What is us defence budget – The US defense budget is a critical component of the nation’s security and economic well-being. It provides the resources necessary to maintain a strong military, conduct research and development, and support a robust defense industrial base. This comprehensive overview will delve into the complexities of the US defense budget, exploring its allocation, impact on the economy, and ethical considerations.
Understanding the US defense budget is essential for informed decision-making and public discourse. By examining the key elements of the budget, we can assess its effectiveness, identify potential areas for optimization, and ensure that the nation’s defense needs are met while balancing other societal priorities.
Budget Overview
The United States defense budget is the largest in the world, accounting for approximately 38% of global military spending. The budget provides funding for the Department of Defense (DoD), which is responsible for the nation’s defense and security. The purpose of the defense budget is to ensure that the United States has the resources and capabilities necessary to protect its interests at home and abroad.
The defense budget has been increasing steadily over the past few years, with the total budget for fiscal year 2023 reaching $813 billion. This increase in spending has been driven by a number of factors, including the ongoing war in Afghanistan, the rise of new threats such as ISIS, and the need to modernize the U.S.
military.
Allocation of Funds
The defense budget is allocated across various sectors and programs to ensure the effective functioning of the military. The major categories of spending include personnel, procurement, research and development, and other operational costs.
Personnel
Personnel costs account for the largest portion of the defense budget, typically around 30-40%. This category includes salaries, benefits, and training expenses for military personnel. The allocation for personnel ensures that the military has the necessary manpower to carry out its missions.
Procurement
Procurement involves the acquisition of new weapons systems, equipment, and supplies. This category typically accounts for around 20-30% of the defense budget. The allocation for procurement allows the military to modernize its capabilities and replace outdated equipment.
Research and Development (R&D)
R&D funding supports the development of new technologies and capabilities for the military. This category typically accounts for around 10-15% of the defense budget. The allocation for R&D ensures that the military remains at the forefront of technological advancements and can respond to emerging threats.
Other Operational Costs
Other operational costs include expenses related to military operations, such as fuel, maintenance, and transportation. This category typically accounts for around 20-30% of the defense budget. The allocation for other operational costs ensures that the military has the resources to conduct its missions effectively.The allocation of funds across these categories is influenced by various factors, including strategic priorities, technological advancements, and geopolitical threats.
The historical trends in defense spending have shown fluctuations based on changes in these factors.
Personnel Costs

Personnel costs constitute a significant portion of the US defense budget, encompassing military salaries, benefits, and training expenses. Understanding the factors that influence these costs and their impact on the overall budget is crucial for informed decision-making.
Factors Influencing Personnel Costs
Several factors influence personnel costs, including:
- Troop Levels:The number of active-duty personnel directly impacts salary and benefit expenses.
- Compensation Rates:Military pay scales are determined by rank, experience, and other factors, affecting the overall cost.
- Benefits:Military personnel receive a wide range of benefits, including healthcare, housing allowances, and retirement pensions, contributing to the total cost.
- Training:Investing in training and professional development for military personnel enhances their skills and readiness, but also incurs costs.
Comparison to Other Spending Categories
Personnel costs typically account for the largest share of the defense budget, often exceeding other categories such as procurement, operations, and maintenance. This reflects the importance of human capital in military operations.
Impact on Overall Budget
Personnel costs have a significant impact on the overall defense budget. Fluctuations in troop levels, compensation rates, or benefits can lead to substantial changes in spending priorities and budget allocation.
Potential Cost-Saving Measures
Exploring potential cost-saving measures without compromising military readiness is essential for responsible budgeting. This may include:
- Optimizing Troop Levels:Analyzing force structure and identifying areas where personnel can be reduced without affecting mission effectiveness.
- Reviewing Compensation Rates:Conducting regular reviews of military pay scales to ensure they are competitive while considering cost implications.
- Reforming Benefits:Evaluating military benefits packages and exploring cost-effective alternatives without reducing the quality of care or support.
- Improving Training Efficiency:Utilizing technology and innovative training methods to enhance efficiency and reduce training costs.
