Trend Report Army: Navigating the Future of Warfare delves into the evolving landscape of modern militaries, exploring the profound impact of technological advancements, strategic shifts, and societal changes. This report examines the current trends in military technology, the changing nature of warfare, and the critical role of the army in a rapidly evolving world. From the integration of artificial intelligence to the rise of hybrid warfare, we explore the challenges and opportunities facing armies in the 21st century.
This report analyzes the impact of these trends on military recruitment, training, operations, and equipment, highlighting the key challenges and opportunities for armies worldwide. We examine the ethical considerations surrounding the use of advanced technology in warfare, the role of the army in society, and the future of military innovation.
Understanding the Military Landscape
The global military landscape is undergoing a rapid transformation, driven by advancements in technology, evolving threats, and changing geopolitical dynamics. The integration of artificial intelligence, robotics, and cyberwarfare into military operations is fundamentally altering the nature of warfare, posing both opportunities and challenges for nations seeking to maintain their security.
Military Technology Advancements
The rapid pace of technological innovation is driving significant advancements in military capabilities, creating new weapons systems, enhancing battlefield awareness, and revolutionizing the way conflicts are waged.
The Trend Report Army, a clandestine organization rumored to exist within the military, operates in the shadows, gathering intelligence and analyzing trends that could impact global security. Their reports are said to be highly detailed, even delving into the minutiae of army points and their potential impact on troop morale and operational effectiveness. Though their existence remains unconfirmed, whispers of their influence persist, adding an air of intrigue to the world of military intelligence.
| Technology | Capabilities | Potential Impact | Examples |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hypersonic Missiles | Speeds exceeding Mach 5, high maneuverability, difficult to intercept | Threat to existing defense systems, potential for rapid strikes, increased risk of escalation | Russia’s Kinzhal missile, China’s DF-ZF hypersonic glide vehicle |
| Directed-Energy Weapons | Precision targeting, potential for non-lethal effects, rapid fire capabilities | Disruption of enemy communications, electronic warfare, potential for defensive applications | High-power microwave weapons, laser systems |
| Advanced Drones | Persistent surveillance, precision strikes, low-cost operations | Increased battlefield awareness, targeted attacks, potential for autonomous operations | US Air Force MQ-9 Reaper, Turkish Bayraktar TB2 |
| Cyber Warfare | Disruption of enemy communications, data theft, infrastructure sabotage | Erosion of trust in information, disruption of critical services, potential for escalation | Stuxnet worm, NotPetya ransomware |
| Artificial Intelligence | Automated decision-making, enhanced situational awareness, improved logistics | Increased speed and accuracy of military operations, potential for autonomous weapons systems, ethical considerations | AI-powered target identification, autonomous drones, battlefield simulation systems |
| Robotics | Recon, surveillance, combat support, potential for autonomous operations | Increased efficiency and safety for soldiers, ethical considerations surrounding autonomous weapons systems | Boston Dynamics’ Spot robot, military robots for bomb disposal |
Evolving Nature of Warfare
The traditional concept of warfare is being challenged by the rise of hybrid and asymmetric conflicts, where adversaries employ a combination of conventional and unconventional tactics to achieve their objectives.
“The battlefield of the future will be characterized by a blurring of lines between traditional and unconventional warfare, making it more difficult to distinguish between friend and foe.”
*[General Mark Milley, Chairman of the Joint Chiefs of Staff]*
- Hybrid Warfare: Hybrid warfare combines conventional military tactics with unconventional methods, such as information warfare, cyberattacks, and economic sanctions. This approach seeks to achieve strategic objectives without resorting to full-scale conventional war. Examples include Russia’s annexation of Crimea and its ongoing intervention in eastern Ukraine, where a combination of military force, cyberattacks, and disinformation campaigns were employed to achieve strategic goals.
- Asymmetric Warfare: Asymmetric warfare occurs when adversaries with vastly different resources and capabilities engage in conflict. This often involves non-state actors using unconventional tactics to exploit the weaknesses of their opponents. The rise of terrorist organizations and the use of suicide bombings are examples of asymmetric warfare, posing significant challenges to traditional military strategies.
- Information Warfare: Information warfare is the use of information and communication technologies to influence, disrupt, or degrade an adversary’s ability to wage war. This can include spreading disinformation, hacking into critical infrastructure, or disrupting enemy communications. Information warfare is becoming increasingly important in modern conflicts, as it can be used to shape public opinion, undermine enemy morale, and influence decision-making.
Emerging Technologies in Modern Militaries
The integration of emerging technologies, such as artificial intelligence, robotics, and cyberwarfare, is transforming modern militaries, creating both opportunities and challenges.
