Is there a e12 rank in the military – Is there an E-12 rank in the military? This question sparks curiosity and a bit of mystery, as the US military has a well-defined rank structure, but some may wonder if a “super soldier” rank exists. The answer, however, is not as straightforward as it might seem. The military’s rank system is complex, with its own history, rules, and regulations, and the concept of an E-12 rank requires a deeper understanding of the system.
The “E” in E-series ranks denotes enlisted personnel, distinguishing them from officers. The US military uses a numerical system to represent enlisted ranks, with E-1 being the lowest and E-9 the highest. This system is designed to create a clear hierarchy, ensuring order and discipline, and providing a path for career progression. Each rank carries specific responsibilities, authority, and training requirements, reflecting the individual’s role within the military structure.
Understanding Military Rank Structure: Is There A E12 Rank In The Military
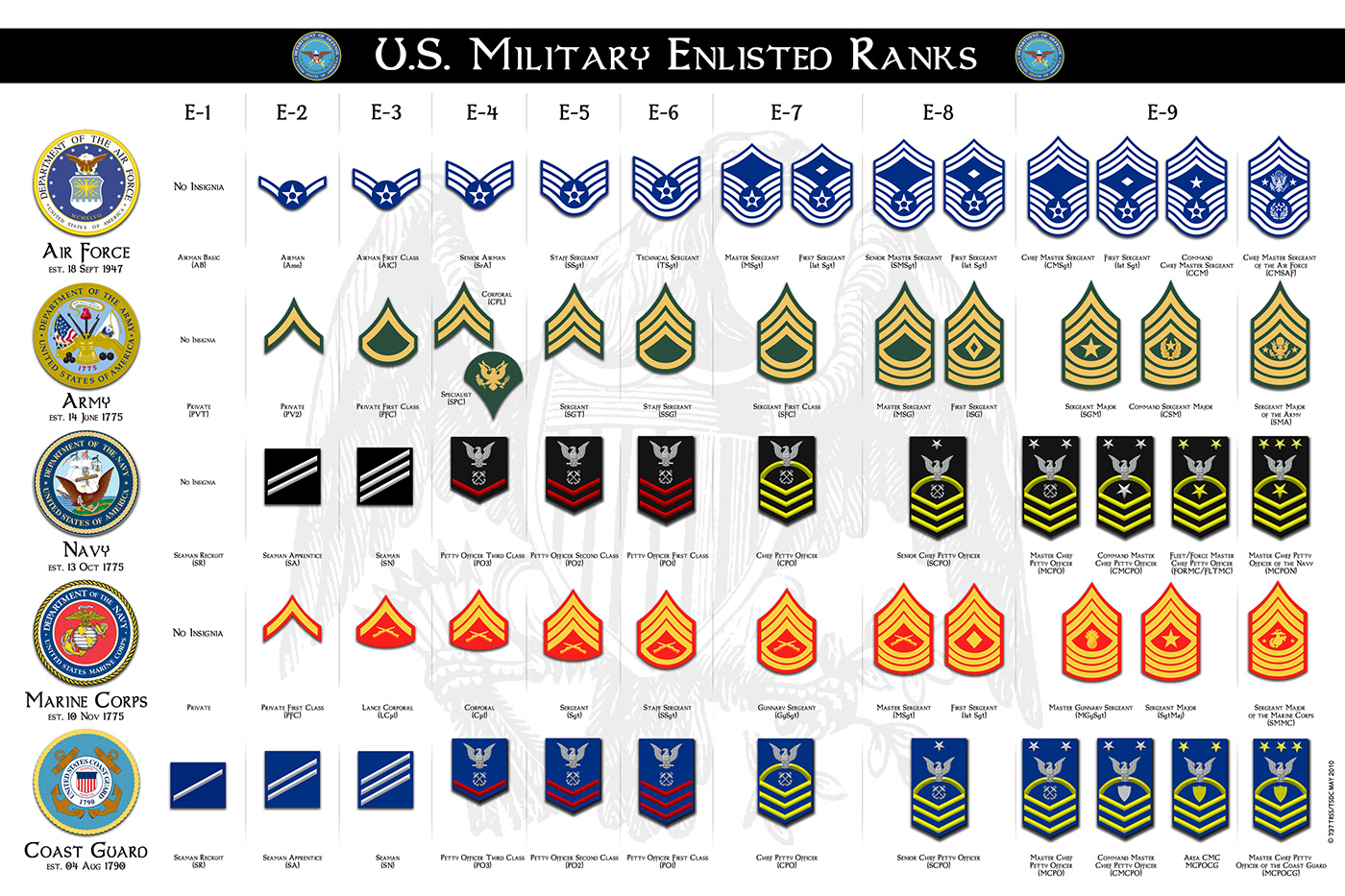
Military rank systems are hierarchical structures that organize personnel within armed forces. These systems establish lines of authority, responsibility, and communication. Understanding military ranks is crucial for comprehending the organizational framework of armed forces.
