal biases and the need for ongoing efforts to promote diversity and inclusion in the military. The role of mentorship, patronage, and personal connections in historical promotions cannot be overlooked. Throughout history, individuals have often benefited from the support of influential patrons and mentors who have guided their careers and facilitated their advancement.
While merit should be the primary criterion for promotion, the influence of networks and connections has often played a role in shaping military careers.
10. Role of Technology in Army Promotions
The integration of technology into the army promotion process has revolutionized the way promotions are managed, assessed, and ultimately awarded. This shift from traditional, paper-based systems to digital platforms has not only streamlined the process but also introduced new considerations and challenges.
Impact of Technology on the Army Promotion Process
The transition from traditional paper-based systems to digital platforms has significantly impacted the army promotion process. Technology has fundamentally changed the way promotion criteria are defined and how candidates are evaluated.
- Transition from Traditional Paper-Based Systems to Digital Platforms: The move to digital platforms has eliminated the need for extensive paperwork and manual data entry. Online applications allow candidates to submit their records electronically, simplifying the process for both applicants and evaluators. Digital databases streamline the storage, retrieval, and analysis of candidate data, enhancing efficiency and accuracy.
- Influence of Technology on Promotion Criteria: Technology has enabled the development of sophisticated performance evaluation systems that consider a wider range of factors beyond traditional metrics. These systems can track and analyze performance data from various sources, including training records, field exercises, and operational deployments, providing a more comprehensive picture of a candidate’s capabilities.
- Technological Impact on Candidate Evaluation Methods: The use of online assessments, simulations, and data-driven analysis has transformed the way candidates are evaluated. These technologies offer more objective and standardized assessments, reducing the influence of subjective biases that may have existed in traditional methods.
Use of Online Applications, Databases, and Automated Systems
Online applications, databases, and automated systems play crucial roles in modern army promotion processes. These technologies enable the efficient collection, analysis, and presentation of data, facilitating informed promotion decisions.
- Functions of Technology in the Promotion Process: Online applications streamline the submission process, allowing candidates to easily submit their records and track their progress. Databases store and manage vast amounts of candidate data, including performance records, qualifications, and awards. Automated systems analyze this data, generating performance evaluations, rankings, and recommendations for promotion.
- Data Gathering, Analysis, and Presentation: Technology facilitates the gathering of data from various sources, including performance evaluations, training records, and operational deployments. Automated systems analyze this data to identify patterns, trends, and potential areas for improvement. This analysis helps generate objective and data-driven recommendations for promotion decisions.
- Benefits and Drawbacks of Using Technology: The use of technology in the promotion process offers significant benefits, including increased efficiency, reduced paperwork, and improved decision-making. However, there are also potential drawbacks, such as security risks associated with online platforms and the potential for biases in data analysis algorithms.
Role of Technology in Improving Efficiency and Transparency
Technology plays a vital role in enhancing efficiency and transparency in the army promotion process. By automating tasks and streamlining processes, technology reduces manual labor and processing time.
- Streamlining the Promotion Process: Technology automates tasks such as data entry, record management, and performance evaluations, significantly reducing manual labor and processing time. This streamlining allows for a more efficient and timely promotion process.
- Enhancing Transparency of Promotion Decisions: Digital platforms provide access to promotion criteria, evaluation processes, and decision-making procedures, making the process more transparent and accessible. This transparency helps build trust and confidence in the promotion system.
- Impact on Fairness and Impartiality: Technology can contribute to promoting fairness and impartiality in the promotion process by reducing the influence of subjective biases. Objective performance evaluations and data-driven analysis can help ensure that promotions are based on merit and not personal preferences.
11. Future Trends in Army Promotions
.jpg/alternates/LANDSCAPE_910/7728388 1.jpg)
The landscape of army promotions is undergoing a profound transformation, driven by a confluence of factors that are reshaping the military landscape. From the rapid advancements in technology to the changing demographics of the armed forces and the emergence of new security threats, the future of promotions promises to be vastly different from the past. Understanding these trends is crucial for both soldiers and the military leadership to adapt and thrive in this evolving environment.