- AI in Military Decision-Making: AI is being used to analyze vast amounts of data, predict enemy actions, and support strategic planning. This can lead to faster and more informed decision-making, but it also raises ethical concerns about the potential for bias and the role of humans in the decision-making process.
- Robotic Combat Platforms: Robots are increasingly being used in reconnaissance, surveillance, and even combat roles. This can reduce risk to human soldiers, but it also raises ethical and legal considerations surrounding the use of autonomous weapons systems.
- Cyberwarfare as a Strategic Tool: Cyberattacks are being used to disrupt enemy communications, steal intelligence, and cripple critical infrastructure. This can have a significant impact on military operations, but it also raises concerns about the potential for unintended consequences and the need for international norms to govern cyberwarfare.
Military Operations and Tactics
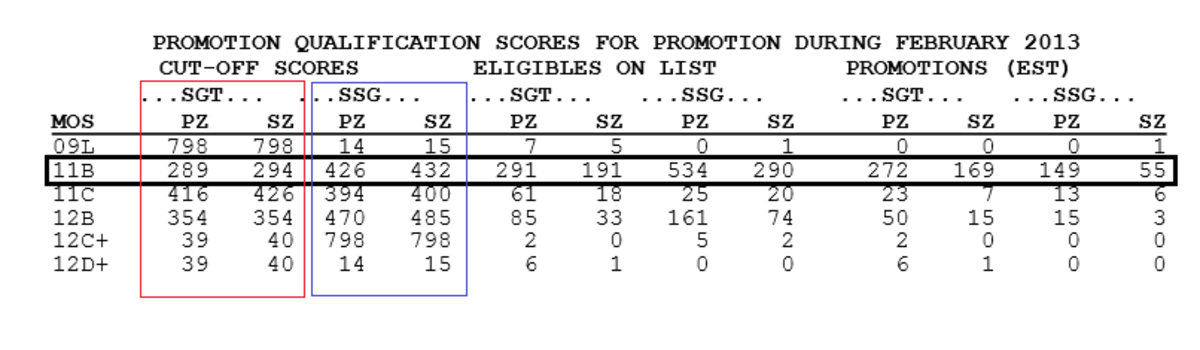
The modern battlefield is increasingly complex and dynamic, characterized by the rise of hybrid warfare, the proliferation of advanced technologies, and the evolving nature of threats. This section delves into the changing landscape of military operations and tactics, exploring the impact of these trends on warfare.
Hybrid Warfare
Hybrid warfare is a contemporary form of conflict that combines conventional military forces with unconventional tactics, such as information warfare, cyberattacks, economic sanctions, and political manipulation. This approach aims to achieve strategic objectives without resorting to large-scale conventional warfare.
- Examples of hybrid warfare include Russia’s annexation of Crimea in 2014 and its ongoing intervention in eastern Ukraine. These operations involved a combination of military force, cyberattacks, disinformation campaigns, and political pressure.
- The challenges posed by hybrid warfare include the difficulty in attributing responsibility for attacks, the blurring of lines between military and civilian targets, and the potential for escalation into conventional conflict.
Technology’s Impact on Battlefield Tactics
Technological advancements are revolutionizing battlefield tactics and strategies, influencing everything from weapon systems to communication and intelligence gathering.
- Unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs), commonly known as drones, have become increasingly prevalent in modern warfare, providing real-time surveillance, reconnaissance, and precision strike capabilities. The use of drones has significantly altered the way military forces conduct operations, allowing for more targeted and less collateral damage.
- Artificial intelligence (AI) is rapidly transforming military operations, enhancing situational awareness, automating tasks, and improving decision-making processes. AI-powered systems can analyze vast amounts of data, identify patterns, and predict future events, providing commanders with critical insights for planning and execution.
- Cyberwarfare has emerged as a significant dimension of modern conflict, with adversaries employing cyberattacks to disrupt critical infrastructure, steal sensitive information, and influence public opinion. The growing reliance on technology in military operations makes it vulnerable to cyberattacks, emphasizing the need for robust cyber defense capabilities.
Counter-Terrorism, Peacekeeping, and Humanitarian Assistance
Military operations are increasingly involved in counter-terrorism, peacekeeping, and humanitarian assistance efforts.
- Counter-terrorism operations involve combating terrorist groups and preventing terrorist attacks. These operations often require specialized training, intelligence gathering, and the ability to operate in complex and unpredictable environments.
