E10 military rank represents the highest attainable position within the enlisted ranks, signifying a pinnacle of experience, leadership, and expertise. This elite designation sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a story that is rich in detail and brimming with originality from the outset.
E10s are the backbone of the military, serving as trusted advisors, mentors, and tactical experts. Their responsibilities extend far beyond their immediate unit, encompassing strategic planning, operational execution, and the well-being of countless personnel. This rank is a testament to years of dedicated service and unwavering commitment, showcasing the unwavering dedication and unwavering commitment of those who reach this pinnacle of military service.
E10 in Global Military Systems
The E10 rank, often associated with the highest enlisted position in the United States military, has its own unique interpretation and structure in other countries’ military systems. Understanding the global context of this rank provides a broader perspective on its role and significance within different armed forces.
Investigate the pros of accepting gs-11 military rank equivalent in your business strategies.
Comparison with Equivalent Ranks
Comparing the E10 rank to equivalent ranks in other countries’ military systems requires considering both rank structure and responsibilities. While the E10 in the US military corresponds to the Sergeant Major of the Army, the highest enlisted position, other countries may have different rank designations or organizational structures.
- United Kingdom: The equivalent of the E10 rank in the British Army is Warrant Officer Class 1 (WO1). While both hold senior enlisted positions, the WO1 in the UK may have more direct command responsibilities than the Sergeant Major of the Army in the US.
- Canada: In the Canadian Forces, the Chief Warrant Officer (CWO) holds a similar position to the E10 in the US. CWOs are senior enlisted leaders who provide technical expertise and leadership within their respective branches of the Canadian Forces.
- France: The French Army’s equivalent to the E10 is Adjudant-Chef (ADJ-CH). This rank is considered the highest enlisted position in the French Army and carries significant responsibilities in terms of leadership and technical expertise.
Structure of E10 Positions in Global Militaries
The structure of E10 positions can vary significantly across different global militaries, reflecting the unique organizational needs and historical influences of each country.
- United States: The E10 rank in the US military is typically held by the Sergeant Major of the Army, who serves as the highest enlisted advisor to the Chief of Staff of the Army. This position involves providing strategic advice on enlisted matters, promoting enlisted morale and welfare, and advocating for enlisted personnel.
- United Kingdom: The Warrant Officer Class 1 (WO1) in the British Army can hold a variety of positions, including Regimental Sergeant Major (RSM), Command Sergeant Major (CSM), and Staff Sergeant Major (SSM). These positions are typically responsible for the overall discipline, training, and welfare of their respective units.
- Germany: The Oberstabsfeldwebel (OSFw) in the German Army is the equivalent of the E10 rank. This position is typically held by senior enlisted leaders who provide expertise in specific areas, such as logistics, training, or operations.
Cultural and Historical Influences, E10 military rank
Cultural and historical influences have shaped the development and evolution of the E10 rank across different nations.
- United States: The E10 rank in the US military has been influenced by the country’s history of volunteerism and the emphasis on meritocratic advancement within the armed forces. The Sergeant Major of the Army position reflects the importance of senior enlisted leadership in providing guidance and support to junior personnel.
- United Kingdom: The British Army’s tradition of warrant officers, dating back to the medieval period, has influenced the structure and responsibilities of the WO1 rank. Warrant officers are typically highly skilled and experienced individuals who have earned their positions through years of service and expertise.
- France: The French Army’s emphasis on technical expertise and professionalization has shaped the role of the Adjudant-Chef. This rank is often held by individuals who have specialized skills in a particular field, such as engineering, communications, or logistics.