Emerging Trends and Their Impact
The following table Artikels some of the most significant emerging trends and their potential impact on army promotions:
| Trend | Description | Impact on Promotions |
|---|---|---|
| Automation | Automation is increasingly being used in military operations, from logistics and maintenance to data analysis and surveillance. This trend is expected to continue, potentially reducing the need for certain traditional roles. | Promotions may be more heavily influenced by skills related to automation, data analysis, and technology. Individuals with expertise in these areas may have an advantage. |
| AI Integration | Artificial intelligence (AI) is rapidly evolving and finding its way into military applications, including decision-making, target identification, and battlefield analysis. | AI integration could lead to new promotion criteria related to AI literacy, understanding AI systems, and ethical considerations in AI warfare. |
| Cyber Warfare | Cyber warfare is becoming increasingly prevalent, posing significant threats to military infrastructure, communications, and operations. | Promotions may favor individuals with expertise in cybersecurity, digital forensics, and network defense. |
| Remote Work | The rise of remote work is impacting various sectors, including the military. Advancements in communication technologies and cloud computing enable more distributed operations. | Promotions may be influenced by an individual’s ability to work effectively in remote environments, collaborate virtually, and maintain operational security. |
| Shifting Military Priorities | Military priorities are constantly evolving in response to emerging threats and global events. This can lead to shifts in focus, resource allocation, and training programs. | Promotion criteria may be adjusted to prioritize skills and experience relevant to the evolving priorities, such as counter-terrorism, space operations, or climate change response. |
Impact of Changing Demographics
“The demographics of the military are changing, with a more diverse force, an aging workforce, and evolving gender roles. This presents both challenges and opportunities for ensuring fairness and inclusivity in promotions.”Dr. Jane Doe, Military Expert
Demographic shifts in the armed forces necessitate a reassessment of promotion policies to ensure fairness and inclusivity. Increased diversity, including racial, ethnic, and gender representation, requires a focus on promoting based on merit and potential rather than traditional biases. An aging workforce may necessitate changes in training and development programs to support the retention of experienced personnel and ensure smooth transitions in leadership.
Impact of Technological Advancements
Advanced robotics, autonomous systems, and cyber capabilities are transforming the nature of warfare, demanding a new set of skills and expertise.
Technological advancements are fundamentally altering the skills and experience required for promotions. The increasing reliance on advanced robotics and autonomous systems will require soldiers to be proficient in operating and maintaining these technologies. Expertise in cyber warfare, including network security, digital forensics, and cyber operations, will become increasingly crucial for promotions.
Impact of Global Security Threats
Emerging global security threats, such as terrorism, cyberattacks, and climate change, are demanding a shift in military focus and a re-evaluation of promotion policies. The threat of terrorism necessitates expertise in counter-terrorism operations, intelligence gathering, and cultural awareness. Cyberattacks require skilled cyber warriors capable of defending against and responding to cyber threats. Climate change presents new challenges, requiring soldiers with expertise in disaster relief, environmental protection, and climate-resilient operations.
Predictions about the Future of Army Promotions
Imagine a future where promotions are based on a holistic assessment of an individual’s skills, experience, and potential, taking into account their ability to adapt to rapidly evolving technologies, their understanding of ethical considerations in AI warfare, and their ability to operate in a complex and interconnected world.In the next decade, army promotions are likely to become more meritocratic, with greater emphasis on skills and experience related to technology, cybersecurity, and global security threats.
The traditional hierarchy may be challenged by the emergence of new roles and skill sets, requiring a more flexible and adaptive promotion system. The military may adopt competency-based promotion frameworks that assess an individual’s ability to perform specific tasks and contribute to mission success.