- Peacekeeping missions are deployed to maintain peace and security in conflict-affected areas, often working with local authorities to facilitate dialogue, disarm combatants, and protect civilians. Peacekeeping operations often involve the use of force to protect themselves and civilians, but they primarily focus on non-military approaches such as mediation, conflict resolution, and humanitarian assistance.
- Humanitarian assistance operations provide relief and support to populations affected by natural disasters, conflict, or other crises. Military forces can be deployed to provide logistical support, medical care, and other essential services to those in need.
5. Military Equipment and Technology
The rapid evolution of military technology has profoundly reshaped the modern battlefield, creating new capabilities, challenges, and ethical dilemmas. This section explores the current state of military equipment and technology, focusing on weapon systems, vehicles, communication technologies, unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs), and cyberwarfare.
5.1 Weapon Systems
This section analyzes the current state of hypersonic missile technology, directed energy weapons, and laser-guided munitions.
- Hypersonic Missile Technology
Hypersonic missiles are a game-changer in modern warfare, posing a significant challenge to traditional missile defense systems. These missiles travel at speeds exceeding Mach 5, making them extremely difficult to track and intercept. Their high speed and maneuverability allow them to strike targets with unprecedented precision and speed, significantly reducing reaction time for adversaries. The development of hypersonic missiles has prompted a global arms race, with countries like China, Russia, and the United States investing heavily in this technology.- Capabilities
Hypersonic missiles have several advantages over traditional ballistic missiles. They can fly at lower altitudes, making them less vulnerable to detection and interception. Their high speed allows them to evade traditional missile defense systems, which are designed to intercept slower-moving targets. They can also maneuver in flight, making it even more difficult to predict their trajectory and intercept them. - Implications for Global Security
The proliferation of hypersonic missiles raises significant concerns about global security. They could potentially destabilize the balance of power, making it more difficult to deter aggression and increasing the risk of escalation. Their ability to strike targets quickly and with precision could also lead to a more rapid and destructive conflict.
- Capabilities
- Directed Energy WeaponsDirected energy weapons (DEWs) are a relatively new class of weapons that use concentrated energy, such as lasers or microwaves, to inflict damage. These weapons are still in their early stages of development, but they have the potential to revolutionize warfare.
- Potential Applications
DEWs can be used for a variety of military purposes, including offensive and defensive operations.They can be used to disable enemy sensors, disrupt communications, or even inflict damage on personnel or equipment. In defensive applications, DEWs can be used to intercept incoming missiles or aircraft.
- Limitations and Future Potential
DEWs currently face several limitations, including range, power requirements, and atmospheric conditions. However, ongoing research and development are addressing these limitations, and DEWs are expected to play a more significant role in future warfare.
- Potential Applications
- Laser-Guided MunitionsLaser-guided munitions (LGMs) are precision-guided weapons that use lasers to target and strike specific targets. They are highly accurate and effective, making them a valuable asset in modern warfare.
- Effectiveness in Modern Warfare
LGMs have proven to be highly effective in modern warfare, particularly in urban environments where collateral damage is a major concern. They have been used extensively in recent conflicts, such as the wars in Iraq and Afghanistan, with a high degree of accuracy. - Comparison with Traditional Unguided Bombs
LGMs are significantly more accurate than traditional unguided bombs. Unguided bombs rely on gravity and wind to reach their target, which can result in significant collateral damage. LGMs, on the other hand, can be precisely targeted, minimizing the risk of civilian casualties. - Examples of Use in Recent Conflicts
LGMs have been used extensively in recent conflicts, including the wars in Iraq and Afghanistan. They have been used to strike targets such as enemy vehicles, buildings, and military personnel. Their accuracy and effectiveness have made them a valuable asset in modern warfare.
- Effectiveness in Modern Warfare
Military Budgets and Spending
The global military landscape is constantly evolving, shaped by a complex interplay of geopolitical tensions, technological advancements, and domestic political factors. A key indicator of these dynamics is military spending, which reflects the priorities and capabilities of nations around the world. This section delves into the global trends in military spending from 2010 to 2023, analyzing the factors driving these trends and the implications for international security.
Global Trends in Military Spending
This section examines the global trends in military spending from 2010 to 2023, focusing on total spending, spending growth, and spending as a percentage of GDP.
Total Spending
- The United States has consistently held the top spot in global military spending, accounting for approximately 35% of total global spending in 2023.
- China has experienced significant growth in its military budget, becoming the second-largest spender in 2023, accounting for around 15% of global spending.
- Russia, India, and Saudi Arabia round out the top five spenders, with their budgets representing a significant portion of global military expenditure.
Spending Growth
- The average annual growth rate of global military spending from 2010 to 2023 has been around 1.5%, with significant variations across regions and countries.