Training and Qualifications for E10
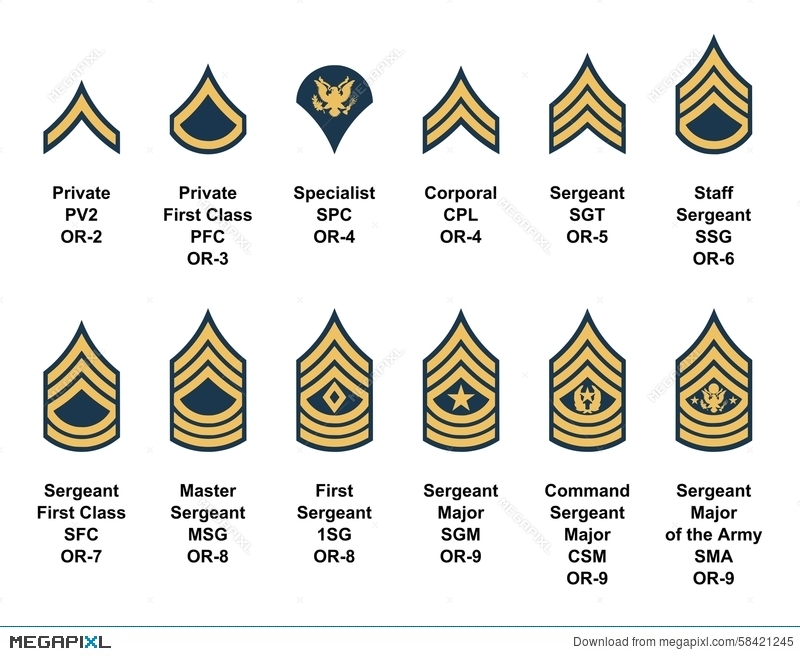
Reaching the E10 rank, the pinnacle of enlisted service, demands an extraordinary commitment to professional development and a consistent record of exceptional performance. Individuals aspiring to this prestigious position undergo rigorous training and accumulate a wealth of experience across various facets of their respective military branches.
Training and Education
The path to E10 is paved with a series of progressively challenging training programs and educational opportunities. These programs are designed to equip individuals with the knowledge, skills, and leadership qualities necessary to excel at the highest levels of military service.
- Basic Training: All enlisted personnel, regardless of their future career path, begin their military journey with basic training. This intensive program instills fundamental military skills, discipline, and physical fitness.
- Advanced Individual Training (AIT): Following basic training, individuals specialize in their chosen military occupational specialty (MOS). AIT programs provide in-depth training in specific technical and tactical skills, preparing them for their designated roles.
- Non-Commissioned Officer (NCO) Courses: As individuals progress through the enlisted ranks, they participate in NCO courses, which focus on leadership, management, and tactical decision-making. These courses enhance their ability to lead and mentor junior enlisted personnel.
- Senior NCO Courses: The highest-ranking NCOs participate in advanced leadership courses designed to develop their strategic thinking, policy comprehension, and ability to operate at the highest levels of military command.
- Formal Education: Many E10s hold college degrees or advanced certifications, demonstrating their commitment to continuous learning and intellectual growth.
Skills and Experience
E10s are seasoned veterans with a diverse range of skills and experience, honed through years of dedicated service. These skills are essential for effectively leading and managing large units and complex operations.
- Technical Proficiency: E10s possess deep expertise in their respective MOS, enabling them to provide expert guidance and mentorship to junior personnel.
- Leadership and Management: E10s are adept at leading and managing large teams, motivating personnel, and fostering a cohesive work environment.
- Tactical and Strategic Thinking: E10s possess a strong understanding of military tactics and strategy, enabling them to make sound decisions in complex and high-pressure situations.
- Communication and Interpersonal Skills: E10s are effective communicators, able to clearly articulate their vision and inspire confidence in their subordinates.
- Problem-Solving and Decision-Making: E10s are skilled problem-solvers and decision-makers, capable of analyzing complex situations and developing effective solutions.
Career Progression Path
The path to E10 is a long and demanding journey that requires consistent dedication and a commitment to professional development.
- Enlisted Entry: Individuals begin their military careers as enlisted personnel, typically starting at the E1 rank.
- Promotion through the Ranks: Through consistent performance, dedication, and completion of required training, individuals are promoted through the enlisted ranks (E2, E3, E4, etc.).
- Leadership Roles: As individuals progress, they take on increasing leadership responsibilities, leading small teams and units.
- Senior NCO Positions: The most experienced and highly qualified NCOs are selected for senior leadership positions, where they oversee larger units and play a significant role in operational planning and execution.
- E10 Selection: The selection process for E10 is highly competitive, with only the most exceptional NCOs being considered. This selection process often involves rigorous evaluations, interviews, and performance reviews.
E10 in Modern Warfare
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/USNavyEnlisted-57ed3b8e3df78c690f77e34b.png)
The E10 rank, often referred to as a “Sergeant Major” or “Master Chief Petty Officer,” represents the pinnacle of enlisted leadership in modern militaries. These individuals are highly experienced, skilled, and trusted professionals who play a vital role in ensuring the success of military operations. Their impact extends beyond their immediate unit, influencing the overall effectiveness and readiness of the armed forces.
This section delves into the multifaceted world of E10s in modern warfare, exploring their responsibilities, the impact of technology on their role, and the challenges and opportunities they face.
