Defence maritime services play a critical role in safeguarding national interests and ensuring global stability. From protecting critical infrastructure to securing trade routes and conserving marine resources, these services are essential for maintaining a secure and prosperous maritime environment.
In this comprehensive overview, we will explore the scope, significance, and key challenges of defence maritime services. We will examine the role of maritime defence in safeguarding national sovereignty, maintaining regional stability, and contributing to international cooperation and diplomacy.
Maritime Defence Services Overview

Maritime defence services encompass a wide range of specialized services aimed at protecting maritime interests, ensuring maritime security, and safeguarding coastal and offshore assets. These services play a vital role in maintaining national sovereignty, preventing maritime threats, and facilitating safe and secure maritime activities.
Key services offered by maritime defence providers include:
- Naval patrols: Regular patrols by naval vessels to monitor and secure maritime borders, deter illegal activities, and respond to emergencies.
- Maritime surveillance: Continuous monitoring of maritime areas using sensors, radars, and other technologies to detect and track suspicious vessels, identify potential threats, and provide early warning of security risks.
- Anti-piracy operations: Specialized missions to combat piracy, protect commercial shipping, and ensure the safety of seafarers in piracy-prone areas.
- Maritime security assessments: Comprehensive assessments of maritime risks, vulnerabilities, and threats to develop and implement effective security measures for ports, terminals, and offshore installations.
- Hydrographic surveys: Detailed mapping of the seafloor to provide accurate navigational charts, support offshore operations, and ensure safe passage for vessels.
- Search and rescue operations: Coordinated efforts to locate, assist, and rescue individuals or vessels in distress at sea.
– Strategic Importance of Maritime Defence
Maritime defence plays a pivotal role in safeguarding national sovereignty, territorial integrity, and geopolitical interests. By maintaining control over maritime borders and exclusive economic zones, nations can prevent unauthorized access, protect natural resources, and deter potential adversaries.
Furthermore, maritime defence contributes to regional stability and conflict prevention. By establishing a credible deterrent, navies can discourage aggressive actions and maintain a balance of power. They also facilitate cooperation and diplomacy, providing a platform for dialogue and negotiation between nations with shared maritime interests.
Protection of Critical Infrastructure
Critical maritime infrastructure, such as ports, harbours, oil and gas platforms, and undersea cables, are essential for economic prosperity and national security. These assets are vulnerable to a range of threats, including sabotage, cyber attacks, and terrorism.
To protect this infrastructure, nations employ various measures, including physical security, surveillance systems, and cyber defence capabilities. Regular inspections, maintenance, and risk assessments are also crucial to identify and mitigate potential vulnerabilities.
Key Stakeholders in Maritime Defence
Maritime defence involves a complex network of stakeholders, each playing a vital role in safeguarding maritime security and ensuring the safety of global waterways.
The primary stakeholders in maritime defence include navies, coast guards, and civilian agencies. Each of these entities has distinct responsibilities and capabilities, working together to maintain maritime order and protect national interests.
Navies
Navies are the primary maritime defence forces responsible for protecting a nation’s territorial waters, exclusive economic zones, and other maritime interests. Their roles include:
- Defending against external threats, such as hostile navies, submarines, and aircraft.
- Maintaining naval superiority and deterring potential adversaries.
- Projecting power and influence abroad, supporting national security objectives.
Coast Guards
Coast guards are primarily responsible for maintaining law and order within a nation’s territorial waters and coastal areas. Their duties include:
- Enforcing maritime laws and regulations, including fisheries management, pollution control, and border protection.
- Conducting search and rescue operations, responding to maritime emergencies.
- Protecting coastal infrastructure, ports, and waterways from threats.
Civilian Agencies
Civilian agencies play a crucial role in supporting maritime defence efforts. These agencies include:
- Maritime safety authorities: Responsible for ensuring the safety of commercial shipping, regulating navigation, and preventing marine pollution.
- Customs and border protection agencies: Enforcing customs regulations, preventing smuggling, and monitoring maritime borders.
- Fisheries management agencies: Regulating fishing activities, protecting marine ecosystems, and enforcing sustainable fishing practices.