- While the United States has maintained a relatively stable level of spending, China has witnessed a substantial increase in its military budget, averaging an annual growth rate of around 5% during this period.
- Several other countries, including India and Saudi Arabia, have also experienced significant increases in their military spending.
Spending as a Percentage of GDP
- The United States spends a relatively high percentage of its GDP on military expenditures, typically around 3.5% to 4%, while countries like China and Russia allocate a lower percentage of their GDP to defense.
- There are significant variations in military spending as a percentage of GDP across different regions, reflecting varying levels of economic development, security threats, and political priorities.
- The average global military spending as a percentage of GDP has remained relatively stable over the past decade, hovering around 2%.
Factors Driving Military Budget Allocations, Trend report army
This section explores the key factors driving military budget allocations, including geopolitical tensions, technological advancements, and domestic political factors.
Geopolitical Tensions
- The ongoing rivalry between the United States and China, particularly in the Indo-Pacific region, has contributed to increased military spending by both countries.
- The Russia-Ukraine conflict has also driven significant military spending increases, particularly in European countries seeking to enhance their defense capabilities.
- Regional conflicts and tensions, such as those in the Middle East and the Korean Peninsula, continue to influence military budget decisions in affected countries.
Technological Advancements
- The rapid development of advanced technologies, such as artificial intelligence, hypersonic weapons, and cyber warfare capabilities, has significantly impacted military spending priorities.
- Countries are investing heavily in research and development to acquire these technologies, leading to increased military budgets and a shift in military capabilities.
- The increasing reliance on technology in warfare has also led to a greater focus on cybersecurity and the development of cyber defense strategies.
Domestic Political Factors
- Public opinion, particularly in the context of perceived security threats, can influence military spending decisions.
- Political campaigns and elections often involve discussions about defense spending, with candidates making promises to increase or decrease military budgets.
- Domestic political factors, such as economic conditions and the influence of defense industry lobbyists, can also play a role in shaping military spending priorities.
Military Spending Priorities
This section compares and contrasts the military spending priorities of different countries, focusing on regional security threats, strategic objectives, and military capabilities.
Regional Security Threats
- Countries facing immediate security threats, such as terrorism or territorial disputes, often prioritize spending on counterterrorism operations, border security, or conventional forces.
- For example, countries in the Middle East, such as Saudi Arabia and Israel, have allocated significant resources to their militaries to address regional conflicts and security threats.
- Countries with limited resources may prioritize specific capabilities, such as air defense systems, to deter potential aggressors.
Strategic Objectives
- Countries with global ambitions, such as the United States and China, tend to prioritize spending on advanced military capabilities, including nuclear weapons, aircraft carriers, and advanced weapons systems.
- Countries with regional ambitions may focus on developing capabilities to project power within their region, such as building up their navies or investing in advanced air defense systems.
- Strategic objectives can also influence the development of specific military doctrines, such as deterrence or defense in depth.
Military Capabilities
- Countries with a focus on conventional warfare may prioritize spending on ground forces, tanks, artillery, and aircraft.
- Countries with a strong nuclear deterrent may prioritize spending on nuclear weapons, missile defense systems, and related infrastructure.
- The rise of cyber warfare has led to increased investment in cyber defense capabilities, including specialized units, training programs, and technological advancements.
Military Cooperation and Alliances
The global security landscape is characterized by increasingly complex and interconnected threats, demanding a collaborative approach to address shared challenges. Military cooperation and alliances have become indispensable tools for nations to enhance their security, project power, and maintain stability in a multipolar world. This section explores the evolving dynamics of military alliances, the role of international organizations, and key trends in cross-border military training and joint operations.
The Evolving Landscape of Military Alliances
Military alliances are formal agreements between nations that commit to mutual defense and cooperation. These alliances provide a framework for collective security, deterring potential adversaries and fostering stability. The Cold War era saw the formation of two major alliances: the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) and the Warsaw Pact. However, the end of the Cold War and the emergence of new security threats have led to a significant shift in the global alliance landscape.
- NATO, originally established to counter Soviet expansion, has expanded its membership and mission. It has increasingly focused on countering terrorism, promoting democracy, and responding to regional conflicts.
- The Asia-Pacific region has witnessed the rise of new alliances and partnerships, such as the Quadrilateral Security Dialogue (QUAD), comprising the United States, Japan, India, and Australia. These alliances aim to counter China’s growing influence and maintain a free and open Indo-Pacific.
- The emergence of non-state actors and transnational threats has prompted the formation of new alliances, such as the Global Coalition Against Daesh (ISIL). These coalitions bring together diverse nations to combat common enemies and share intelligence, resources, and expertise.
