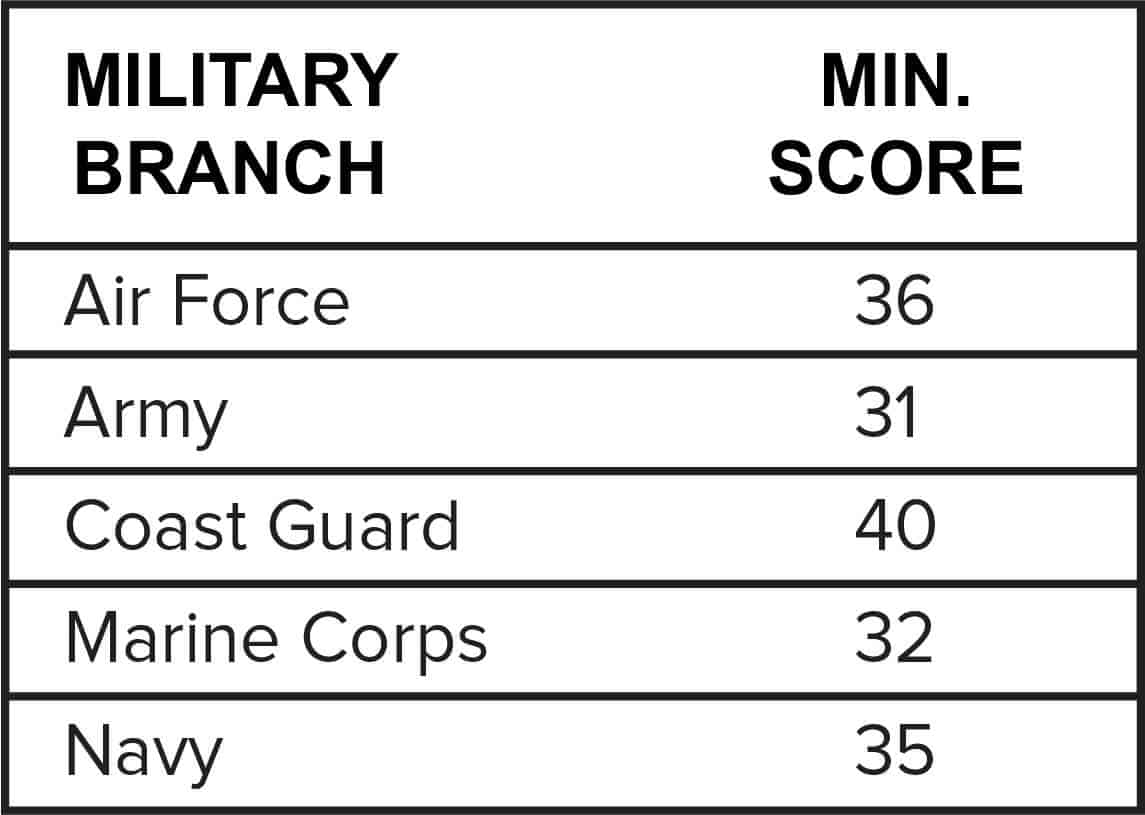
Army cut off scores are the numerical benchmarks that determine a candidate’s eligibility for military service. These scores act as a gatekeeper, ensuring that only individuals who meet the stringent requirements for physical fitness, academic qualifications, and mental aptitude are considered for enlistment.
The army utilizes a complex system of cut off scores that varies based on factors such as the specific branch of service, job requirements, and the overall applicant pool. Understanding these scores is crucial for anyone aspiring to join the ranks of the military, as they represent the minimum standards required for success in this demanding profession.
Understanding Army Cut Off Scores
Army cut off scores are a critical component of the military recruitment process, playing a vital role in ensuring that only the most qualified individuals are selected for service. These scores act as a standardized measure to evaluate candidates’ suitability for various roles within the armed forces, contributing to the overall effectiveness and efficiency of the army.
Significance of Army Cut Off Scores
Cut off scores serve as a crucial filter during the army’s recruitment process, ensuring that only individuals meeting specific criteria are considered for service. They act as a benchmark to assess candidates’ aptitude, physical fitness, and other essential attributes, guaranteeing that only those capable of meeting the demanding requirements of military service are selected. The use of cut off scores helps to maintain a high standard of recruits, ensuring that the army comprises individuals who are physically and mentally prepared to face the challenges of military life.
Factors Influencing Cut Off Scores
Several factors contribute to the army’s decision-making process when setting cut off scores. These factors ensure that the scores accurately reflect the current needs and priorities of the armed forces.
- Job requirements: The specific skills and qualifications needed for different roles within the army directly influence the cut off scores. For example, a role requiring advanced technical skills might have a higher cut off score for aptitude tests compared to a role emphasizing physical fitness.
- Current recruitment needs: The army’s need for specific skills or personnel, such as medical professionals or engineers, can impact cut off scores. If the army requires a large number of individuals with specialized skills, the cut off scores might be adjusted to attract a wider pool of qualified candidates.
- Overall applicant pool: The quality of the applicant pool can influence the cut off scores. If the army receives a large number of highly qualified applicants, the cut off scores may be set higher to ensure only the most exceptional individuals are selected.
- Past performance data: Historical data on the performance of previous recruits plays a role in determining cut off scores. The army analyzes past performance data to identify trends and patterns, using this information to adjust cut off scores for future recruitment cycles.
- Budgetary constraints: Budget limitations can influence the setting of cut off scores. If the army has limited resources, it might set higher cut off scores to reduce the number of recruits, ensuring that the available resources are allocated effectively.