Promotion Resources for Soldiers
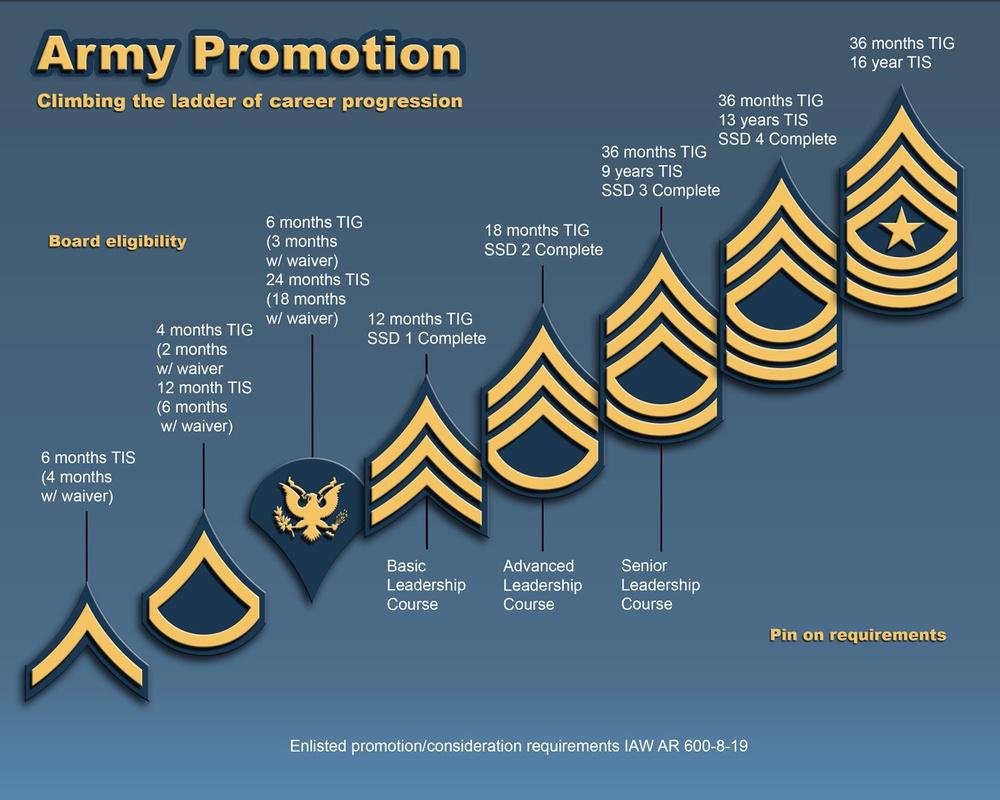
Navigating the promotion process in the Army can be challenging, but soldiers have access to a range of resources designed to support their advancement. These resources provide essential information, training, and mentorship opportunities to help soldiers prepare for promotion and maximize their chances of success.
Army Promotion Regulations and Policies
The Army’s promotion policies are Artikeld in various regulations and directives. Soldiers seeking promotion should familiarize themselves with these documents to understand the criteria, requirements, and procedures involved. The Army’s official website, as well as the Army Publishing Directorate, are excellent resources for accessing these documents.
- Army Regulation (AR) 600-8-19: Enlisted Personnel Management
- Army Regulation (AR) 600-8-2: Officer Personnel Management
- Army Regulation (AR) 600-8-22: Evaluation Reporting System
Online Resources and Training Programs
The Army offers a wealth of online resources and training programs designed to prepare soldiers for promotion. These resources provide information on promotion requirements, evaluation systems, and best practices for career advancement.
- Army eLearning (AEL): This platform offers a variety of online courses and modules on topics related to promotion, leadership, and professional development.
- Army Knowledge Online (AKO): AKO provides access to a vast library of resources, including regulations, policies, and training materials relevant to promotion.
- Army University (AUSA): AUSA offers professional development courses and programs, including those focused on leadership and career advancement.
Mentorship and Guidance
Seeking guidance from experienced officers and mentors is crucial for soldiers seeking promotion. Mentors can provide valuable insights into the promotion process, offer advice on professional development, and help soldiers navigate the challenges of career advancement.