The Impact of Technology on Military Culture

The integration of technology into the modern military has not only revolutionized warfare but has also profoundly impacted the culture and values of armies worldwide. From the way soldiers communicate and train to the types of skills they need to be successful, technology has reshaped the very fabric of military life.
The Influence of Social Media and Online Communication
The pervasiveness of social media and online communication has had a significant impact on military culture. Soldiers are now constantly connected, both on and off duty, and this has led to a blurring of the lines between personal and professional life. The ease of communication has also created new challenges for maintaining operational security and preventing the spread of sensitive information.
- Increased Transparency and Public Awareness: Social media has made it easier for soldiers to share their experiences and perspectives on military life, leading to increased transparency and public awareness of military operations and challenges. This can have both positive and negative consequences, as it can foster public support but also expose sensitive information.
- New Forms of Communication and Collaboration: Online communication platforms have facilitated new forms of collaboration and information sharing within and between military units. This has led to more efficient decision-making and improved situational awareness.
- Challenges to Operational Security: The ease with which soldiers can share information online poses a significant challenge to operational security. Unintentional leaks of sensitive information can compromise missions and endanger troops.
The Impact of Virtual Reality on Military Training
Virtual reality (VR) technology is transforming military training by providing immersive and realistic simulations that can prepare soldiers for real-world scenarios. VR training allows soldiers to experience combat situations in a safe and controlled environment, developing critical skills and enhancing their preparedness.
- Enhanced Training Realism: VR simulations offer a high degree of realism, allowing soldiers to experience combat situations, weapon systems, and tactics in a safe and controlled environment. This immersive training can improve situational awareness, decision-making, and tactical proficiency.
- Cost-Effectiveness and Accessibility: VR training can be more cost-effective than traditional training methods, as it reduces the need for live-fire exercises and expensive equipment. VR training can also be accessed remotely, making it more accessible to soldiers in different locations.
- Development of Critical Skills: VR simulations can be used to train soldiers in a variety of skills, including marksmanship, navigation, medical procedures, and tactical decision-making. This allows soldiers to develop critical skills in a safe and controlled environment.
Military Ethics and Responsibility
The use of advanced technology in warfare raises profound ethical considerations, demanding a careful examination of the implications for military conduct and the broader societal impact. As military forces embrace technological advancements, the need for ethical frameworks and responsible leadership becomes paramount.
Ethical Considerations in the Use of Advanced Technology
The rapid evolution of military technology presents both opportunities and challenges for ethical decision-making. Advanced weapons systems, autonomous platforms, and data-driven warfare strategies introduce new ethical dilemmas.
- Autonomous Weapons Systems: The development and deployment of autonomous weapons systems raise concerns about accountability, the potential for unintended consequences, and the erosion of human control over the use of force. The lack of human oversight in decision-making processes raises questions about responsibility for actions taken by autonomous systems.
- Cyber Warfare: The use of cyber weapons and cyber operations poses ethical challenges related to the definition of war, the distinction between legitimate targets and civilian infrastructure, and the potential for unintended escalation.
- Data Collection and Surveillance: The increasing reliance on data collection and surveillance technologies in military operations raises concerns about privacy, civil liberties, and the potential for misuse of information. The ethical implications of collecting and analyzing vast amounts of personal data must be carefully considered.
- Artificial Intelligence and Decision-Making: The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) into military systems raises ethical questions about the role of human judgment in decision-making. The potential for bias in AI algorithms and the lack of transparency in decision-making processes require careful scrutiny.