Military Rank Designations
Military ranks are typically designated using a combination of numbers and letters. These designations vary across different branches of service and countries. The use of numbers and letters often reflects the rank’s seniority, level of responsibility, and historical evolution.
- Numbers: Numbers often indicate the seniority of a rank. For instance, in the United States Army, a Sergeant (E-5) is senior to a Corporal (E-4), and a Lieutenant Colonel (O-5) is senior to a Major (O-4).
- Letters: Letters often denote the rank’s pay grade or category. For example, in the United States military, the letter “E” represents enlisted personnel, “O” represents commissioned officers, and “W” represents warrant officers. These letters are often followed by a number, signifying the pay grade.
Examples of Common Military Rank Designations
Here are some common military rank designations, including those using numbers and letters:
| Branch of Service | Rank | Designation |
|---|---|---|
| United States Army | Private | E-1 |
| United States Navy | Seaman Recruit | E-1 |
| United States Air Force | Airman Basic | E-1 |
| United States Marine Corps | Private First Class | E-2 |
| United States Army | Sergeant First Class | E-7 |
| United States Navy | Chief Petty Officer | E-7 |
| United States Air Force | Master Sergeant | E-7 |
| United States Marine Corps | Gunnery Sergeant | E-7 |
| United States Army | Lieutenant Colonel | O-5 |
| United States Navy | Commander | O-5 |
| United States Air Force | Colonel | O-6 |
| United States Marine Corps | Colonel | O-6 |
Historical Development of Military Rank Systems
Military rank systems have evolved over centuries, reflecting changes in warfare, societal structures, and military organization.
“The modern military rank system has its roots in the feudal armies of medieval Europe, where ranks were largely based on lineage and social status.”
In the early modern period, the rise of standing armies led to the development of more formalized rank structures based on merit and experience. The introduction of gunpowder and the development of more complex military tactics further influenced the evolution of rank systems.
“The development of modern military rank systems is a complex process that has been shaped by a variety of factors, including technological advancements, social changes, and the evolving nature of warfare.”
E-Series Ranks in the US Military
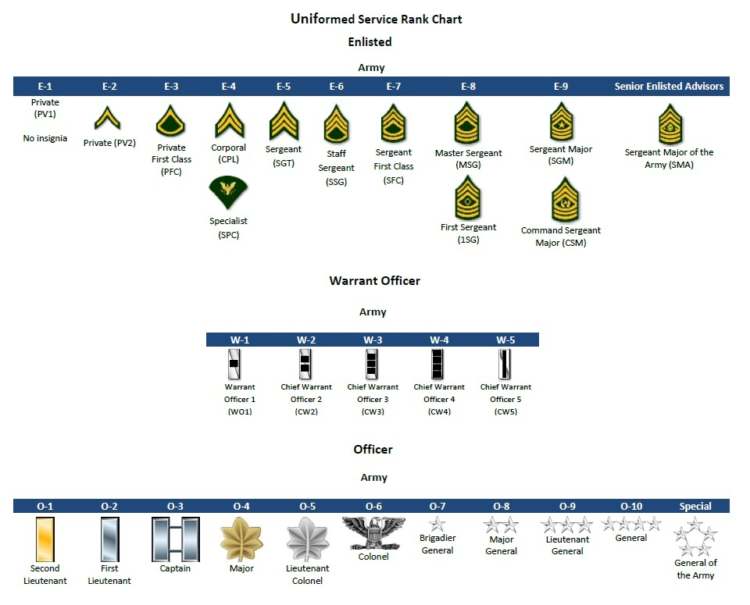
The E-series ranks, also known as enlisted ranks, are a fundamental part of the US military’s hierarchical structure. Understanding the progression and nuances of these ranks is crucial for anyone seeking to learn about the military’s organizational framework.
Defining the “E” in E-Series Ranks
The “E” in E-series ranks stands for “Enlisted.” This designation distinguishes enlisted personnel from officers, who hold commissioned ranks denoted by letters like “O” (for Officer) or “W” (for Warrant Officer). Enlisted personnel are responsible for carrying out the day-to-day operations and tasks within their respective branches of the military.