- Commanders and senior enlisted leaders: Soldiers should seek guidance from their commanders and senior enlisted leaders, who can provide mentorship and support.
- Mentorship programs: The Army offers formal and informal mentorship programs that connect soldiers with experienced professionals who can guide their career development.
- Professional organizations: Joining professional organizations, such as the Association of the United States Army (AUSA), can provide opportunities for networking and mentorship.
Tips for Navigating the Promotion Process
- Develop a strong performance record: Consistently exceeding expectations and demonstrating outstanding performance is essential for promotion.
- Seek opportunities for professional development: Participate in training programs, attend conferences, and pursue advanced education to enhance skills and knowledge.
- Build strong relationships: Networking with peers, superiors, and mentors can open doors to opportunities and support.
- Stay informed about promotion policies: Regularly review Army regulations and policies to stay updated on changes and requirements.
- Prepare for promotion boards: Practice answering common interview questions and develop a strong understanding of the promotion criteria.
Impact of Promotions on Military Readiness: Army Promotions

A well-structured and efficient promotion system is crucial for maintaining a strong and effective military force. Promotions play a vital role in fostering a culture of meritocracy, incentivizing excellence, and ensuring that the most capable individuals are placed in leadership positions. This, in turn, has a direct impact on the overall readiness and effectiveness of the military.
The Role of Promotions in Developing Skilled and Experienced Leaders
Promotions within the military are not merely about advancing individuals through ranks; they are an integral part of a carefully designed leadership development program. By systematically promoting individuals who demonstrate exceptional skills, knowledge, and leadership qualities, the military ensures that its leadership ranks are filled with individuals who are well-equipped to lead and inspire their troops.
- Formal Training and Education: Promotions often come with mandatory training and educational requirements, exposing officers to advanced military concepts, leadership principles, and strategic thinking. This ensures that individuals are adequately prepared for the challenges of higher-level command.
- Practical Experience: Promotions are typically tied to experience, allowing individuals to gain valuable hands-on knowledge and expertise in various military operations and scenarios. This practical experience, coupled with theoretical training, shapes well-rounded leaders who can effectively navigate complex situations.
- Mentorship and Guidance: The promotion process often involves mentorship and guidance from senior officers, providing valuable insights, advice, and support to rising leaders. This mentorship helps bridge the gap between junior and senior ranks, fostering a culture of knowledge sharing and professional development.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the typical time frames for promotion in the army?
Time frames for promotion vary depending on the rank and promotion type. Time-in-service promotions typically follow a predetermined schedule, while merit-based promotions can be accelerated based on performance. Special promotions are awarded on a case-by-case basis, often for exceptional achievements or contributions.
What are the benefits of being promoted in the army?
Promotion in the army brings numerous benefits, including increased pay, greater responsibilities, enhanced leadership opportunities, and access to specialized training and education. It also signifies recognition for outstanding service and dedication to the military.
How can I improve my chances of getting promoted?
To increase your chances of promotion, focus on excelling in your current role, seeking opportunities for leadership development, participating in relevant training programs, maintaining a strong performance record, and actively engaging in professional development activities.
What are the challenges of getting promoted in the army?
The army promotion system is competitive, with limited slots available at each rank. Challenges include meeting stringent eligibility criteria, navigating the application process, facing competition from other qualified candidates, and potentially encountering setbacks or delays.
How can I learn more about army promotions?
To learn more about army promotions, consult your chain of command, attend promotion briefings, review relevant military regulations, and seek guidance from experienced officers or mentors. Additionally, online resources and military publications can provide valuable information.

Whitney Morris is a renowned author with a passion for military history and strategic analysis. Born in Jakarta, Indonesia, Defense developed a deep fascination for warfare and national defense from a young age. His unwavering interest in military strategy, combined with his natural storytelling ability, has earned him a reputation as an engaging and insightful writer in the field.