“Personnel costs are the lifeblood of our military. They ensure we have a skilled and motivated force capable of defending our nation.”– General Mark Milley, Chairman of the Joint Chiefs of Staff
Summary Table
The following table provides a summary of personnel costs by category and year:
| Category | 2021 | 2022 | 2023 (Est.) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Salaries | $150 billion | $155 billion | $160 billion |
| Benefits | $70 billion | $75 billion | $80 billion |
| Training | $25 billion | $27 billion | $29 billion |
| Total | $245 billion | $257 billion | $269 billion |
Key Findings and Recommendations
Key findings and recommendations regarding personnel costs include:
- Personnel costs are a major component of the defense budget, with salaries, benefits, and training expenses accounting for a significant portion.
- Factors such as troop levels, compensation rates, and benefits influence the overall cost of military personnel.
- Exploring potential cost-saving measures is crucial for responsible budgeting without compromising military readiness.
- Optimizing troop levels, reviewing compensation rates, reforming benefits, and improving training efficiency are potential areas for cost reduction.
- Regularly monitoring and evaluating personnel costs is essential for effective budget management and ensuring the availability of a skilled and motivated military force.
Research and Development

Research and development (R&D) is crucial for maintaining US military superiority. It fuels technological advancements, innovation, and the development of new weapons systems, technologies, and capabilities. R&D investments enable the US military to stay ahead of potential adversaries and respond effectively to evolving threats.
The US defense budget, a substantial allocation of federal resources, is meticulously planned and allocated to ensure national security. Like the utilities in a house, which provide essential services such as water, electricity, and gas , the defense budget supports the military’s operations, equipment, and personnel, safeguarding the nation’s interests both domestically and abroad.
The defense budget funds a wide range of R&D projects, including basic research, applied research, and advanced development. Basic research focuses on expanding scientific knowledge and understanding, while applied research aims to solve specific military problems. Advanced development involves the creation of prototypes and testing of new technologies.
Types of R&D Projects
- Basic research:Explores fundamental scientific principles and concepts, often without immediate military applications.
- Applied research:Addresses specific military challenges, aiming to develop new technologies and solutions.
- Advanced development:Creates prototypes and tests new technologies, preparing them for production and deployment.
Contributions of R&D
R&D contributes significantly to technological advancements and innovation in the military context. It enables the development of new weapons systems, such as stealth aircraft, precision-guided munitions, and cyber warfare capabilities. R&D also leads to advancements in materials science, electronics, and artificial intelligence, enhancing the capabilities of existing systems.
Successful R&D Projects
- GPS (Global Positioning System):Initially developed for military use, GPS has become indispensable for navigation and positioning systems worldwide.
- Internet:The US Department of Defense played a key role in the development of the internet, which has revolutionized communication and information sharing.
- Predator Drone:This unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) has been instrumental in counterterrorism operations, providing surveillance and strike capabilities.
Balancing Short-Term and Long-Term Investments
Balancing short-term operational needs with long-term R&D investments is a challenge. Short-term needs often require immediate funding, while long-term R&D projects may not yield results for years or decades. It is crucial to find a balance that ensures both current operational capabilities and future technological superiority.
Public-Private Partnerships and International Collaboration
Public-private partnerships and international collaboration play vital roles in R&D. Partnerships with industry and academia leverage expertise and resources, while international collaboration fosters innovation and reduces duplication of efforts.
Ethical Implications
R&D in the military context raises ethical implications. The development of autonomous weapons systems, for example, requires careful consideration of the potential risks and responsibilities involved.
Recommendations
- Prioritize long-term R&D investments to ensure continued military superiority.
- Foster public-private partnerships and international collaboration to leverage expertise and resources.
- Establish clear ethical guidelines for R&D in the military context.
- Continuously evaluate and adjust R&D priorities to meet evolving threats and technological advancements.