E-Series Rank Progression
E-series ranks progress from the lowest to the highest, each level representing increasing responsibility, authority, and experience. The numerical designation following the “E” indicates the rank’s position within the hierarchy. Here’s a table outlining the progression of E-series ranks:
| Rank Name | Numerical Designation | Pay Grade |
|---|---|---|
| Private (E-1) | E-1 | 1 |
| Private (E-2) | E-2 | 2 |
| Private First Class (E-3) | E-3 | 3 |
| Specialist (E-4) | E-4 | 4 |
| Corporal (E-4) | E-4 | 4 |
| Sergeant (E-5) | E-5 | 5 |
| Staff Sergeant (E-6) | E-6 | 6 |
| Technical Sergeant (E-6) | E-6 | 6 |
| Sergeant First Class (E-7) | E-7 | 7 |
| Master Sergeant (E-7) | E-7 | 7 |
| First Sergeant (E-8) | E-8 | 8 |
| Master Sergeant (E-8) | E-8 | 8 |
| Sergeant Major (E-9) | E-9 | 9 |
| Command Sergeant Major (E-9) | E-9 | 9 |
| Sergeant Major of the Army (E-9) | E-9 | 9 |
E-Series Ranks in Different Branches
The specific names and numerical designations of E-series ranks may vary slightly across the different branches of the US military. However, the overall structure and progression remain largely consistent.
| Branch | E-1 | E-2 | E-3 | E-4 | E-5 | E-6 | E-7 | E-8 | E-9 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Army | Private | Private (PVT) | Private First Class (PFC) | Specialist (SPC) | Sergeant (SGT) | Staff Sergeant (SSG) | Sergeant First Class (SFC) | Master Sergeant (MSG) | Sergeant Major (SGM) |
| Navy | Seaman Recruit (SR) | Seaman Apprentice (SA) | Seaman (SN) | Petty Officer Third Class (PO3) | Petty Officer Second Class (PO2) | Petty Officer First Class (PO1) | Chief Petty Officer (CPO) | Senior Chief Petty Officer (SCPO) | Master Chief Petty Officer (MCPO) |
| Air Force | Airman Basic (AB) | Airman (AMN) | Airman First Class (A1C) | Senior Airman (SrA) | Staff Sergeant (SSgt) | Technical Sergeant (TSgt) | Master Sergeant (MSgt) | Senior Master Sergeant (SMSgt) | Chief Master Sergeant (CMSgt) |
| Marines | Private (Pvt) | Private First Class (PFC) | Lance Corporal (LCpl) | Corporal (Cpl) | Sergeant (Sgt) | Staff Sergeant (SSgt) | Gunnery Sergeant (GySgt) | Master Sergeant (MSgt) | Sergeant Major (SgtMaj) |
| Coast Guard | Seaman Recruit (SR) | Seaman Apprentice (SA) | Seaman (SN) | Petty Officer Third Class (PO3) | Petty Officer Second Class (PO2) | Petty Officer First Class (PO1) | Chief Petty Officer (CPO) | Senior Chief Petty Officer (SCPO) | Master Chief Petty Officer (MCPO) |
Additional Insights
E-series ranks have evolved over time, reflecting changes in military structure and the demands of modern warfare. The significance of these ranks extends beyond mere titles. They represent a progression of responsibilities, authority, and leadership capabilities. Enlisted personnel at different E-series levels undergo specialized training and education to equip them with the necessary skills and knowledge for their roles. This training can range from basic military skills to advanced technical expertise, depending on the individual’s career path and rank.
Exploring the E-12 Rank

The United States military utilizes a hierarchical rank structure, with enlisted personnel categorized by the “E-series.” While ranks range from E-1 (Private) to E-9 (Sergeant Major/Master Chief), the existence of an E-12 rank has been a subject of speculation and debate.
The Absence of an E-12 Rank
The United States military does not have an E-12 rank. The highest achievable enlisted rank is E-9. This structure is established by the Department of Defense and Artikeld in the “Joint Travel Regulations” (JTR), which govern travel and transportation for all branches of the military. The absence of an E-12 rank can be attributed to several factors:
- Historical Context: The current rank structure has evolved over time, with the highest enlisted rank historically being E-7. The introduction of E-8 and E-9 ranks in the 1980s and 1990s aimed to provide greater leadership opportunities and career progression for senior enlisted personnel.
- Rationale Behind the Rank Structure: The current rank structure reflects the need for a balance between leadership and accountability. E-9 ranks are typically responsible for leading large units and advising senior officers. The introduction of an E-12 rank could potentially create a level of authority that might conflict with the officer corps.
- Potential Implications of Introducing an E-12 Rank: Introducing an E-12 rank could create significant changes in the military’s hierarchy. It could potentially impact the career progression of current E-9 personnel, leading to a more complex and potentially contentious rank structure.
