Cut off scores army, a critical element in military recruitment, act as a gatekeeper, ensuring that potential recruits meet the rigorous standards required for service. These scores are not simply arbitrary numbers; they represent a complex interplay of factors designed to evaluate physical fitness, cognitive ability, and educational background. They are a reflection of the military’s commitment to maintaining a high caliber of personnel capable of fulfilling demanding roles, often in challenging and dangerous environments.
This exploration delves into the world of cut off scores army, examining their significance, the factors that influence their determination, and how they vary across different military branches and roles. We will also explore the evolving landscape of military recruitment, considering the impact of emerging technologies and the changing demands of modern warfare.
Understanding Cut-Off Scores in Military Recruitment
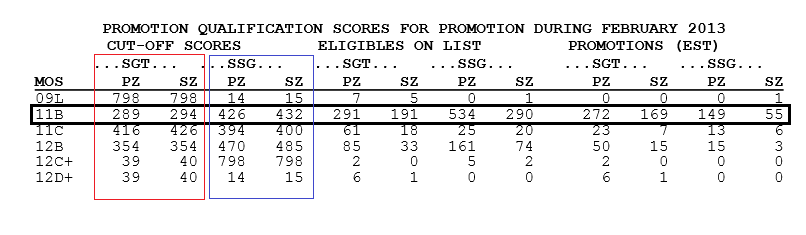
The military, like any organization seeking to maintain high standards and efficiency, utilizes cut-off scores as a crucial tool in the recruitment process. These scores, based on various assessments, act as a screening mechanism to identify individuals who possess the necessary aptitude, physical capabilities, and overall suitability for specific roles within the armed forces.
Significance of Cut-Off Scores
Cut-off scores play a significant role in military recruitment by serving as a standardized measure of a candidate’s potential.
- Cut-off scores act as a screening mechanism, ensuring that only individuals who meet the minimum requirements for a particular role are considered for selection.
- For the military, cut-off scores provide a structured and objective approach to assessing a large pool of applicants, streamlining the recruitment process and ensuring the selection of qualified individuals.
- For potential recruits, cut-off scores provide a clear understanding of the expectations and standards required for military service, allowing them to assess their own capabilities and make informed decisions about their suitability.
While cut-off scores offer benefits, it’s essential to acknowledge their potential drawbacks:
- Cut-off scores might not always capture the full spectrum of an individual’s potential, potentially overlooking candidates who possess unique skills or strengths not adequately assessed by standardized tests.
- Setting rigid cut-off scores could potentially exclude individuals from diverse backgrounds or those who may have faced challenges that have impacted their performance on standardized tests.
Factors Influencing Cut-Off Score Determination
The determination of cut-off scores is a complex process influenced by various factors.
- The specific military role or branch plays a significant role in setting cut-off scores. For example, the physical fitness requirements for infantry roles will differ from those for medical personnel or pilots.
- Cognitive ability, as measured by aptitude tests, is a crucial factor in determining cut-off scores. These tests assess a candidate’s problem-solving abilities, critical thinking skills, and overall intellectual capacity, which are essential for effective military service.
- Educational background also plays a role, with higher cut-off scores often associated with roles requiring specialized knowledge or technical skills.
- Historical data and recruitment needs influence cut-off scores. By analyzing past recruitment trends and current manpower requirements, the military can adjust cut-off scores to ensure adequate recruitment for specific roles.
Variation in Cut-Off Scores
Cut-off scores vary considerably across different military branches and roles, reflecting the specific demands of each position.
- For example, the Army might have higher physical fitness standards for infantry roles compared to the Air Force, while the Navy might have stricter cognitive ability requirements for submarine roles.
Here’s a table comparing cut-off scores for different military branches for specific roles:| Branch | Role | Physical Fitness Score | Cognitive Ability Score | Educational Background ||—|—|—|—|—|| Army | Infantry | 80+ | 70+ | High School Diploma || Navy | Pilot | 70+ | 90+ | Bachelor’s Degree || Air Force | Medical Personnel | 60+ | 80+ | Bachelor’s Degree in Medicine || Marines | Infantry | 90+ | 75+ | High School Diploma |The rationale behind these variations lies in the specific demands of each role.