Technological Advancements in Maritime Defence

The maritime domain is undergoing a technological revolution, driven by advancements in unmanned systems, artificial intelligence (AI), and cyber defence capabilities. These advancements are transforming the way navies operate, enhancing operational efficiency, and effectiveness.
Unmanned Vessels
Unmanned vessels, including surface ships, submarines, and aerial vehicles, are becoming increasingly prevalent in maritime defence. These vessels can be operated remotely or autonomously, allowing navies to extend their reach and capabilities without putting personnel at risk. Unmanned vessels are also capable of performing a wide range of missions, such as surveillance, reconnaissance, mine countermeasures, and anti-submarine warfare.
AI-Powered Surveillance Systems
AI-powered surveillance systems are transforming the way navies collect and analyse data from the maritime environment. These systems can process vast amounts of data from sensors, cameras, and other sources to detect and track potential threats. AI algorithms can also be used to identify patterns and anomalies that may indicate hostile activity, helping navies to anticipate and respond to threats more effectively.
Cyber Defence Capabilities
Cyber defence capabilities are essential for protecting naval systems and networks from cyber attacks. These capabilities include intrusion detection and prevention systems, firewalls, and encryption technologies. Navies are also investing in cyber threat intelligence and incident response capabilities to detect and mitigate cyber threats.
International Cooperation in Maritime Defence

International cooperation is crucial for maritime defence due to the global nature of maritime threats. Transnational threats like piracy, terrorism, and illegal trafficking require collective action and information sharing among nations.
Multilateral Agreements
Multilateral agreements provide a framework for international cooperation in maritime defence. They establish rules, responsibilities, and mechanisms for joint operations and intelligence sharing.
- United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea (UNCLOS):Defines the legal framework for maritime activities, including territorial waters, exclusive economic zones, and continental shelves.
- International Maritime Organization (IMO):Promotes maritime safety and environmental protection through regulations and guidelines.
- North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO):Provides collective defence and security for member states, including maritime operations.
Joint Exercises, Defence maritime services
Joint exercises are essential for building interoperability and enhancing coordination between navies. They involve simulations, training exercises, and real-time operations.
- RIMPAC (Rim of the Pacific Exercise):The world’s largest international maritime exercise, involving 25 nations.
- Exercise Malabar:A trilateral naval exercise between India, the United States, and Japan.
- Sea Shield:A NATO-led maritime exercise focusing on anti-submarine warfare.
Policy Recommendations
To enhance international cooperation in maritime defence, consider the following policy recommendations:
- Strengthen existing multilateral agreements and establish new ones to address emerging threats.
- Increase participation in joint exercises to improve interoperability and coordination.
- Establish information-sharing platforms to facilitate real-time threat assessments and response coordination.
- Promote capacity building in maritime defence for developing nations to enhance their ability to contribute to collective security.
“International cooperation is the cornerstone of effective maritime defence. By working together, nations can pool their resources, share information, and enhance their collective ability to protect their maritime interests.”
Admiral James Stavridis, former Supreme Allied Commander of NATO
Challenges in Maritime Defence
Maritime defence faces numerous challenges that threaten global security and stability. These challenges include piracy, terrorism, and climate change.
Piracy remains a significant threat in certain regions, particularly in the Gulf of Aden and the Indian Ocean. Terrorist groups have also targeted maritime vessels and infrastructure, highlighting the vulnerability of maritime assets to such threats.
Climate Change and Maritime Defence
Climate change poses significant challenges to maritime defence, including rising sea levels, changing weather patterns, and increased frequency and intensity of extreme weather events. These factors can impact naval operations, infrastructure, and coastal communities.
Legal and Regulatory Framework for Maritime Defence

Maritime defence operations are guided by a complex legal and regulatory framework comprising international law and national legislation. Adherence to these frameworks is crucial for ensuring responsible and effective maritime defence practices.
International law, such as the United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea (UNCLOS), establishes the legal basis for maritime defence activities, including the rights and responsibilities of states in their territorial waters and beyond.
National Legislation
National legislation complements international law by providing specific regulations and guidelines for maritime defence within a country’s jurisdiction. These laws may cover issues such as the establishment of maritime defence zones, the use of force, and the protection of marine resources.