- Comparison to Other Military Branches or Nations: While some other countries, like the United Kingdom, have a similar rank structure with an equivalent to an E-12, the US military’s focus on officer leadership and the established balance within its rank structure has influenced the absence of an E-12 rank.
E-Series Ranks in the US Military, Is there a e12 rank in the military
The following table summarizes the E-series ranks in the US military:
| Rank Name | Pay Grade | Typical Responsibilities | Authority Level |
|---|---|---|---|
| Private (E-1) | 1 | Basic training, entry-level duties | Lowest level of authority |
| Private First Class (E-2) | 2 | More advanced training, team member roles | Slightly higher authority than E-1 |
| Specialist (E-3) | 3 | Specialized training, technical skills | Intermediate level of authority |
| Corporal (E-4) | 4 | Supervisory role, leading small teams | Moderate level of authority |
| Sergeant (E-5) | 5 | Supervising larger teams, planning and execution of tasks | Higher level of authority |
| Staff Sergeant (E-6) | 6 | Leading platoons, managing resources | Significant level of authority |
| Sergeant First Class (E-7) | 7 | Leading companies, mentoring junior enlisted personnel | High level of authority |
| Master Sergeant/Senior Chief Petty Officer (E-8) | 8 | Leading battalions/squadrons, advising senior officers | Very high level of authority |
| Sergeant Major/Master Chief Petty Officer (E-9) | 9 | Leading brigades/wings, providing strategic guidance | Highest level of authority among enlisted personnel |
The Significance of Rank in the Military
The military is a highly structured organization, and rank plays a crucial role in maintaining order, discipline, and efficiency. A clear hierarchy based on rank ensures smooth operations, effective communication, and accountability within the armed forces.
Do not overlook explore the latest data about craig morgan military rank.
The Importance of Rank in Maintaining Order and Discipline
Rank is the foundation of military discipline and order. It establishes a chain of command, outlining the lines of authority and responsibility within a unit. Every member of the military, from the lowest enlisted rank to the highest officer, understands their place in this hierarchy. This structure ensures that orders are passed down effectively, tasks are assigned appropriately, and discipline is maintained.
Rank and Responsibilities, Authority, and Leadership Opportunities
Rank directly impacts an individual’s responsibilities, authority, and leadership opportunities. Higher ranks typically have greater responsibilities, more authority, and access to more leadership roles. For example, a junior enlisted member might be responsible for basic tasks like cleaning and maintenance, while a senior enlisted member might lead a team or oversee a specific operation. Officers, who are appointed by the government, have even greater responsibilities and authority, including commanding units and making strategic decisions.
Enlisted Personnel (E-Series) and Officers (O-Series) in the Military Hierarchy
The military hierarchy is divided into two main categories: enlisted personnel (E-series) and officers (O-series). Enlisted personnel are non-commissioned members who are responsible for carrying out orders and performing specific tasks. Officers, on the other hand, are commissioned members who lead and manage units and are responsible for strategy and planning. While both groups are essential to the military’s success, they have distinct roles and responsibilities within the hierarchy.
Potential for Future Rank Changes

While the current E-12 rank stands as the highest enlisted rank in the US military, there’s always a possibility of future rank changes. This is particularly true as the military evolves to meet emerging challenges and adapts to technological advancements. Several factors could influence the decision to create new ranks, particularly within the E-series. These factors include:
Technological Advancements
Technological advancements can lead to new roles and responsibilities within the military, potentially requiring a new rank structure to reflect these changes. For example, the rise of cyber warfare and artificial intelligence could necessitate specialized roles requiring higher levels of expertise and leadership. This could warrant the creation of new ranks to accommodate these evolving roles and responsibilities.
Evolving Military Strategies
As military strategies evolve, the need for different types of leadership and expertise may arise. This could necessitate the creation of new ranks to accommodate these changes. For example, the increasing emphasis on joint operations could lead to the creation of ranks that reflect the need for inter-service coordination and collaboration.
Current Discussions and Proposals
While there are no formal proposals or discussions currently underway regarding changes to the E-series rank structure, the possibility of future changes remains a topic of ongoing consideration. The military constantly evaluates its structure and organization to ensure it remains effective and adaptable to future challenges.
The Future of Military Ranks
The traditional military rank structure, with its rigid hierarchy and established roles, is facing unprecedented challenges in the 21st century. The rapid evolution of technology, the changing nature of warfare, and evolving societal values are all converging to reshape the way militaries operate and, consequently, the way they organize their ranks. This essay will explore the potential future of military ranks, considering the influence of technology, the changing nature of warfare, evolving societal values, and the need for adaptation.