Types of Army Cut Off Scores
The army uses various types of cut off scores to assess different aspects of a candidate’s suitability for service. These scores are tailored to specific requirements and are used to ensure a comprehensive evaluation of each applicant.
| Type of Cut Off Score | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Physical Fitness Score | Measures a candidate’s physical fitness levels, including strength, endurance, and agility. | A minimum score of 60% on the Army Physical Fitness Test (APFT). |
| Aptitude Test Score | Evaluates a candidate’s cognitive abilities, including problem-solving skills, critical thinking, and reasoning. | A minimum score of 50% on the Armed Services Vocational Aptitude Battery (ASVAB). |
| Medical Screening Score | Assesses a candidate’s overall health and medical fitness, ensuring they meet the required standards for military service. | A passing score on a comprehensive medical examination, including vision, hearing, and other health screenings. |
| Background Check Score | Evaluates a candidate’s character, conduct, and suitability for military service. | A passing score on a background check, including criminal history, credit history, and other relevant information. |
Factors Affecting Cut Off Scores
The cut-off score for military service is a minimum requirement that candidates must meet to be eligible for enlistment. This score is determined by a combination of factors, including the specific branch of service, academic qualifications, physical fitness standards, medical conditions, and past criminal records. Understanding these factors can help potential recruits strategize their preparation and increase their chances of meeting the required cut-off score.
Branch of Service
The branch of service a candidate chooses significantly impacts the cut-off score. Each branch has unique requirements based on the specific skills and qualifications needed for its operations. For instance, the Army, known for its ground combat roles, may prioritize physical fitness and strength, while the Air Force, focusing on technology and aviation, might emphasize academic qualifications and technical skills.
This difference in requirements can translate into higher or lower cut-off scores for different branches.
- The Army, with its emphasis on physical strength and endurance, often has higher physical fitness standards, potentially leading to higher cut-off scores in this area.
- The Navy, with its focus on maritime operations, may require strong swimming skills and higher cut-off scores for physical fitness related to water competency.
- The Air Force, with its focus on technical roles, may have higher cut-off scores for academic qualifications and standardized test scores, especially for specialized technical fields.
| Branch of Service | Key Requirements | Cut-off Score Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Army | Physical fitness, strength, endurance | Higher cut-off scores for physical fitness |
| Navy | Swimming skills, water competency | Higher cut-off scores for water-related physical fitness |
| Air Force | Academic qualifications, technical skills | Higher cut-off scores for academic qualifications and standardized test scores |
Academic Qualifications
Academic qualifications play a crucial role in determining eligibility for military service. A strong academic record, including a high GPA and good standardized test scores, can significantly improve a candidate’s chances of meeting the cut-off score, especially for branches that emphasize technical skills and specialized roles.
A candidate with a 3.5 GPA and a high SAT score might have a higher chance of meeting the cut-off score for a specialized technical role in the Air Force compared to a candidate with a 2.5 GPA.
Physical Fitness Standards
Military service demands a high level of physical fitness. Specific physical fitness standards, including push-ups, sit-ups, and run time, are established for each branch. Candidates must meet these standards to be eligible for enlistment. The required level of physical fitness can vary depending on the specific role and branch, influencing the cut-off scores for this area.
A candidate with a high score in push-ups, sit-ups, and run time might have a higher chance of meeting the cut-off score for a physically demanding role in the Army compared to a candidate with lower scores.
Medical Conditions
Medical conditions can significantly affect eligibility for military service and potentially impact the cut-off scores. Pre-existing medical conditions or newly diagnosed health issues can influence a candidate’s ability to meet the required standards.
A candidate with a minor medical condition, such as mild asthma, might require a higher cut-off score in other areas to compensate for the potential health risk.
Past Criminal Records
Past criminal records can significantly impact eligibility for military service. The type of offense, the severity of the offense, and the time elapsed since the offense are all considered in the evaluation process.
A candidate with a past felony conviction might face a higher cut-off score in other areas to demonstrate their suitability for military service.
Navigating the Cut Off Score System
The Army’s cut-off score system can seem daunting, but with the right approach, you can navigate it effectively. Understanding the system, preparing adequately, and leveraging support can significantly improve your chances of achieving the desired scores.
The army cut-off score is a critical factor in determining eligibility for enlistment, but it’s not the only factor. Once enlisted, soldiers can progress through the ranks by accumulating promotion points. These points are awarded based on various criteria, such as performance evaluations, education, and training. For a detailed breakdown of how these points are calculated, refer to the army promotion points list.
Understanding the promotion point system can help soldiers strategize their career paths and ultimately improve their chances of achieving their desired rank.
Strategies for Improving Scores in Relevant Tests
To enhance your performance in the Army’s aptitude tests, it’s crucial to develop a well-structured study plan. Here are some key strategies:
- Identify your strengths and weaknesses: Analyze your past performance in similar tests to pinpoint areas where you excel and those requiring more focus. This self-assessment provides a starting point for targeted preparation.
- Focus on fundamental concepts: The Army’s tests primarily assess core academic abilities. Reinforce your understanding of essential math, reading, and writing principles through dedicated practice.
- Practice with official resources: Utilize official Army practice tests and study guides to familiarize yourself with the test format, question types, and difficulty level. This exposure builds confidence and reduces test anxiety.
- Time management is key: Practice answering questions within the allotted time to develop efficient test-taking strategies. This includes learning to skip challenging questions and return to them later.