Importance of Compliance and Enforcement
Compliance with the legal and regulatory framework is essential for several reasons. First, it ensures that maritime defence operations are conducted in a responsible and ethical manner, respecting the rights and interests of other states and non-state actors.
Second, compliance helps prevent conflicts and misunderstandings between states by providing a clear understanding of the rules and procedures governing maritime defence activities.
Finally, effective enforcement of the legal and regulatory framework is necessary to deter violations and ensure that those who breach the rules are held accountable.
Training and Education for Maritime Defence Personnel

Training and education are essential for maintaining a skilled and capable maritime defence workforce. Maritime defence personnel require specialized knowledge and skills to operate complex equipment, navigate challenging environments, and respond effectively to threats.
Training Programs and Courses
Maritime defence organizations offer a range of training programs and courses tailored to the specific needs of their personnel. These programs cover topics such as:* Navigation and seamanship
- Ship handling and damage control
- Weapons systems and tactics
- Communication and information systems
- Maritime law and regulations
Continuous Professional Development
Continuous professional development (CPD) is crucial for maritime defence personnel to stay abreast of technological advancements and evolving threats. CPD programs provide opportunities for personnel to enhance their skills and knowledge through:* Refresher courses
- Workshops and seminars
- Online learning platforms
- On-the-job training
Simulation Exercises
Simulation exercises play a vital role in enhancing operational readiness by providing a realistic training environment. These exercises simulate various scenarios and challenges, allowing personnel to practice their skills and make informed decisions under pressure.
Training Levels and Qualifications
The levels of training and education available for maritime defence personnel vary depending on their roles and responsibilities. The following table Artikels the different levels along with the corresponding qualifications:| Level | Qualification | Responsibilities ||—|—|—|| Basic | Seaman | Performs basic duties such as lookout, steering, and maintenance || Intermediate | Able Seaman | Carries out more advanced tasks, including navigation, damage control, and weapons handling || Advanced | Petty Officer | Supervises and leads junior personnel, performs complex operations || Specialist | Chief Petty Officer | Holds specialized expertise in areas such as navigation, engineering, or weapons systems || Officer | Commissioned Officer | Commands and manages ships and units, makes strategic decisions |
Benefits of Training and Education
Training and education programs provide numerous benefits for maritime defence personnel, including:* Enhanced operational readiness
- Improved decision-making capabilities
- Increased confidence and competence
- Career advancement opportunities
- Contribution to the overall effectiveness of maritime defence forces
“Training is essential for maintaining the skills and knowledge required to operate effectively in the maritime domain,” said Admiral John Richardson, former Chief of Naval Operations of the United States Navy.”Simulation exercises are invaluable for testing our personnel’s abilities and preparing them for real-world scenarios,” added General Sir Nick Carter, former Chief of the Defence Staff of the United Kingdom.
– Identify key challenges and opportunities presented by emerging trends in maritime defence, such as the potential for increased efficiency and effectiveness, as well as the need for new approaches to training and education.
Emerging trends in maritime defence present both challenges and opportunities for navies worldwide. These trends include the increasing use of autonomous systems, artificial intelligence (AI), and other advanced technologies. While these technologies have the potential to increase the efficiency and effectiveness of maritime defence operations, they also present new challenges, such as the need for new approaches to training and education.
Challenges
One of the key challenges presented by emerging trends in maritime defence is the need for new approaches to training and education. Traditional training methods are no longer adequate to prepare personnel for the complex and rapidly changing environment of modern maritime warfare.
Defence maritime services play a crucial role in protecting a nation’s territorial waters and maritime assets. These services, encompassing activities such as naval patrols, anti-submarine warfare, and mine countermeasures, are essential components of a comprehensive defence strategy. To understand the scope and significance of defence maritime services, it is imperative to first delve into the broader concept of defence, which encompasses the measures and actions taken to safeguard a nation’s security and interests.
As articulated by defence experts, defence encompasses a wide range of activities, from military operations to diplomatic efforts, all aimed at deterring or responding to threats to national security.
New approaches to training and education are needed to ensure that personnel are equipped with the skills and knowledge necessary to operate and maintain these new technologies.