The Influence of Technology on Military Ranks
Advancements in artificial intelligence (AI), autonomous systems, and cyber warfare are transforming the battlefield and are likely to have a profound impact on military rank structures. AI and autonomous systems are increasingly being used to perform tasks that were previously carried out by humans, such as target identification, navigation, and even combat. This raises questions about the role of human commanders and the need for traditional leadership structures.
The rise of cyber warfare introduces new challenges and requires specialized skills. Cybersecurity experts, network analysts, and digital warfare specialists may require new rank designations or specialized roles within the military hierarchy.
- For example, the US Navy has already established the “Cyber Warfare Officer” (CWO) designation, reflecting the growing importance of cyber capabilities.
- As AI and autonomous systems become more sophisticated, the military may need to develop new rank structures that reflect the changing nature of warfare and the need for specialized skills in these areas.
The Impact of Changing Warfare on Military Ranks
The nature of warfare is changing rapidly, with an emphasis on speed, agility, and information dominance. Traditional hierarchical structures, which rely on centralized command and control, may be less effective in this new environment. The rise of distributed operations, where smaller, more agile units operate independently, could necessitate a shift away from traditional rank structures. The military may need to adopt more decentralized decision-making processes, empowering lower-ranking personnel to take initiative and make critical decisions in real-time.
- For example, the US Army is experimenting with new leadership models that emphasize adaptability and distributed decision-making, such as the “Mission Command” doctrine.
- These changes may require the development of new rank structures that reflect the increased importance of agility, adaptability, and decentralized decision-making.
The Influence of Societal Values on Military Ranks
Evolving societal values, particularly in terms of gender, race, and sexual orientation, are influencing the makeup of the military and will likely shape the future of military rank structures. As militaries become more diverse, it is essential to ensure that rank systems are inclusive and equitable. This means creating opportunities for all individuals to advance based on merit, regardless of their background.
- For example, the US military has made significant strides in promoting women and minorities to leadership positions, but there is still work to be done to ensure that rank structures are truly inclusive.
- The growing importance of diversity and inclusion within the military may lead to the adoption of new leadership models and rank structures that reflect the changing demographics of the force.
Adapting Military Rank Structures for the Future
Adapting military rank structures to remain relevant and effective in the future presents both challenges and opportunities. The military must strike a balance between tradition and innovation. While preserving the core values and traditions that have underpinned military success for centuries, it is essential to embrace new technologies and adapt to the changing nature of warfare.
- One of the key challenges is ensuring that new rank structures are compatible with existing systems and processes. This may require a phased approach to implementation, with careful consideration of the potential impact on morale, training, and operational readiness.
- Another challenge is ensuring that new rank structures are perceived as fair and equitable by all members of the military. This requires open communication and engagement with personnel at all levels.
- However, the potential rewards of adapting military rank structures are significant. By embracing innovation and adapting to the changing world, militaries can ensure that they remain effective and relevant in the future.
Preparing Future Military Leaders
Leadership development programs and training initiatives play a crucial role in preparing future military leaders for the challenges of the 21st century. These programs should focus on developing the skills and competencies that are essential for success in the modern military, such as critical thinking, problem-solving, adaptability, and the ability to lead in a diverse and technologically advanced environment.
- For example, the US Army War College has incorporated new curriculum elements that address the challenges of cyber warfare, artificial intelligence, and the changing nature of warfare.
- By investing in leadership development, militaries can ensure that they have the leaders they need to meet the challenges of the future.
General Inquiries
What are the highest enlisted ranks in the US military?
The highest enlisted ranks in the US military are E-9, known as Sergeant Major of the Army, Master Chief Petty Officer of the Navy, Chief Master Sergeant of the Air Force, Sergeant Major of the Marine Corps, and Master Chief Petty Officer of the Coast Guard.
What are the responsibilities of a Sergeant Major of the Army (SMA)?
The SMA serves as the principal advisor to the Army Chief of Staff on all matters pertaining to enlisted personnel. They are responsible for the welfare, training, and professional development of enlisted soldiers.
Are there any plans to add new ranks to the US military?
While there are no official plans to add new ranks, the military’s rank structure is constantly evolving to meet the needs of the modern battlefield. New technologies and strategies could potentially necessitate adjustments to the current rank system.

Emma Nehls is a military writer and historian with a passion for exploring the intricacies of warfare and the human experience within the military. With extensive knowledge and a deep understanding of military strategy, tactics, and historical contexts, Nehls brings a unique perspective to his writings.