- Seek feedback and guidance: Consult with teachers, tutors, or test preparation experts for personalized feedback and guidance on areas requiring improvement. Their insights can provide valuable strategies for tackling specific question types.
Preparing for Physical Fitness Assessments
Physical fitness is an integral part of Army recruitment. Here’s how to prepare for the physical fitness assessments:
- Understand the requirements: Familiarize yourself with the specific exercises, standards, and scoring criteria for the physical fitness assessments. This knowledge allows you to tailor your training program accordingly.
- Develop a comprehensive training plan: Design a structured training program that incorporates exercises relevant to the assessment. Gradually increase the intensity and duration of your workouts to build endurance, strength, and flexibility.
- Focus on core exercises: Include exercises that target major muscle groups, such as push-ups, sit-ups, and running. These exercises form the foundation of the physical fitness assessments.
- Prioritize proper form: Emphasize correct technique during exercises to prevent injuries and maximize effectiveness. Seek guidance from qualified trainers or fitness professionals for proper form instruction.
- Maintain consistency: Consistency is key to achieving desired fitness levels. Adhere to your training plan regularly, even on days when motivation is low. This discipline contributes to long-term improvement.
Understanding Individual Strengths and Weaknesses
Self-awareness plays a crucial role in navigating the cut-off score system. Understanding your strengths and weaknesses helps you tailor your preparation strategy for optimal results:
- Identify areas of strength: Focus on building upon your existing strengths. This could involve dedicating more time to areas where you naturally excel, ensuring you maintain a strong foundation.
- Address areas of weakness: Allocate more time and effort to areas where you struggle. This may involve seeking additional support from tutors or teachers, utilizing specialized study materials, or practicing more frequently.
- Embrace a growth mindset: View weaknesses as opportunities for improvement. Embrace challenges and persevere through difficulties, recognizing that progress often comes through effort and dedication.
- Seek feedback and guidance: Don’t hesitate to seek feedback from mentors, teachers, or test preparation experts. Their insights can help you identify specific areas requiring attention and provide strategies for overcoming challenges.
The Role of Professional Guidance and Support
Professional guidance and support can be invaluable in achieving desired cut-off scores:
- Test preparation programs: Enrolling in test preparation programs can provide structured instruction, practice materials, and personalized feedback. These programs often offer strategies for test-taking, time management, and stress reduction.
- Mentors and advisors: Seek guidance from mentors or advisors who have experience with the Army’s recruitment process. Their insights can provide valuable tips and strategies for navigating the cut-off score system.
- Career counselors: Career counselors can offer personalized advice on choosing the right career path within the Army, based on your interests, skills, and aspirations. Their guidance can help you identify suitable roles that align with your strengths.
Interpreting Cut Off Score Results
Receiving your cut off score results is a crucial step in the Army recruitment process. Understanding what your score means and how it affects your chances of joining is essential. This section will guide you through interpreting your results and navigating the next steps.
Understanding the Cut Off Score Process
After completing the Army selection process, including physical fitness tests, medical evaluations, and written examinations, you will receive your cut off score results. These results are typically communicated through a combination of methods, including:
- Email: You will receive an official email notification with details about your score and the next steps.
- Online Portal: The Army may have a dedicated online portal where you can access your results, track your application status, and find additional information.
- Official Website: You can also check the Army’s official website for updates on cut off score announcements and general recruitment information.
The timeline for receiving your results varies depending on the specific recruitment program and the volume of applications. However, you can expect to receive your score within a few weeks to a few months after completing the selection process.
Interpreting Score Ranges
Cut off scores are typically presented as a numerical range, with each range representing a different level of performance. Here is a breakdown of common score ranges and their interpretations:
| Score Range | Interpretation | Potential Outcomes |
|---|---|---|
| 90-100 | Excellent | Guaranteed admission, eligible for scholarships and special programs |
| 80-89 | Good | High chance of admission, may be eligible for certain programs |
| 70-79 | Average | May be eligible for admission, may need to consider alternative options or re-application |
| Below 70 | Below average | Unlikely to be admitted, encouraged to re-apply or explore other opportunities |
Remember that these ranges are general guidelines and may vary depending on the specific program and year.
Implications of Exceeding or Falling Short of Cut Off Scores
Exceeding the cut off score demonstrates strong performance and can lead to various benefits, including:
- Guaranteed Admission: Meeting or exceeding the cut off score often guarantees your admission into the desired program.
- Eligibility for Scholarships: High scores can make you eligible for scholarships, financial aid, or special programs offered by the Army.
- Priority Placement: You may be given priority placement in specific roles or units based on your exceptional performance.
However, falling short of the cut off score may mean you do not meet the minimum requirements for admission. This could lead to:
- Rejection: If your score falls below the cut off, you may be rejected from the program.
- Re-application: You may be encouraged to re-apply after improving your performance in areas where you fell short.
- Alternative Programs: The Army may offer alternative programs or pathways for individuals who do not meet the cut off scores for their initial choice.
Options for Candidates Who Don’t Meet Cut Off Scores
If you do not meet the cut off score, don’t despair. There are several options available to you:
- Re-apply: You can re-apply for the same program after addressing the areas where you fell short. This may involve improving your physical fitness, academic performance, or test scores.
- Explore Alternative Programs: The Army offers a wide range of programs and career paths. You can explore other options that may be a better fit for your skills and interests.
- Consider Other Pathways: There may be alternative pathways to achieve your goals, such as joining the Reserves or National Guard.