12. Military Innovation and Research
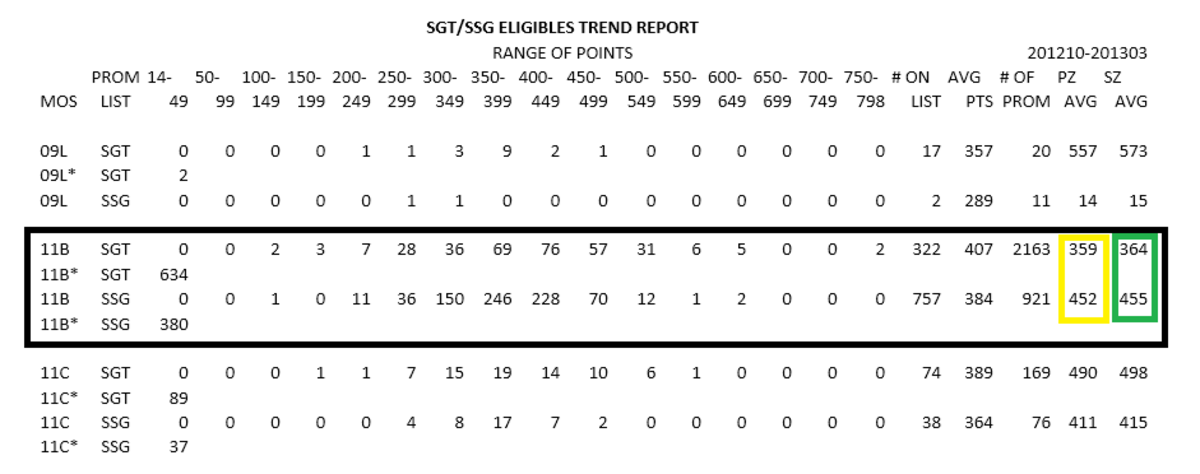
Military innovation and research (R&D) are critical drivers of military modernization and effectiveness. They shape the future of warfare by developing new technologies, tactics, and strategies. This section analyzes the trends in military R&D, the roles of key players, and the key areas of research that are shaping the future of warfare.
Trends in Military Research and Development
The past decade has witnessed significant shifts in military R&D, driven by evolving threats, technological advancements, and changing geopolitical dynamics. The following table highlights some of the key trends in military R&D:
| Trend | Description | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Increased Focus on Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) | Military organizations are investing heavily in AI and ML to enhance situational awareness, automate tasks, improve decision-making, and develop autonomous systems. | Development of AI-powered drones, autonomous vehicles, and advanced targeting systems. |
| Emphasis on Hypersonic Weapons and Space Warfare | The development of hypersonic weapons and space-based capabilities is a key priority for many militaries, aiming to gain strategic advantages and counter emerging threats. | Investments in hypersonic missiles, space-based sensors, and anti-satellite weapons. |
| Advancements in Cyber Warfare and Information Operations | Cyber warfare and information operations are becoming increasingly sophisticated, requiring advanced technologies and strategies to defend against cyberattacks and manipulate information. | Development of cyber defense systems, offensive cyber capabilities, and information warfare strategies. |
| Focus on Precision-Guided Munitions and Directed Energy Weapons | Military R&D is focused on developing highly precise weapons and directed energy technologies to enhance targeting accuracy and reduce collateral damage. | Development of advanced guided missiles, laser weapons, and high-energy microwave systems. |
| Emphasis on Network-Centric Warfare and Data Analytics | Military organizations are prioritizing the development of network-centric capabilities and data analytics tools to improve information sharing, coordination, and decision-making. | Investments in secure communication networks, data fusion systems, and advanced analytics platforms. |
Role of Universities, Private Companies, and Government Agencies in Military Innovation
Military innovation is often a collaborative effort involving universities, private companies, and government agencies. Each entity plays a distinct role in driving innovation in the military sector.
- Universities: Universities contribute to military innovation through research, education, and the development of new technologies. They provide a platform for basic research, train future generations of scientists and engineers, and often collaborate with government agencies and private companies on specific projects.
- Example: The Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) has a long history of collaboration with the Department of Defense, contributing to the development of advanced technologies such as radar systems, stealth materials, and autonomous vehicles.
- Private Companies: Private companies are major players in military innovation, developing and producing a wide range of technologies, systems, and equipment for the military. They often invest heavily in research and development, driven by market demand and the pursuit of technological superiority.
- Example: Lockheed Martin, Boeing, and Raytheon are leading aerospace and defense companies that develop and manufacture advanced aircraft, missiles, and other military systems.
- Government Agencies: Government agencies play a central role in funding, directing, and overseeing military R&D. They establish research priorities, allocate funding, and manage the development and acquisition of new technologies and systems.
- Example: The Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA) is a government agency responsible for funding high-risk, high-reward research projects with the potential to transform military capabilities.
Collaboration between universities, private companies, and government agencies is essential for driving military innovation. These partnerships enable the sharing of knowledge, resources, and expertise, leading to faster development and deployment of new technologies. However, challenges such as funding constraints, bureaucratic hurdles, and ethical concerns can hinder collaboration and innovation.
Key Areas of Research and Development Shaping the Future of Warfare
Several key areas of R&D are shaping the future of warfare, with the potential to transform military capabilities and strategies.
- Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning: AI and ML are revolutionizing warfare by enabling autonomous systems, improving decision-making, and enhancing situational awareness. These technologies can automate tasks, analyze vast amounts of data, and identify patterns that humans may miss.