Opportunities
Emerging trends in maritime defence also present a number of opportunities for navies worldwide. These trends have the potential to increase the efficiency and effectiveness of maritime defence operations. For example, autonomous systems can be used to perform dangerous and repetitive tasks, freeing up personnel to focus on more complex tasks.
AI can be used to improve decision-making and situational awareness.
Economic Impact of Maritime Defence Services
Maritime defence services have a significant economic impact on coastal communities and national economies. They create jobs, stimulate infrastructure development, and support a wide range of industries.
Job Creation
Maritime defence activities create jobs in a variety of sectors, including shipbuilding, ship repair, and naval engineering. These jobs are often high-paying and offer opportunities for career advancement. In addition, maritime defence services can create indirect jobs in supporting industries, such as transportation, logistics, and tourism.
Defence maritime services play a crucial role in safeguarding maritime borders and ensuring the safety of coastal regions. One common defensive strategy employed in maritime warfare is known as a 3-4 defence ( what is a 3 4 defence ).
This tactic involves deploying ships in a specific formation to maximize defensive capabilities against potential threats. By understanding the principles of a 3-4 defence, defence maritime services can effectively deter and counter enemy incursions, protecting critical maritime assets and ensuring the security of coastal waters.
Infrastructure Development
Maritime defence activities often require the development of new or upgraded infrastructure, such as ports, shipyards, and training facilities. This infrastructure can benefit the entire community, not just the military. For example, new ports can be used for commercial shipping, and new shipyards can be used to build and repair civilian vessels.
Other Economic Benefits
Maritime defence services can also provide other economic benefits, such as:
- Increased tourism revenue
- Enhanced national security
- Support for scientific research and development
The economic impact of maritime defence services is significant and multifaceted. These services create jobs, stimulate infrastructure development, and support a wide range of industries. They also provide other economic benefits, such as increased tourism revenue, enhanced national security, and support for scientific research and development.
– Best Practices in Maritime Defence
Best practices in maritime defence encompass a range of strategies, tactics, and technologies that have proven effective in enhancing maritime security. By sharing lessons learned from successful operations worldwide, we can identify and implement best practices that contribute to the overall effectiveness of maritime defence operations.
Effective maritime defence strategies often involve a combination of deterrence, surveillance, and response capabilities. Deterrence measures aim to prevent potential threats from materializing, while surveillance systems provide early warning and situational awareness. Rapid response capabilities ensure timely and effective intervention in case of an incident.
Effective Tactics
- Layered Defence:Employing multiple layers of defence, such as surveillance, interceptors, and response units, to provide comprehensive protection.
- Intelligence-Driven Operations:Using intelligence to identify potential threats, prioritize targets, and optimize resource allocation.
- Inter-Agency Cooperation:Coordinating efforts between different agencies, including law enforcement, coast guard, and military, to enhance information sharing and operational effectiveness.
Innovative Technologies
- Advanced Surveillance Systems:Utilizing advanced technologies such as radar, sonar, and satellite imagery to enhance detection and tracking capabilities.
- Unmanned Systems:Employing unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) and unmanned surface vehicles (USVs) for extended surveillance, reconnaissance, and target engagement.
- Cybersecurity Measures:Implementing robust cybersecurity measures to protect critical infrastructure and information systems from cyber threats.
Case Studies of Maritime Defence Operations: Defence Maritime Services

Maritime defence operations play a crucial role in safeguarding national interests and ensuring maritime security. Analyzing case studies of notable maritime defence operations provides valuable insights into their objectives, challenges, and outcomes, enabling us to learn from past experiences and enhance future planning.
Case Studies in a Tabular Format
| Operation Name | Year | Objectives | Challenges | Outcomes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Operation Neptune Spear | 2011 | Capture or kill Osama bin Laden | Limited intelligence, hostile environment | Successful raid, elimination of high-value target |
| Operation Inherent Resolve | 2014-present | Defeat ISIS in Iraq and Syria | Complex geopolitical landscape, asymmetric warfare | Significant territorial losses for ISIS, ongoing stabilization efforts |
| Operation Atalanta | 2008-present | Counter piracy off the coast of Somalia | Vast operating area, international coordination | Reduced piracy incidents, increased maritime security |
Analysis of Lessons Learned
These case studies offer valuable lessons for future maritime defence planning:
Precise intelligence and situational awareness are critical for successful operations.