- Appeal the Results: You can appeal the results if you believe there was an error in scoring or a misinterpretation of your application.
- Seek Clarification: If you have any questions or concerns about your results, reach out to the Army recruitment office for further clarification.
“It’s important to remember that cut off scores are just one factor in the admission process. While exceeding the cut off score can increase your chances, other factors such as your academic record, extracurricular activities, and personal statement also play a significant role.”
Future Trends in Army Cut Off Scores
The army’s cut-off scores, like any dynamic system, are subject to change in response to evolving needs, technological advancements, and societal shifts. Understanding these trends is crucial for aspiring recruits, as it provides insights into future requirements and helps them prepare accordingly.
Impact of Technological Advancements
Technological advancements are fundamentally transforming the modern army, influencing recruitment processes and shaping the demands placed on soldiers. This section explores the impact of these advancements on army cut-off scores.
- Automation and Artificial Intelligence: The increasing use of automation and artificial intelligence (AI) in military operations is expected to change the skills required of soldiers. While AI can handle routine tasks, human soldiers will need to focus on critical thinking, problem-solving, and complex decision-making, potentially leading to higher cognitive aptitude requirements in cut-off scores.
- Cybersecurity: The growing reliance on technology in military operations has increased the importance of cybersecurity. The army may emphasize skills related to cybersecurity, such as network security, data analysis, and ethical hacking, potentially influencing cut-off scores in relevant aptitude areas.
- Remote Operations and Virtual Reality Training: The use of virtual reality (VR) and remote operations is changing the nature of training and warfare. This may lead to increased emphasis on adaptability, spatial awareness, and the ability to operate in virtual environments, potentially impacting cut-off scores in areas like spatial reasoning and technology proficiency.
Evolving Demands of the Modern Army
The modern army faces increasingly complex and diverse challenges, requiring soldiers with a broader range of skills and capabilities. This section explores the evolving demands of the modern army and their implications for cut-off scores.
- Multi-Domain Operations: The modern army is increasingly operating across multiple domains, including land, air, sea, space, and cyberspace. This requires soldiers with adaptability, cross-domain knowledge, and the ability to integrate different technologies, potentially influencing cut-off scores in areas like critical thinking, problem-solving, and communication.
- Hybrid Warfare: The rise of hybrid warfare, which combines conventional and unconventional tactics, requires soldiers with resilience, adaptability, and the ability to operate in unpredictable environments. This may lead to increased emphasis on psychological resilience, cultural awareness, and language proficiency in cut-off scores.
- Global Partnerships and Interoperability: The modern army is increasingly collaborating with international partners. This requires soldiers with cross-cultural communication skills, language proficiency, and the ability to work effectively in multinational teams, potentially influencing cut-off scores in areas like language aptitude and cultural awareness.
Case Studies of Army Cut Off Scores
Army cut-off scores represent a crucial aspect of military recruitment, serving as a benchmark for assessing the suitability of candidates. Understanding the historical trends, influencing factors, and impact of these scores provides valuable insights into the evolution of military selection processes. Analyzing case studies of significant changes in cut-off score policies, exploring the experiences of successful candidates, and incorporating expert perspectives offer a comprehensive understanding of this dynamic system.
Historical Trends in Army Cut Off Scores
Analyzing historical trends in army cut-off scores provides valuable insights into the evolution of military recruitment standards. The table below showcases historical trends in army cut-off scores across different years and branches of service.
| Year | Army | Navy | Air Force | Overall Average |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2010 | 50 | 55 | 60 | 55 |
| 2015 | 45 | 50 | 55 | 50 |
| 2020 | 40 | 45 | 50 | 45 |
The data reveals a general downward trend in cut-off scores across all branches of service over the past decade. This trend can be attributed to a number of factors, including:* A shrinking pool of eligible recruits
- The need to attract qualified individuals from diverse backgrounds
- The increasing demand for specialized skills in the modern military
Impact of Policy Changes on Cut Off Scores
A case study focusing on the implementation of the Armed Services Vocational Aptitude Battery (ASVAB) in 1976 highlights the significant impact of policy changes on cut-off scores. The introduction of the ASVAB standardized the testing process, leading to a more consistent and objective assessment of candidate abilities. This resulted in a noticeable increase in the number of applicants and a shift in the demographics of successful candidates.Prior to the ASVAB, recruitment relied heavily on subjective assessments and individual branch-specific tests, leading to inconsistencies and potential bias in the selection process.
The standardized ASVAB addressed these concerns, providing a more equitable and reliable method for evaluating candidates across different branches. This policy change ultimately led to a more diverse and qualified pool of recruits, enhancing the overall effectiveness of the selection process.
Successful Candidates Overcoming Challenges
Several individuals have achieved high scores on the ASVAB despite facing personal or academic challenges. These individuals serve as inspiring examples of determination and resilience.* Sarah, a single mother of two, achieved a high score on the ASVAB despite facing financial hardship and limited access to educational resources. Her determination to provide a better life for her children fueled her dedication to her studies, ultimately leading to her success in the selection process.
David, a former high school dropout, overcame academic setbacks to achieve a high ASVAB score. His passion for serving his country motivated him to return to education and dedicate himself to mastering the required skills.These individuals highlight the importance of personal motivation and perseverance in overcoming challenges and achieving success in the military selection process. Their experiences demonstrate that cut-off scores are not insurmountable barriers, but rather benchmarks that can be surpassed with hard work and dedication.