Role of E10 Personnel
E10s are entrusted with a wide range of responsibilities, encompassing leadership, mentorship, training, and operational expertise. They serve as the primary link between junior enlisted personnel and senior officers, ensuring effective communication, coordination, and execution of military objectives.
- Leadership and Mentorship: E10s are responsible for leading, mentoring, and developing junior enlisted personnel. They instill discipline, foster team cohesion, and guide the professional growth of their subordinates. They often act as role models, demonstrating leadership by example and inspiring their teams to strive for excellence.
- Training and Development: E10s play a crucial role in training and developing new recruits and junior enlisted personnel. They impart essential skills, knowledge, and tactics, ensuring that units are prepared to meet the demands of modern warfare.
- Operational Expertise: E10s possess deep operational expertise, having gained years of experience in various military roles and environments. They provide strategic insights and tactical guidance, contributing to the planning and execution of missions.
- Administrative and Logistics Support: E10s are often responsible for overseeing administrative and logistical tasks within their units. They manage resources, ensure equipment readiness, and coordinate support services, contributing to the overall efficiency and effectiveness of operations.
Impact of Technology
The rapid advancement of technology has significantly impacted the role and responsibilities of E10s. They are now expected to not only understand and adapt to new technologies but also to integrate them effectively into military operations.
- AI and Robotics: The emergence of AI and robotics is transforming the battlefield. E10s are increasingly tasked with managing and utilizing these technologies, requiring them to develop new skills and adapt to a more automated environment. For example, E10s may be responsible for overseeing the deployment and operation of unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) or autonomous ground vehicles, requiring them to understand the capabilities and limitations of these systems.
- Cyber Warfare and Information Warfare: The growing importance of cyber warfare and information warfare has created new challenges for E10s. They must be aware of cyber threats and vulnerabilities, understand the principles of information warfare, and be able to defend their units against cyberattacks. E10s may be tasked with leading cyber security teams, developing information warfare strategies, or conducting training on cyber defense measures.
- Data Analytics and Decision Making: E10s are increasingly expected to utilize data analytics to support decision-making. They must be able to interpret and analyze data from various sources, including intelligence reports, sensor data, and battlefield reports, to provide timely and accurate insights to their commanders.
Notable E10 Leaders: E10 Military Rank
While the E10 rank is a theoretical concept, it’s fascinating to look at historical figures who achieved a similar level of influence and impact, even if their titles didn’t explicitly reflect the E10 designation. These individuals often held positions of immense power and responsibility, leading armies, nations, or even entire empires. Their contributions and leadership styles offer valuable insights into the qualities and strategies that define exceptional leadership at the highest levels.
Notable E10 Leaders: Historical Examples
These individuals, while not formally designated as E10, embody the spirit of leadership associated with this hypothetical rank. Their achievements and leadership styles serve as compelling examples of the impact that exceptional individuals can have on the course of history.
- Alexander the Great: King of Macedon, Alexander the Great was a military genius who conquered vast territories, spreading Greek culture and establishing a vast empire that stretched from Greece to India. His leadership style was characterized by his unwavering ambition, tactical brilliance, and the ability to inspire loyalty in his troops. Alexander’s strategic campaigns, particularly his use of combined arms and flanking maneuvers, revolutionized military thinking and influenced military tactics for centuries to come.
- Genghis Khan: Founder of the Mongol Empire, Genghis Khan was a brilliant military leader who united the Mongol tribes and launched a series of conquests that resulted in the creation of the largest contiguous land empire in history. His leadership was marked by his strategic acumen, ruthless efficiency, and the implementation of innovative military tactics, such as the use of cavalry archers and the “feigned retreat” maneuver.
Genghis Khan’s leadership fostered a sense of unity and purpose among the Mongols, allowing them to achieve remarkable military successes.
- Napoleon Bonaparte: Emperor of France, Napoleon Bonaparte was a brilliant military strategist and political leader who rose to prominence during the French Revolution. He led French armies to numerous victories in Europe, transforming the French military into a formidable force. Napoleon’s leadership was characterized by his audacity, strategic brilliance, and his ability to inspire his troops. His use of rapid marches, flanking maneuvers, and combined arms tactics influenced military thinking for generations.