Collaboration and coordination among multiple stakeholders, including international partners, is essential.
Adaptability and flexibility are crucial in responding to evolving threats and challenges.
Technological advancements, such as unmanned systems and precision-guided munitions, can enhance operational effectiveness.
Training and education of personnel are paramount to ensure proficiency and mission success.
Emerging Technologies and Recommendations
Emerging technologies, such as artificial intelligence and autonomous systems, are transforming maritime defence operations. These technologies can enhance situational awareness, improve decision-making, and increase operational efficiency.To enhance maritime defence capabilities, we recommend:
Investing in research and development of cutting-edge technologies.
Strengthening international partnerships and cooperation.
Providing continuous training and education for personnel.
Developing comprehensive strategies to address evolving threats and challenges.
Future Outlook for Maritime Defence Services
The future of maritime defence services is shaped by technological advancements, geopolitical shifts, and emerging threats. Technological advancements such as autonomous systems, artificial intelligence, and advanced sensors will enhance the capabilities of maritime defence forces. Geopolitical shifts, including rising tensions and territorial disputes, will increase the demand for maritime defence services.
Potential Technological Advancements
- Autonomous systems will enable unmanned vessels and underwater vehicles to perform missions independently, increasing efficiency and reducing risk to personnel.
- Artificial intelligence will enhance decision-making, threat detection, and situational awareness, leading to improved response times and effectiveness.
- Advanced sensors will provide real-time data on maritime activities, improving surveillance and intelligence gathering capabilities.
Geopolitical Shifts
Rising tensions between nations and territorial disputes in strategic maritime regions will increase the demand for maritime defence services to protect national interests and ensure freedom of navigation.
Emerging Threats
- Asymmetric threats from non-state actors, such as piracy and terrorism, will require adaptable and agile maritime defence strategies.
- Cyber threats to maritime infrastructure and communication systems will pose new challenges to maritime defence forces.
- Environmental threats, such as climate change and pollution, will impact maritime operations and require specialized capabilities.