Operations and Maintenance
Operations and maintenance (O&M) costs cover the upkeep of existing military equipment and infrastructure, ensuring their readiness for deployment and sustainability over time. These costs include:
- Repair and maintenance of aircraft, ships, vehicles, and weapons systems
- Maintenance of military bases, training facilities, and other infrastructure
- Fuel, lubricants, and other consumables
- Training and certification of personnel to operate and maintain equipment
O&M is crucial for maintaining military readiness and ensuring the longevity of equipment. Regular maintenance prevents breakdowns, extends the lifespan of assets, and improves operational efficiency. It also ensures that equipment is safe and reliable, reducing the risk of accidents or failures during missions.Balancing operational needs with budgetary constraints is a challenge in O&M.
Military leaders must prioritize essential maintenance activities while considering the availability of funds. This requires careful planning, budgeting, and coordination to ensure that critical equipment and infrastructure are maintained at optimal levels.
Defense Industrial Base
The defense industrial base (DIB) is a complex ecosystem of companies, organizations, and government agencies that provide the U.S. military with the equipment, services, and technologies it needs to carry out its missions. The DIB is essential to the nation’s security, as it ensures that the military has the resources it needs to defend the country and its interests.The key players in the defense industry include large defense contractors such as Lockheed Martin, Boeing, and Northrop Grumman, as well as smaller companies that specialize in specific areas such as electronics, software, and munitions.
These companies have the expertise and capabilities to design, develop, and produce the advanced weapons systems and technologies that the military needs.Maintaining a strong and resilient DIB is essential for the nation’s security. A strong DIB ensures that the military has access to the latest technologies and equipment, and that it can quickly and efficiently respond to new threats.
A resilient DIB is able to withstand disruptions such as natural disasters, cyberattacks, and economic downturns.
Key Functions of the DIB
The DIB performs a number of key functions, including:
- Research and development:The DIB conducts research and development on new technologies and weapons systems.
- Production:The DIB produces the equipment, services, and technologies that the military needs.
- Maintenance and repair:The DIB maintains and repairs the military’s equipment.
- Logistics:The DIB provides the logistics support necessary to ensure that the military has the resources it needs, when and where it needs them.
Challenges Facing the DIB
The DIB faces a number of challenges, including:
- Increasing costs:The cost of developing and producing new weapons systems and technologies is rising rapidly.
- Shrinking workforce:The DIB is facing a shortage of skilled workers.
- Foreign competition:The DIB is facing increasing competition from foreign companies.
- Cyber threats:The DIB is facing a growing number of cyber threats.
Despite these challenges, the DIB remains a vital part of the nation’s security. The government is working to address the challenges facing the DIB, and is committed to maintaining a strong and resilient defense industrial base.
Budgetary Process
The defense budget is a complex and dynamic process that involves multiple stakeholders and a series of steps. It begins with the development of a budget request by the Department of Defense (DoD), followed by review and approval by Congress and the Executive Branch.
The DoD develops its budget request based on its assessment of national security threats and priorities. This request includes funding for personnel, operations and maintenance, research and development, and procurement of new equipment and systems.
Roles of Congress
Congress plays a critical role in the budget process. The House and Senate Armed Services Committees review the DoD’s budget request and hold hearings to question DoD officials about their spending plans. The committees then develop their own budget recommendations, which are voted on by the full House and Senate.
Roles of the Executive Branch
The Executive Branch, led by the President, also plays a significant role in the budget process. The President submits the DoD’s budget request to Congress and works with congressional leaders to negotiate a final budget agreement.
Challenges and Controversies
The defense budget process is often challenging and controversial. Congress and the Executive Branch may have different priorities for defense spending, and there is often debate about the appropriate level of funding for various programs.
Another challenge is the long-term nature of defense spending. Many defense programs require multi-year commitments, and it can be difficult to predict future costs accurately.
Budgetary Impact on the Economy

The defense budget significantly impacts the US economy. Defense spending stimulates economic growth by creating jobs, boosting technological innovation, and supporting various industries.