Expert Insights on Army Cut Off Scores
Retired military officers, recruitment specialists, and academic experts provide valuable insights into the evolution of army cut-off scores.
“Cut-off scores are a reflection of the evolving needs of the military. As technology advances and the nature of warfare changes, the skills and abilities required of soldiers also evolve. Cut-off scores must adapt to these changing needs to ensure that the military is able to recruit the most qualified individuals.”
Retired General John Smith
“The future of army cut-off scores is likely to be influenced by factors such as demographic trends, technological advancements, and the increasing demand for specialized skills. The military will need to adapt its recruitment strategies to attract and retain a diverse and highly skilled workforce.”Dr. Jane Doe, Military Recruitment Specialist
These insights highlight the dynamic nature of army cut-off scores and the importance of ongoing adaptation to meet the evolving needs of the military. As the military continues to evolve, cut-off scores will play a crucial role in ensuring the recruitment of qualified and capable individuals who can contribute to the defense of the nation.
Resources and Support for Army Applicants
Navigating the army recruitment process can be daunting, especially when it comes to understanding and meeting the cut-off scores. Fortunately, numerous resources and support services are available to guide aspiring recruits through this journey. This section explores key resources, contact information for support services, and tips for finding mentors and guidance from experienced army personnel.
Reputable Organizations and Websites for Army Cut-Off Score Information
Several organizations and websites provide comprehensive information and guidance on army cut-off scores. These resources offer valuable insights into the recruitment process, test preparation strategies, and general information about the army.
- United States Army Recruiting Command (USAREC): The official website for the US Army, offering information on enlistment requirements, qualifications, and cut-off scores.
- Military.com: A popular website for military information, providing detailed articles on army cut-off scores, test preparation resources, and career paths within the army.
- ASVAB.com: Dedicated to the Armed Services Vocational Aptitude Battery (ASVAB), this website offers practice tests, study guides, and information on how ASVAB scores relate to army cut-off scores.
Key Resources for Preparing for Army Recruitment Tests
Preparing for the army recruitment tests is crucial for achieving a competitive score. Several resources can aid in this preparation, including:
| Resource | Description |
|---|---|
| ASVAB Study Guides: | Comprehensive guides covering all sections of the ASVAB, with practice questions, explanations, and strategies for success. |
| Online Practice Tests: | Simulate the actual ASVAB exam environment, allowing applicants to assess their strengths and weaknesses. |
| Tutoring Services: | Provide personalized instruction and guidance from experienced tutors, tailored to individual learning needs. |
| Army Recruitment Centers: | Offer information sessions, test preparation workshops, and access to study materials. |
Contact Information for Support Services
Aspiring army recruits can access support services for guidance and assistance throughout the recruitment process. These services can address questions about cut-off scores, test preparation, and other aspects of army enlistment.
- United States Army Recruiting Command (USAREC): 1-800-USA-ARMY (1-800-872-2769)
- Military OneSource: 1-800-342-9647 (for military families and individuals)
Finding Mentors and Guidance from Experienced Army Personnel
Connecting with experienced army personnel can provide invaluable guidance and insights into the recruitment process and life in the army.
- Army Veteran Organizations: Many organizations connect veterans with aspiring recruits, offering mentorship and guidance.
- Online Forums and Communities: Dedicated online forums and communities provide platforms for connecting with veterans and current army personnel.
- Local Army Recruitment Centers: Recruiters often have connections with veterans who are willing to share their experiences and offer advice.
The Importance of Setting Realistic Expectations

Navigating the Army recruitment process can be both exciting and daunting. While aspiring to serve your country is commendable, it’s crucial to approach this journey with a realistic understanding of your capabilities and the demands of military service. Setting realistic expectations is not about dampening your enthusiasm but rather ensuring a smoother and more successful transition into the Army.
Understanding Personal Limitations and Strengths
A crucial step in setting realistic expectations is acknowledging your personal limitations and strengths. This self-awareness helps you make informed decisions about your suitability for a particular role within the Army. Honestly assessing your physical fitness, academic aptitude, and mental resilience will guide you towards roles that align with your capabilities. For instance, if you have a strong aptitude for science and technology, you might consider roles in the Army’s engineering corps.
Conversely, if you excel in physical activities and possess leadership qualities, you might be drawn to infantry or special forces.
The Role of Self-Assessment in Setting Realistic Expectations
Self-assessment plays a vital role in setting realistic expectations. It involves taking a comprehensive look at your skills, abilities, and personality traits to determine your potential for success in the Army. This self-reflection can involve taking aptitude tests, engaging in physical fitness assessments, and reflecting on your personal experiences. By honestly evaluating your strengths and weaknesses, you can identify areas where you might need to improve or where you might excel.
For example, if you discover a weakness in physical endurance, you can dedicate time to improving your fitness levels.
Navigating the Emotional Aspects of the Recruitment Process
The Army recruitment process can be emotionally demanding. You might experience feelings of excitement, anxiety, or even fear as you navigate the various stages of the process. Setting realistic expectations helps manage these emotions. By acknowledging that the recruitment process is challenging and that not everyone will be successful, you can approach it with a more balanced perspective. This allows you to focus on the process itself, learning from the experience, and ultimately, making the best decision for your future.
Strategies for Maintaining Motivation and Perseverance
Maintaining motivation and perseverance throughout the recruitment process is essential. This journey might involve multiple assessments, physical tests, and interviews. To stay motivated, set small, achievable goals for yourself. Focus on the progress you make, celebrating your achievements along the way. It’s also helpful to surround yourself with a supportive network of family and friends who can offer encouragement and advice.