In summary, the future of maritime defence services will be characterized by technological advancements, geopolitical shifts, and emerging threats. Maritime defence forces will need to adapt to these challenges by investing in new technologies, strengthening international cooperation, and developing innovative strategies to ensure global stability and security.
Infographics and Data Visualization
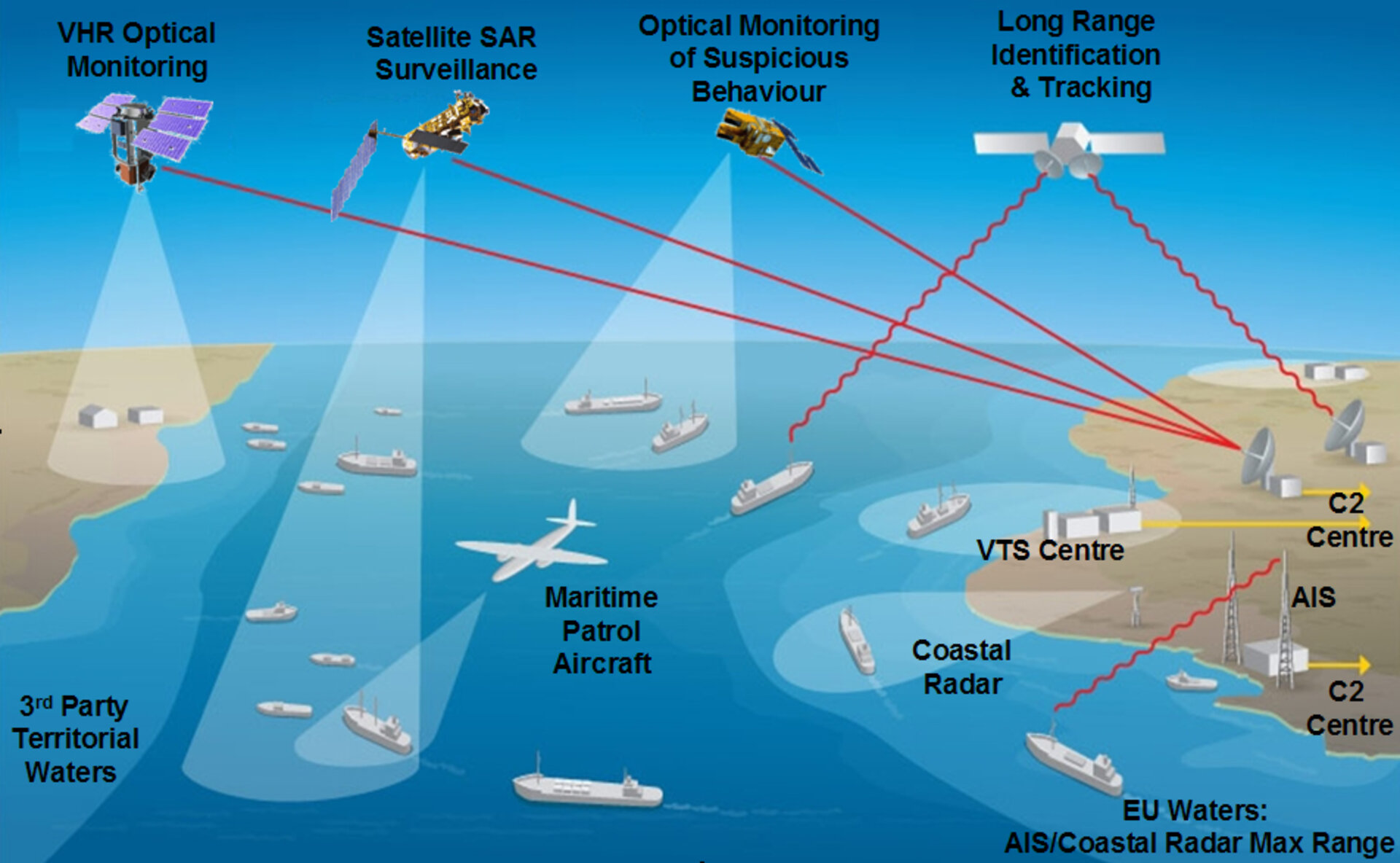
Infographics and data visualization play a crucial role in presenting complex information related to maritime defence services in an accessible and engaging manner. By employing charts, graphs, and maps, these visual representations help stakeholders quickly grasp key findings and trends.
Visualizing data through infographics and data visualization offers several advantages. First, it enhances the comprehension of complex information by simplifying and breaking it down into easily digestible chunks. Second, it facilitates comparisons and highlights patterns that might otherwise go unnoticed.
Third, it makes data more memorable and impactful, leaving a lasting impression on the audience.
Data Visualization Techniques
A range of data visualization techniques can be employed to effectively communicate maritime defence-related information. These techniques include:
- Charts:Bar charts, line charts, and pie charts are commonly used to represent data in a clear and concise manner. They are particularly useful for comparing different metrics and tracking changes over time.
- Graphs:Scatter plots and histograms are valuable for visualizing relationships between variables and identifying trends. Scatter plots help identify correlations, while histograms show the distribution of data.
- Maps:Geographic maps are essential for visualizing spatial data related to maritime defence. They can depict the location of naval assets, shipping lanes, and areas of strategic importance.
Clarifying Questions
What is the primary objective of defence maritime services?
To protect national interests, ensure maritime security, and contribute to global stability by safeguarding critical infrastructure, securing trade routes, and conserving marine resources.
How does maritime defence contribute to national sovereignty?
By safeguarding territorial waters, protecting maritime borders, and deterring threats to national security.
What are the key challenges facing defence maritime services?
Piracy, terrorism, climate change, and the proliferation of advanced technologies.

Whitney Morris is a renowned author with a passion for military history and strategic analysis. Born in Jakarta, Indonesia, Defense developed a deep fascination for warfare and national defense from a young age. His unwavering interest in military strategy, combined with his natural storytelling ability, has earned him a reputation as an engaging and insightful writer in the field.