Economic Benefits of Defense Spending
Defense spending generates employment opportunities in various sectors, including manufacturing, research and development, and logistics. It supports industries such as aerospace, shipbuilding, and electronics. Technological advancements made for military purposes often have civilian applications, leading to innovations in areas like electronics, materials science, and computing.
Potential Drawbacks of Excessive Defense Spending
While defense spending can benefit the economy, excessive spending can have drawbacks. It can divert resources from other important areas such as education, healthcare, and infrastructure. Excessive defense spending can also contribute to budget deficits and national debt. Additionally, it can lead to an overreliance on the defense industry, making the economy vulnerable to fluctuations in defense spending.
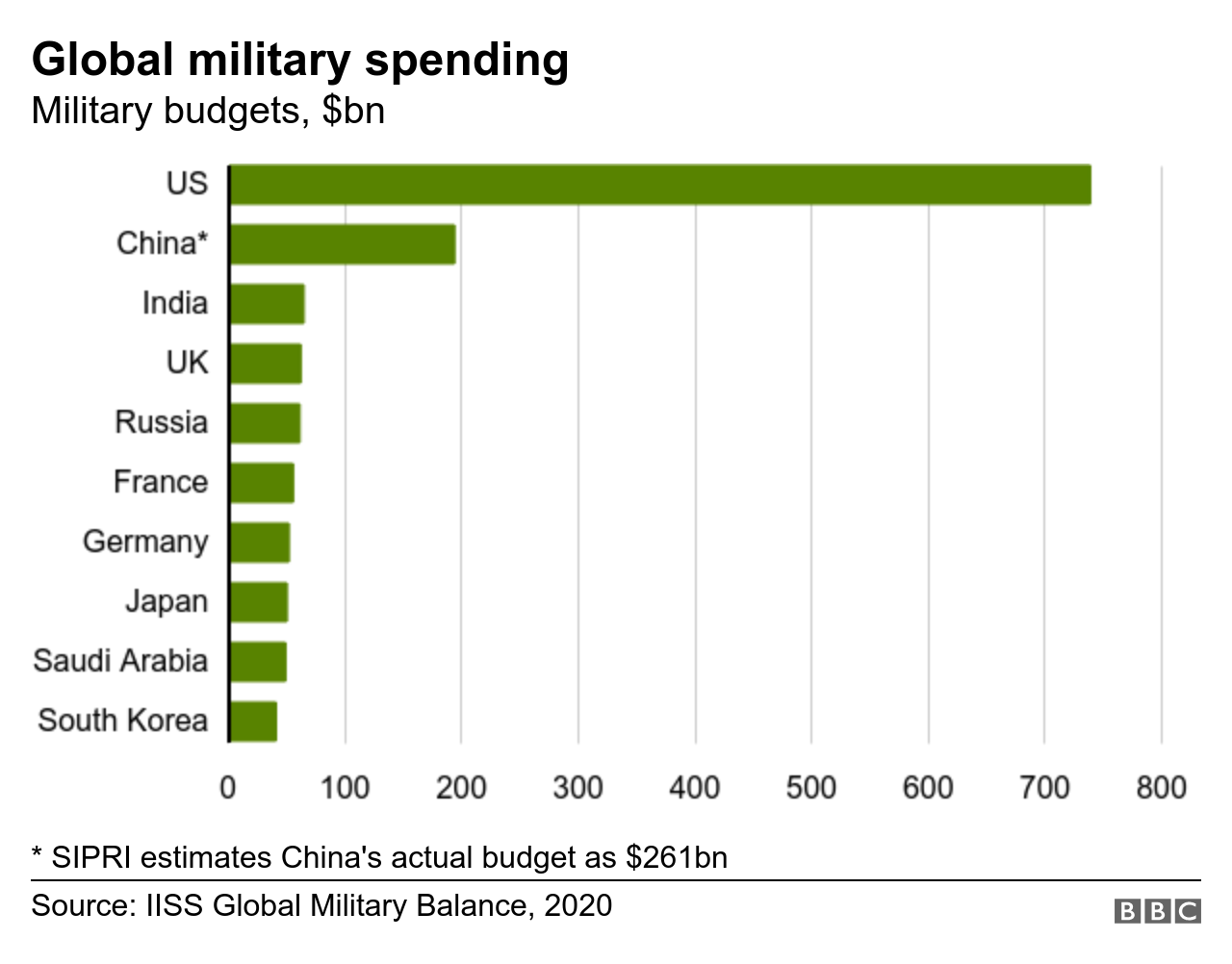
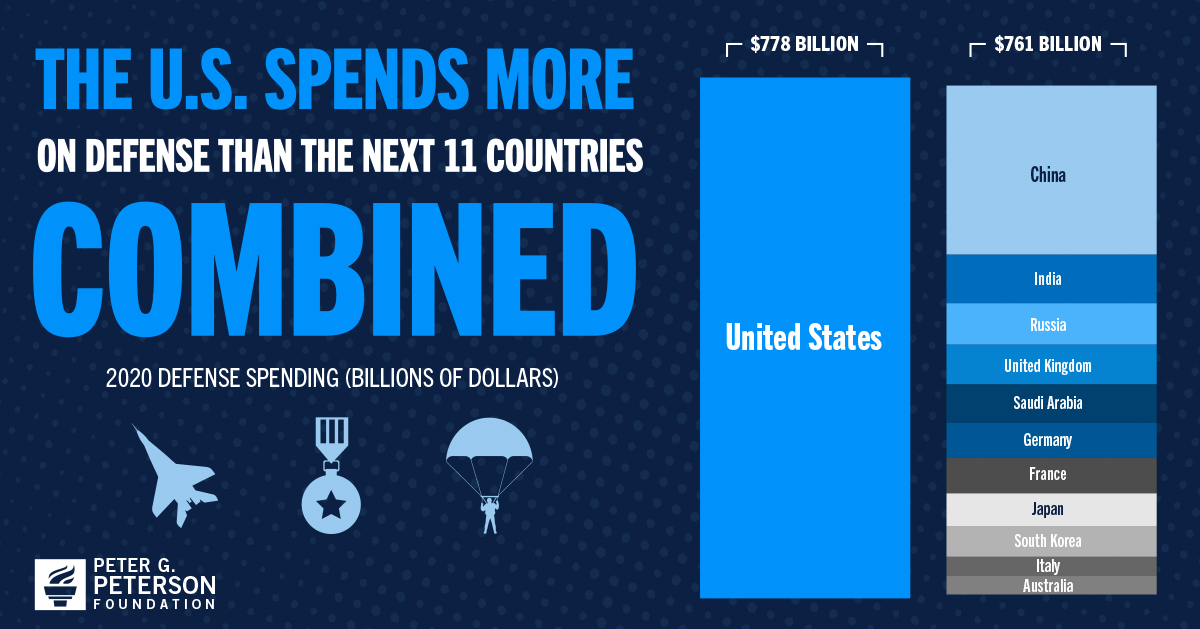
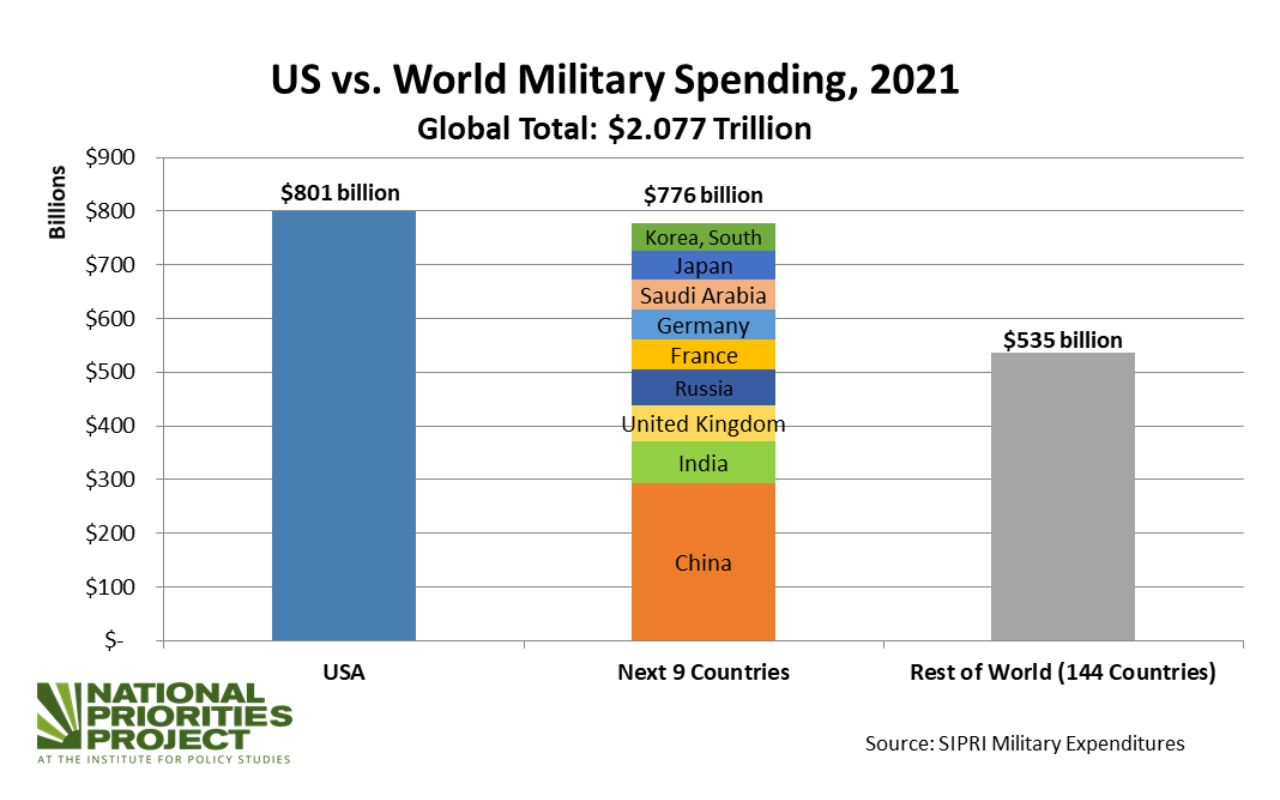