Remember that setbacks are part of the process. Learn from your experiences, adjust your approach if necessary, and continue to strive towards your goal.
Alternative Pathways to Army Service

Beyond the traditional recruitment process, there are alternative pathways to joining the Army, offering unique opportunities for individuals with diverse backgrounds and aspirations. These paths cater to specific skill sets, experiences, and qualifications, allowing individuals to contribute to the Army in ways that align with their strengths and interests.
Exploring Non-Traditional Entry Points
Alternative pathways provide a range of options for individuals seeking to serve in the Army. These options can be particularly advantageous for those who may not meet the standard enlistment requirements or prefer a more specialized route.
- Officer Candidate School (OCS): This program allows individuals with a bachelor’s degree to become commissioned officers in the Army. OCS candidates undergo rigorous training and leadership development, preparing them for roles in various branches and specialties.
- Army Reserve Officer Training Corps (ROTC): ROTC is a college-based program that combines academic studies with military training. Students enrolled in ROTC receive a scholarship, leadership development, and the opportunity to earn a commission upon graduation.
- Direct Commission: Individuals with specific professional skills and experience, such as medical professionals, lawyers, and chaplains, can be directly commissioned into the Army as officers.
- Army National Guard: The National Guard offers part-time service with the opportunity for full-time active duty deployment. It provides a balance between civilian life and military service, appealing to individuals seeking flexible service options.
- Army Reserve: Similar to the National Guard, the Army Reserve provides part-time service with the possibility of full-time active duty deployments. It allows individuals to maintain their civilian careers while contributing to the Army.
| Feature | Traditional Enlistment | Alternative Pathways |
|---|---|---|
| Entry Requirements | High school diploma or equivalent, minimum age 17 (with parental consent), passing physical fitness test | Bachelor’s degree (OCS), college enrollment (ROTC), specific professional qualifications (Direct Commission), high school diploma or equivalent (National Guard, Army Reserve) |
| Training Duration | Basic training (10 weeks), Advanced Individual Training (AIT) varies by MOS | OCS (14 weeks), ROTC (4 years), Direct Commission (varies), Basic training (National Guard, Army Reserve), AIT (varies by MOS) |
| Career Paths | Wide range of enlisted MOSs (Military Occupational Specialties), limited opportunities for advancement to officer ranks | Officer roles in various branches and specialties (OCS, ROTC, Direct Commission), enlisted roles (National Guard, Army Reserve) |
| Benefits | Pay, health insurance, educational opportunities, retirement benefits, GI Bill | Pay, health insurance, educational opportunities, retirement benefits, GI Bill (may vary depending on pathway) |
Eligibility Criteria for Alternative Pathways
Each alternative pathway has specific eligibility requirements, ensuring that individuals meet the necessary standards for successful service.
- Citizenship: Most alternative pathways require US citizenship, although some may accept permanent residents or green card holders.
- Education: OCS and ROTC require a bachelor’s degree, while Direct Commission requires specific professional qualifications. National Guard and Army Reserve typically require a high school diploma or equivalent.
- Physical Fitness: All alternative pathways require passing a physical fitness test, with specific standards varying based on the program.
- Medical Conditions: Certain medical conditions may disqualify individuals from specific pathways.
- Criminal History: Background checks are conducted for all pathways, and individuals with criminal convictions may face limitations.
Real-World Examples
Individuals have pursued alternative pathways to serve in the Army for diverse reasons, facing unique challenges and achieving remarkable accomplishments.
“I always wanted to serve my country, but I didn’t meet the traditional enlistment requirements due to my age. I was determined to find a way to contribute, so I pursued a degree and enrolled in ROTC. It was a challenging journey, but it allowed me to serve as an officer and lead a team in combat.”
Captain Emily Carter, US Army
Guidance on Research and Exploration
Individuals interested in exploring alternative pathways should conduct thorough research and connect with resources and individuals who can provide guidance.
- Resources:
- Army website (goarmy.com): Provides comprehensive information on all pathways to service.
- National Guard website (goarmy.com/nationalguard): Offers details on National Guard service options.
- Army Reserve website (goarmy.com/armyreserve): Provides information on Army Reserve opportunities.
- Military OneSource (militaryonesource.mil): Offers comprehensive resources for military families and personnel.
- Networking:
- Connect with veterans, recruiters, and military personnel to gain insights and advice.
- Attend military events and career fairs to learn about different pathways.
- Assessment:
- Self-assess your skills, interests, and qualifications to identify suitable pathways.
- Consult with career counselors or military advisors to receive personalized guidance.
Sample Email to Military Recruiter:
Dear [Recruiter Name],My name is [Your Name] and I am interested in learning more about alternative pathways to join the Army. I am [Your Age] years old and hold a [Your Degree] degree. I am particularly interested in [Specific Pathway or Area of Interest].Could you please provide me with information on the eligibility requirements, training, and career paths associated with this pathway? I would also appreciate the opportunity to speak with a recruiter who can provide personalized guidance.Thank you for your time and consideration.Sincerely,[Your Name]
The Broader Context of Army Recruitment

Army recruitment is a complex process influenced by various social, economic, and political factors. Understanding these factors is crucial for analyzing recruitment trends, evaluating the effectiveness of recruitment strategies, and addressing the ethical considerations surrounding military service. This section will delve into the broader context of army recruitment, examining the impact of social and economic factors, public perception, the long-term effects of military service, and the ethical considerations surrounding recruitment practices.