- Technological Impact: AI-powered drones, autonomous vehicles, and advanced targeting systems will transform battlefield operations, increasing efficiency and effectiveness while reducing human risk.
- Future Scenario: In the future, AI-powered systems could be used for reconnaissance, target identification, and even autonomous combat, raising ethical concerns about the role of humans in warfare.
- Hypersonic Weapons and Space Warfare: Hypersonic weapons and space-based capabilities are changing the strategic landscape, enabling rapid strikes and the ability to control space. These technologies pose significant challenges to traditional defense systems and require new strategies for deterrence and defense.
- Technological Impact: Hypersonic missiles can travel at speeds exceeding Mach 5, making them difficult to intercept. Space-based sensors and weapons can provide global surveillance and strike capabilities, revolutionizing warfare in the space domain.
- Future Scenario: In the future, space could become a contested domain, with militaries vying for control of key orbital assets and using space-based weapons to influence events on Earth.
- Cyber Warfare and Information Operations: Cyber warfare and information operations are becoming increasingly sophisticated, requiring advanced technologies and strategies to defend against cyberattacks and manipulate information. These capabilities can disrupt critical infrastructure, steal data, and influence public opinion.
- Technological Impact: Advanced cyber defense systems, offensive cyber capabilities, and information warfare strategies are crucial for defending against cyberattacks and exploiting vulnerabilities in enemy networks.
- Future Scenario: In the future, cyberattacks could be used to cripple critical infrastructure, disrupt communications, and influence elections, potentially destabilizing entire nations.
- Directed Energy Weapons: Directed energy weapons, such as lasers and high-energy microwaves, offer the potential for precise targeting and minimal collateral damage. These technologies are still under development, but they have the potential to revolutionize warfare.
- Technological Impact: Directed energy weapons could be used to disable enemy sensors, disrupt communications, and even destroy targets with pinpoint accuracy.
- Future Scenario: In the future, directed energy weapons could be used to defend against missiles, counter drones, and even engage enemy aircraft, transforming the nature of air warfare.
- Biotechnology and Bioweapons: Biotechnology is rapidly advancing, with the potential to create new weapons and therapies. While bioweapons pose a significant threat, biotechnology also offers opportunities for developing new medical treatments and enhancing human performance.
- Technological Impact: Biotechnology could be used to develop new bioweapons, modify pathogens to make them more virulent, or create genetically engineered soldiers with enhanced capabilities.
- Future Scenario: In the future, bioweapons could be used to target specific populations or cause widespread disease, posing a serious threat to global security.
Organization
Military organization has undergone a dramatic transformation throughout history, evolving from small, decentralized feudal armies to large, complex professional standing forces. The transition from feudal armies, often based on personal loyalties and limited training, to professional standing forces marked a significant shift in the organization and effectiveness of armies. This transition was driven by factors such as the rise of nation-states, the development of new technologies, and the increasing importance of military professionalism.
- The rise of conscription, which emerged in the 19th century, played a crucial role in expanding the size and capabilities of armies. Conscription allowed nations to mobilize large numbers of citizens for military service, enabling the formation of massive armies that were essential for waging modern warfare.
- The impact of industrialization on military organization was profound, leading to the development of more complex and specialized military structures. The industrial revolution facilitated the mass production of weapons and equipment, requiring large-scale logistics and specialized training.
- Technological advancements, such as the development of mechanized warfare and the rise of cyberwarfare, have further transformed military organization. The introduction of tanks, aircraft, and other mechanized vehicles revolutionized battlefield tactics, requiring new organizational structures and training programs. The emergence of cyberwarfare has introduced new challenges, demanding the development of specialized cyber defense capabilities and the integration of cyber operations into military strategies.
Doctrine
Military doctrine, which encompasses the principles and theories guiding military operations, has evolved significantly over time. From ancient battle tactics to modern strategic concepts, military doctrine has adapted to changing circumstances, reflecting advancements in technology, the nature of warfare, and the strategic objectives of nations.
-
The influence of major military thinkers, such as Sun Tzu, Clausewitz, and Jomini, has profoundly shaped military doctrine. Sun Tzu’s “Art of War,” written in ancient China, emphasized the importance of deception, strategy, and understanding the adversary. Clausewitz’s “On War,” published in the 19th century, provided a comprehensive analysis of warfare, highlighting the political and social factors that influence military operations.
Jomini’s work on grand strategy and military planning continues to be influential in modern military thought.