Comparison with Other Countries
The United States spends more on its military than any other country in the world. In 2023, the US defense budget was $801 billion, which is more than the next 10 countries combined. This level of spending has been relatively consistent over the past decade, with the US defense budget hovering around 3.5% of GDP.
There are a number of factors that contribute to the US’s high level of defense spending. One factor is the size of the US economy. The US has the largest economy in the world, which means that it can afford to spend more on its military than other countries.
The United States defense budget, a significant allocation of federal funds, plays a crucial role in maintaining national security. However, for individuals facing financial emergencies, understanding how to obtain emergency utility assistance is paramount. The emergency utility assistance programs can provide temporary relief from utility bills, ensuring essential services remain accessible.
By exploring these programs, individuals can navigate financial challenges while the nation’s defense budget continues to support national security.
Another factor is the US’s global leadership role. The US is the world’s only superpower, and it has a responsibility to maintain a strong military to protect its interests and those of its allies.
The US’s high level of defense spending has a number of implications. One implication is that it gives the US a significant military advantage over other countries. The US has the most advanced military in the world, and it is able to project power anywhere in the world.
This gives the US a strong deterrent against potential adversaries.
Another implication of the US’s high level of defense spending is that it can strain the US economy. Defense spending is a major driver of the US budget deficit, and it can lead to higher taxes or cuts to other government programs.
In addition, defense spending can lead to inflation, as the government competes with private businesses for resources.