- Winston Churchill: Prime Minister of the United Kingdom during World War II, Winston Churchill was a renowned statesman and orator who rallied the British people against Nazi Germany. His leadership during the war was marked by his unwavering determination, his ability to inspire hope and confidence, and his strategic vision. Churchill’s leadership played a crucial role in ensuring the Allied victory in World War II.
7. E10 in Popular Culture
The portrayal of the E10 rank in popular culture has played a significant role in shaping public perception and understanding of E10 leadership. From movies and TV shows to novels and other literary works, E10 characters have been depicted in a wide range of ways, often influencing how audiences view the responsibilities, challenges, and complexities of this high-ranking position. This section explores the impact of these portrayals on public perception and the role of media in shaping understanding of E10 leadership.
Portrayals of E10 in Media
Media portrayals of E10 characters have provided audiences with diverse perspectives on this leadership role.
- Movies often depict E10 characters as individuals with exceptional skills, unwavering determination, and the ability to make difficult decisions under pressure.
- TV shows often explore the power dynamics and ethical dilemmas faced by E10 leaders, showcasing the challenges of balancing personal values with the demands of their position.
- Literary works often delve into the social status, cultural influence, and moral compass of E10 characters, providing nuanced insights into their motivations and complexities.
Impact of Media Portrayals
Media portrayals have a significant impact on public perception of the E10 rank.
- These portrayals can shape public understanding of the responsibilities, challenges, and expectations associated with this leadership role.
- However, media portrayals can also perpetuate biases and stereotypes about E10 individuals, potentially influencing real-world views and perceptions.
Media’s Role in Shaping Understanding
Media plays a crucial role in shaping public understanding of E10 leadership.
- Media can promote specific narratives about E10 individuals, highlighting their strengths, weaknesses, and motivations.
- Media can also challenge existing narratives, offering alternative perspectives and insights into the complexities of E10 leadership.
- The influence of media on public discourse surrounding E10 leadership can have significant implications for how individuals perceive and understand this high-ranking position.
Future of E10 in the Military

The E10 rank, while currently a rarity, holds the potential to become more prominent in future military structures. This is due to the evolving nature of warfare and the increasing complexity of military operations. As technology continues to advance and the battlefield becomes increasingly reliant on information and expertise, the need for highly skilled and experienced leaders at the strategic level will only grow.
Challenges and Opportunities for E10 Leaders
The future of E10 leaders will be shaped by a unique set of challenges and opportunities.
- Adapting to Technological Advancements: E10 leaders will need to be adaptable and proficient in navigating the ever-changing landscape of military technology. This includes mastering artificial intelligence, autonomous systems, and advanced communication networks.
- Managing Complex Operations: The increasing complexity of modern warfare, involving multi-domain operations and global interconnectedness, will require E10 leaders to possess exceptional strategic thinking skills and the ability to coordinate diverse forces across multiple theaters.
- Cultivating Leadership Skills: The E10 rank demands exceptional leadership qualities, including strategic vision, the ability to inspire and motivate subordinates, and the capacity to build strong relationships with allies and partners.
Impact of Technological Advancements
Technological advancements will significantly impact the responsibilities and authority of E10 personnel.
- Enhanced Decision-Making: AI-powered systems will provide E10 leaders with real-time data analysis and predictive capabilities, enabling faster and more informed decision-making in complex situations.
- Remote Command and Control: Advancements in communication technology will allow E10 leaders to remotely command and control forces from distant locations, expanding their reach and influence across the battlefield.
- Cyber Warfare Expertise: E10 leaders will require expertise in cyber warfare to effectively defend against and leverage cyber threats, which are becoming increasingly prominent in modern conflicts.
FAQ Corner
What is the difference between an E10 and an E9?
While both E9 and E10 are senior enlisted ranks, an E10 typically holds a higher level of responsibility and authority, often serving as the top enlisted advisor to a commanding officer. E10s may have greater strategic oversight and influence within a larger command structure.
Are there any specific benefits associated with achieving E10 rank?
E10s often receive higher pay and benefits, including increased retirement benefits and access to specialized training opportunities. They also enjoy a greater degree of prestige and recognition within the military community.
How long does it typically take to reach E10 rank?
The time required to reach E10 varies depending on the branch of service, individual performance, and opportunities for advancement. It typically takes several decades of dedicated service and exemplary performance to reach this highest enlisted rank.

Emma Nehls is a military writer and historian with a passion for exploring the intricacies of warfare and the human experience within the military. With extensive knowledge and a deep understanding of military strategy, tactics, and historical contexts, Nehls brings a unique perspective to his writings.