- Operational concepts, such as maneuver warfare, attrition warfare, and asymmetric warfare, have evolved over time, reflecting the changing dynamics of warfare. Maneuver warfare, which emphasizes speed, flexibility, and surprise, gained prominence in the 20th century, challenging the traditional emphasis on attrition warfare, which focused on wearing down the enemy through sustained combat. Asymmetric warfare, characterized by the use of unconventional tactics and strategies by weaker adversaries against stronger opponents, has emerged as a significant challenge in contemporary warfare.
-
The influence of major military thinkers, such as Sun Tzu, Clausewitz, and Jomini, has profoundly shaped military doctrine. Sun Tzu’s “Art of War,” written in ancient China, emphasized the importance of deception, strategy, and understanding the adversary. Clausewitz’s “On War,” published in the 19th century, provided a comprehensive analysis of warfare, highlighting the political and social factors that influence military operations.
Technology
Technological innovations have played a pivotal role in shaping military history, revolutionizing warfare and influencing the balance of power. From gunpowder to the internet, key technological advancements have transformed battlefield tactics, logistics, and communication.
- The invention of gunpowder in the 13th century marked a turning point in warfare, leading to the development of firearms and cannons. These new weapons significantly increased the lethality of warfare, requiring new defensive strategies and tactical approaches.
- The printing press, invented in the 15th century, revolutionized communication and information dissemination, enabling the spread of military knowledge and the development of new strategies.
- The internet, which emerged in the late 20th century, has transformed communication, intelligence gathering, and the conduct of warfare. The internet has facilitated the rapid exchange of information, the development of cyberwarfare capabilities, and the creation of new military platforms and systems.
- The need to balance transparency with national security concerns.
- The competitive media landscape, where the army must compete for attention with other news sources.
- The potential for media bias or inaccuracies in reporting.
- Using social media platforms to engage with the public and share its story.
- Partnering with media outlets to produce accurate and informative content.
- Building relationships with journalists and media professionals.
- An increased focus on the human cost of war and conflict.
- Greater scrutiny of military spending and procurement practices.
- The rise of citizen journalism and social media as sources of information about military operations.
13. Military History and Legacy: Trend Report Army
The study of military history provides a deep understanding of the evolution of warfare, the factors that shape military strategies, and the enduring impact of past conflicts on the present and future. It allows us to analyze the development of military organization, doctrine, and technology, tracing the historical trends that have shaped the modern military landscape. By examining the lessons learned from past conflicts and military innovations, we can gain valuable insights into the strategic and operational challenges of contemporary warfare.
Historical Trends
The history of warfare is marked by a series of significant trends that have shaped the evolution of military organization, doctrine, and technology. These trends reflect the changing nature of warfare, driven by technological advancements, political shifts, and societal developments.
The Army and the Media

The media plays a pivotal role in shaping public perception of the military. The relationship between the army and the media is complex and multifaceted, often characterized by a delicate balance between transparency, national security, and public accountability.
The Media’s Influence on Public Perception
The media has a significant influence on how the public perceives the military. Through news reports, documentaries, and entertainment media, the public is exposed to a wide range of narratives about the military, its operations, and its personnel. This exposure shapes public opinion on issues such as military spending, recruitment, and the use of force.
“The media is the most powerful entity on earth. They have the power to make the innocent guilty and the guilty innocent.”
Malcolm X
Challenges and Opportunities for Effective Communication
The army faces a number of challenges in communicating its message effectively to the public. These challenges include:
Despite these challenges, the army has opportunities to communicate its message effectively. These opportunities include:
Key Trends in Media Coverage of Military Affairs
Media coverage of military affairs has evolved significantly in recent years. Key trends include:
FAQ Compilation
What are the key technological advancements driving changes in modern warfare?
Key technological advancements driving changes in modern warfare include artificial intelligence, robotics, cyberwarfare, hypersonic missiles, directed energy weapons, and advanced unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs). These technologies are fundamentally altering battlefield dynamics, strategic planning, and the very nature of conflict.
How is the army adapting to the changing nature of warfare?
The army is adapting to the changing nature of warfare by embracing new technologies, developing innovative training methods, and refining its strategic thinking. This includes focusing on hybrid warfare, cyber defense, information warfare, and the ethical considerations surrounding the use of autonomous weapons systems.
What are the key challenges facing armies in the 21st century?
Key challenges facing armies in the 21st century include attracting and retaining qualified personnel, adapting to the evolving nature of warfare, maintaining ethical standards in the use of technology, and navigating the complex relationship between the military and society.

Whitney Morris is a renowned author with a passion for military history and strategic analysis. Born in Jakarta, Indonesia, Defense developed a deep fascination for warfare and national defense from a young age. His unwavering interest in military strategy, combined with his natural storytelling ability, has earned him a reputation as an engaging and insightful writer in the field.