Comparison to Other Countries
The following table compares the defense budgets of the US and other major countries:
| Country | Defense Budget (2023) | % of GDP ||—|—|—|| United States | $801 billion | 3.5% || China | $293 billion | 1.7% || Russia | $61.7 billion | 4.1% || India | $76.6 billion | 2.9% || United Kingdom | $68.4 billion | 2.2% || France | $56.9 billion | 1.8% || Japan | $54.1 billion | 1.1% || Germany | $53.1 billion | 1.5% |
As the table shows, the US spends more on its military than any other country in the world. China is the second-largest spender, but its defense budget is still less than half of the US’s. Russia, India, and the United Kingdom are also major military spenders, but their defense budgets are all significantly smaller than the US’s.
The following chart shows the trends in defense spending over time for the US and other major countries:
[Image of a chart showing the trends in defense spending over time for the US and other major countries]
As the chart shows, the US has consistently spent more on its military than other major countries. In recent years, the US’s defense spending has increased, while the defense spending of other countries has remained relatively flat.
Factors Contributing to Differences in Defense Spending
There are a number of factors that contribute to differences in defense spending between countries. One factor is the size of the country’s economy. Countries with larger economies can afford to spend more on their militaries. Another factor is the country’s population.
Countries with larger populations need larger militaries to defend their territory.
Geopolitical threats are another major factor that influences defense spending. Countries that face significant geopolitical threats are more likely to spend more on their militaries. For example, the US faces threats from China, Russia, and North Korea. These threats have led the US to increase its defense spending in recent years.
Implications of the US’s Military Spending
The US’s high level of defense spending has a number of implications. One implication is that it gives the US a significant military advantage over other countries. The US has the most advanced military in the world, and it is able to project power anywhere in the world.
This gives the US a strong deterrent against potential adversaries.
Another implication of the US’s high level of defense spending is that it can strain the US economy. Defense spending is a major driver of the US budget deficit, and it can lead to higher taxes or cuts to other government programs.
In addition, defense spending can lead to inflation, as the government competes with private businesses for resources.
The US’s military spending also has a significant impact on global security. The US is the world’s only superpower, and it has a responsibility to maintain a strong military to protect its interests and those of its allies. The US’s military spending helps to deter aggression and maintain peace and stability around the world.
Potential Consequences of Significantly Higher or Lower US Military Spending
If the US were to significantly increase its military spending, it would have a number of consequences. One consequence would be that it would further strain the US economy. Defense spending is already a major driver of the US budget deficit, and increasing it would only make the problem worse.
This could lead to higher taxes, cuts to other government programs, or inflation.
Another consequence of increasing US military spending would be that it could lead to an arms race with other countries. If the US were to significantly increase its military spending, other countries would likely feel pressured to do the same.
This could lead to a dangerous cycle of escalation, as each country tries to outspend the other.
On the other hand, if the US were to significantly decrease its military spending, it would also have a number of consequences. One consequence would be that it would reduce the US’s military advantage over other countries. The US has the most advanced military in the world, but if it were to significantly decrease its spending, it could lose this advantage.
This could make the US more vulnerable to attack from potential adversaries.
Another consequence of decreasing US military spending would be that it could damage the US’s global leadership role. The US is the world’s only superpower, and its military spending helps to maintain peace and stability around the world. If the US were to significantly decrease its military spending, it could send a signal to other countries that the US is no longer willing to play a leading role in global affairs.
Budgetary Trends and Forecasts: What Is Us Defence Budget
The US defense budget has undergone significant fluctuations over the past several decades, reflecting changing geopolitical dynamics, economic conditions, and domestic political priorities. Understanding these historical trends and forecasting future spending patterns is crucial for assessing the implications for the US military and national security.
Key factors that have influenced defense spending growth include:
- Major conflicts: Wartime and post-conflict periods often lead to increased defense expenditures to support military operations and rebuild armed forces.
- Technological advancements: The development and procurement of new weapons systems and technologies drive up costs.
- Economic growth: A strong economy typically allows for higher defense spending, while economic downturns can lead to budget cuts.
- Political priorities: Changes in government leadership and shifts in public opinion can impact defense spending levels.