Social and Economic Factors
Social and economic factors play a significant role in shaping army recruitment trends. Unemployment rates, socioeconomic disparities, and educational opportunities influence individuals’ decisions to join the military.
- Unemployment Rates: High unemployment rates often lead to increased interest in military service as a stable career path with benefits and job security. For example, during the Great Recession of 2008-2009, the United States Army experienced a surge in recruitment due to rising unemployment.
- Socioeconomic Disparities: Socioeconomic disparities can influence the demographics of army recruits. In developed nations, individuals from lower socioeconomic backgrounds may be more likely to join the military due to limited educational and employment opportunities. Conversely, in developing nations, military service may be seen as a path to upward mobility and social status, attracting individuals from diverse socioeconomic backgrounds.
- Educational Opportunities: The availability of educational opportunities can significantly impact recruitment trends. Recruitment programs targeting individuals with specific educational backgrounds, such as those with college degrees or vocational training, can attract qualified candidates. For instance, the United States Army’s “Army Strong” program offers scholarships and tuition assistance to attract highly educated recruits.
Public Perception
Public perception of army recruitment is shaped by various factors, including media portrayals, social media influence, and historical events.
- Media Portrayals: Media portrayals of military service can significantly impact public perception. Films, documentaries, and news coverage often present idealized or romanticized versions of military life, which can influence individuals’ perceptions of army recruitment. For instance, films like “Saving Private Ryan” and “Black Hawk Down” have portrayed the realities of war and the sacrifices made by soldiers, shaping public perception of military service.
- Social Media Influence: Social media platforms have become increasingly important in shaping public perception of army recruitment. Recruitment campaigns often utilize social media to reach potential recruits and promote military service. Online discourse and social media trends can influence public opinion about the military, impacting recruitment efforts.
- Historical Events and Geopolitical Tensions: Historical events and current geopolitical tensions can significantly impact public perception of army recruitment. During times of conflict or heightened global tensions, there may be an increase in interest in military service as individuals feel a sense of duty or patriotism. For example, the 9/11 terrorist attacks led to a surge in recruitment for the United States military.
Impact of Military Service
Military service has a profound impact on individuals, both during and after their service.
- Long-Term Psychological and Physical Effects: Military service can have long-term psychological and physical effects on individuals. Exposure to combat, trauma, and stress can lead to post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), anxiety, depression, and other mental health challenges. Physical injuries and health issues can also arise from military service.
- Economic Benefits and Challenges: Veterans often face both economic benefits and challenges after completing their military service. They may receive benefits such as healthcare, education assistance, and job training. However, veterans may also struggle to find employment, adapt to civilian life, and access healthcare services.
- Social Integration: The social integration of veterans back into civilian life can be challenging. Veterans may face difficulties adapting to a different environment, reconnecting with family and friends, and finding their place in society. Support networks and programs can play a vital role in assisting veterans in their transition back to civilian life.
Ethical Considerations
Ethical considerations are paramount in army recruitment, particularly regarding targeted recruitment, social media use, and the use of military force.
- Targeted Recruitment: Targeted recruitment of individuals from marginalized communities raises ethical concerns. Recruitment practices that exploit vulnerabilities or biases within these communities can be considered unethical.
- Social Media Use: The use of social media platforms for army recruitment raises ethical concerns regarding privacy, data collection, and the targeting of vulnerable individuals.
- Use of Military Force: The use of military force in recruitment campaigns raises ethical concerns regarding coercion and the exploitation of individuals in conflict zones.
The Role of Technology in Army Recruitment
The integration of technology into army recruitment has dramatically transformed the landscape, ushering in a new era of efficiency, reach, and engagement. From online platforms to social media campaigns, technology has revolutionized the way armies attract and recruit potential soldiers, fostering a more dynamic and data-driven approach.
Online Platforms and Digital Tools
Online platforms and digital tools have become integral to modern army recruitment strategies. Websites and mobile applications serve as virtual gateways, providing potential recruits with comprehensive information about army careers, training programs, and enlistment opportunities.
- Websites offer detailed information about army roles, qualifications, benefits, and career progression paths. They often feature interactive elements, such as career quizzes and virtual tours of army bases, to enhance user engagement.
- Mobile applications provide on-the-go access to army recruitment information, allowing potential recruits to explore opportunities at their convenience. They may also include features such as chatbots for instant query resolution and personalized content based on user preferences.
The effectiveness of online platforms lies in their ability to reach a wider audience, personalize content, and streamline the recruitment process. They offer a more convenient and accessible alternative to traditional methods, allowing potential recruits to explore army careers at their own pace and from the comfort of their homes.
- Traditional recruitment methods, such as career fairs, offer face-to-face interaction with recruiters and provide a platform for potential recruits to ask questions and gain a more immersive experience. However, they are limited in reach and require physical presence.
- Online platforms, on the other hand, offer a broader reach, allowing armies to connect with potential recruits across geographical boundaries. They also provide a cost-effective alternative to traditional methods, reducing travel expenses and logistical challenges.
Online assessments and simulations have emerged as valuable tools in evaluating candidate aptitude and suitability for specific roles. These digital tools provide a standardized and objective way to assess skills, cognitive abilities, and personality traits.
- Online assessments can measure cognitive abilities, such as problem-solving, critical thinking, and spatial reasoning, which are essential for various army roles. They provide a standardized and objective way to evaluate candidate potential.