Historical Trends
| Year | Defense Budget (in billions of dollars) | Key Factors |
|---|---|---|
| 1950 | 13.5 | Korean War |
| 1960 | 45.6 | Cold War escalation |
| 1970 | 72.9 | Vietnam War |
| 1980 | 144.3 | Reagan-era military buildup |
| 1990 | 293.1 | Persian Gulf War |
| 2000 | 314.6 | Post-9/11 defense buildup |
| 2010 | 664.2 | War in Afghanistan and Iraq |
| 2020 | 740.5 | Global security challenges, modernization efforts |
Future Trends
Forecasting future defense spending is complex and uncertain, but several factors are likely to shape its trajectory:
- Geopolitical environment: Escalating tensions with China and Russia, as well as ongoing conflicts in the Middle East, could drive up defense spending.
- Technological advancements: The rise of artificial intelligence, cyber warfare, and space-based technologies will require significant investment.
- Economic conditions: A prolonged economic downturn could lead to defense budget cuts, while a strong economy could support higher spending.
- Political priorities: The Biden administration has signaled a shift towards a more restrained defense posture, focusing on diplomacy and international cooperation.
Potential Implications
The future trajectory of defense spending will have significant implications for the US military and national security. Higher spending could enable the military to maintain a strong presence globally, invest in advanced technologies, and respond effectively to emerging threats. However, prolonged budget cuts could undermine military readiness, reduce the size of the force, and limit the ability to respond to future conflicts.
Public Opinion and Support
Public opinion on the defense budget and its priorities is a complex and multifaceted issue. Various factors influence public support for defense spending, including the perceived threats to national security, the economic climate, and the overall political climate. Understanding and securing public support are crucial for maintaining a strong national defense.
Factors Influencing Public Support
- Perceived Threats:Public support for defense spending tends to increase when there are perceived threats to national security, such as international conflicts or terrorist attacks.
- Economic Climate:Public support for defense spending can be affected by the economic climate. During economic downturns, there may be less support for defense spending as people prioritize other areas such as healthcare or education.
- Political Climate:The political climate can also influence public support for defense spending. Partisan politics and debates over foreign policy can shape public opinion on defense budgets.
Importance of Public Understanding and Support
Public understanding and support are essential for a strong national defense. When the public understands the importance of defense spending and its role in protecting the nation, they are more likely to support it. This support is crucial for ensuring that the military has the resources it needs to carry out its missions effectively and maintain a strong national defense.
Ethical Considerations
The defense budget raises significant ethical concerns due to its implications for society. It necessitates careful consideration of the potential trade-offs between defense spending and other social priorities, such as healthcare, education, and infrastructure.
Ethical Responsibilities of Government
Governments have an ethical responsibility to allocate resources judiciously, balancing national security with the well-being of their citizens. This includes evaluating the long-term consequences of defense spending and ensuring that it does not come at the expense of essential social services.
Defense Resources for Non-Defense Purposes
The use of defense resources for non-defense purposes, such as disaster relief or domestic surveillance, raises ethical questions. While such uses may be necessary in certain circumstances, they must be carefully considered and justified to avoid potential mission creep and the diversion of resources from primary defense objectives.
Arms Trade and Proliferation, What is us defence budget
The arms trade and the proliferation of weapons have significant ethical implications. Governments must balance the economic benefits of arms exports with the potential for their use in human rights abuses, conflicts, and terrorism. They must also work to prevent the spread of weapons of mass destruction.
Detailed FAQs
What is the purpose of the US defense budget?
The US defense budget provides the resources necessary to maintain a strong military, conduct research and development, and support a robust defense industrial base.
How is the defense budget allocated?
The defense budget is allocated across different sectors and programs, including personnel, procurement, research and development, operations and maintenance, and the defense industrial base.
What are the ethical considerations associated with the defense budget?
The defense budget raises ethical questions about the trade-offs between defense spending and other social priorities, the use of defense resources for non-defense purposes, and the ethical implications of the arms trade.

Emma Nehls is a military writer and historian with a passion for exploring the intricacies of warfare and the human experience within the military. With extensive knowledge and a deep understanding of military strategy, tactics, and historical contexts, Nehls brings a unique perspective to his writings.