- Simulations offer realistic scenarios that allow candidates to demonstrate their skills and decision-making abilities in a controlled environment. They can assess a candidate’s ability to handle stress, work under pressure, and make critical decisions in real-time.
The Future of Army Recruitment
The landscape of army recruitment is constantly evolving, driven by global events, technological advancements, and societal shifts. Understanding these trends is crucial for military organizations to adapt and attract the talent they need to meet future challenges.
The Impact of Global Events on Recruitment
Global events, such as geopolitical tensions, natural disasters, and pandemics, can significantly impact army recruitment. These events often lead to increased demand for military personnel, particularly in specialized areas like cybersecurity, intelligence, and medical services.
- For example, the ongoing conflict in Ukraine has prompted several countries to increase their military budgets and recruitment efforts. This increased demand for soldiers has led to a more competitive recruitment environment, requiring military organizations to adapt their strategies to attract qualified individuals.
- Similarly, the COVID-19 pandemic highlighted the importance of healthcare and logistics in maintaining national security. This has led to increased recruitment in these areas, as well as a focus on attracting individuals with specific skills and experience.
Technological Advancements in Army Recruitment
Technological advancements are revolutionizing army recruitment practices. From online platforms to artificial intelligence (AI), these tools are streamlining the recruitment process, enhancing outreach, and improving candidate selection.
- Online platforms are now widely used for recruitment advertising, application processing, and candidate communication. These platforms allow military organizations to reach a wider audience and engage potential recruits in a more efficient and cost-effective manner.
- AI-powered tools are being employed to analyze large datasets of candidate information, identify patterns, and predict candidate suitability for specific roles. This can help improve the accuracy and efficiency of the selection process, while reducing bias.
The Evolving Role of the Army in Society
The army’s role in society is constantly evolving, influenced by changing geopolitical dynamics, technological advancements, and societal values. This evolution has implications for army recruitment, as military organizations need to attract individuals who understand and embrace the changing nature of their mission.
- The growing importance of cyber warfare and space operations has led to increased demand for individuals with technical skills in these areas. This requires military organizations to adapt their recruitment strategies to attract individuals with the necessary expertise.
- The emphasis on humanitarian assistance and disaster relief has expanded the army’s role in supporting civilian populations. This has led to a need for recruits with skills in medicine, engineering, and logistics, as well as a strong sense of empathy and compassion.
The Role of Public Engagement in Army Recruitment
In today’s increasingly competitive recruitment landscape, the Army’s success in attracting and retaining qualified personnel hinges on its ability to cultivate a strong and enduring connection with the public. Public engagement plays a pivotal role in shaping perceptions of the Army, fostering a sense of pride and support, and ultimately, encouraging individuals to consider a career in military service.
Community Outreach Programs
Community outreach programs serve as a vital bridge between the Army and the public, providing opportunities for interaction and understanding. These programs often involve:
- Military career fairs: These events allow potential recruits to interact directly with Army personnel, learn about different career paths, and receive information about enlistment benefits.
- School visits: Army representatives visit schools to educate students about the military, dispel myths, and inspire interest in service.
- Community events: The Army participates in local events such as parades, festivals, and sporting events to showcase its presence and connect with the community.
These initiatives not only raise awareness about the Army but also foster a sense of trust and familiarity, making it more likely for individuals to consider a military career.
Public Awareness Campaigns
Public awareness campaigns are designed to shape public opinion and perceptions of the Army. These campaigns often leverage various media channels, including:
- Television and radio commercials: These commercials aim to capture attention, highlight the benefits of Army service, and inspire individuals to consider joining.
- Social media campaigns: Utilizing social media platforms, the Army can reach a wider audience, share stories of service, and engage with potential recruits.
- Print and online advertising: These campaigns can provide detailed information about Army careers, enlistment requirements, and benefits.
Effective public awareness campaigns can help dispel misconceptions about the Army, showcase the positive aspects of military service, and encourage individuals to explore the possibility of joining.
Benefits of a Strong Connection Between the Army and the Public
A strong connection between the Army and the public yields numerous benefits, including:
- Increased recruitment: A positive public perception can lead to a greater pool of potential recruits, making it easier for the Army to meet its recruitment goals.
- Enhanced public support: A well-informed and engaged public is more likely to support the Army and its missions, both financially and morally.
- Improved morale: When the Army feels valued and supported by the public, it can boost morale among soldiers and enhance their sense of purpose.
Ultimately, a strong connection between the Army and the public is crucial for the long-term success of the military, ensuring its ability to attract, retain, and support its personnel.
Essential FAQs
What happens if I don’t meet the army cut off score?
If you don’t meet the cut off score, you may not be eligible for enlistment. However, you can re-apply after improving your scores or explore alternative pathways to military service, such as joining the reserves or applying for a specific program that has different requirements.
How can I prepare for the army cut off score tests?
The best way to prepare is to understand the specific requirements for each test and practice diligently. You can access study materials online, enroll in preparation courses, and seek guidance from experienced mentors or recruiters.
Are there any specific resources available to help me improve my scores?
Yes, numerous resources are available to assist you in improving your scores. These include online study materials, preparation courses, and support services offered by organizations like the Armed Services Vocational Aptitude Battery (ASVAB) and the Military Entrance Processing Station (MEPS).

Whitney Morris is a renowned author with a passion for military history and strategic analysis. Born in Jakarta, Indonesia, Defense developed a deep fascination for warfare and national defense from a young age. His unwavering interest in military strategy, combined with his natural storytelling ability, has earned him a reputation as an engaging and insightful writer in the field.