Roles requiring high physical fitness, such as infantry, typically have higher cut-off scores for physical fitness assessments. Similarly, roles requiring specialized knowledge or technical skills, such as pilots or medical personnel, often have higher cut-off scores for cognitive ability and educational background.Cut-off scores are not static and can change over time to reflect evolving military needs and technological advancements. As the military adapts to new threats and technologies, the requirements for specific roles may change, leading to adjustments in cut-off scores.
The Recruitment Process: Cut Off Scores Army
The recruitment process for the Army is a rigorous and multifaceted one, designed to ensure that only the most qualified individuals are selected to serve. It involves a series of stages, each with its own set of criteria and cut-off scores, designed to assess the applicant’s suitability for military service.
Stages of the Recruitment Process
The recruitment process for the Army typically involves several distinct stages, each with specific requirements and cut-off scores.
- Initial Application: The first stage involves submitting an application, either online or in person. The application requires basic personal information, including name, address, contact details, educational qualifications, and work experience. Applicants must also meet certain minimum qualifications, such as age, citizenship, and physical fitness standards.
- Screening: Once the initial application is received, it is screened to ensure that the applicant meets the basic requirements. This stage typically involves verifying the information provided in the application, checking academic transcripts, and conducting a preliminary assessment of the applicant’s suitability. Cut-off scores may be applied at this stage to eliminate candidates who do not meet the minimum qualifications, such as a minimum GPA requirement.
- Assessment: Applicants who pass the initial screening stage are invited to participate in a series of assessments designed to evaluate their physical, mental, and psychological suitability for military service. These assessments may include written tests, physical fitness tests, interviews, group activities, and psychological evaluations. Cut-off scores are often used to determine which candidates progress to the next stage. For example, a minimum score on the Armed Services Vocational Aptitude Battery (ASVAB) may be required to qualify for certain military occupational specialties.
- Background Check: After passing the assessment stage, applicants undergo a comprehensive background check to verify the information provided in their application and to ensure that they have no criminal history or other disqualifying factors. This stage may involve contacting previous employers, checking credit history, and conducting criminal background checks. The background check is crucial in determining the applicant’s suitability for military service and can lead to the disqualification of candidates who fail to meet the required standards.
Cut off scores for the army can vary depending on factors like the branch of service, the specific job, and the year. For example, if you’re interested in the Officer’s Training Academy (OTA), you might want to check out the oml army website for information about their specific requirements. Once you know which branch and job you’re interested in, you can find the specific cut off scores online or through official army recruitment channels.
- Offer of Employment: Applicants who successfully complete all stages of the recruitment process receive an offer of employment. The offer typically includes details about the specific military occupational specialty, salary, benefits, start date, and other important terms and conditions. Cut-off scores play a significant role in determining the final offer, as they help to ensure that only the most qualified candidates are selected for service.
Physical Fitness Tests
Physical fitness is an essential requirement for military service, and the Army conducts rigorous physical fitness tests to assess the applicant’s ability to meet the demands of military training and operations.
- Test Types: The Army Physical Fitness Test (APFT) typically includes three events: push-ups, sit-ups, and a two-mile run. The test is structured with specific time limits and minimum number of repetitions required for each event. For example, the minimum passing score for push-ups is 42 for men and 18 for women, while the minimum passing score for sit-ups is 50 for men and 40 for women.
The two-mile run has different time limits for different age groups.
- Cut-off Scores: The cut-off scores for the APFT are based on industry standards and the specific demands of military service. They are designed to ensure that all recruits meet a minimum level of physical fitness.
- Impact on Overall Selection: Physical fitness scores are an important factor in the overall selection process, but their weight varies depending on the specific military occupational specialty. For physically demanding roles, such as infantry or combat arms, physical fitness scores are given more weight. However, for roles that require more technical or administrative skills, physical fitness scores may be less important.
Academic Qualifications
Academic qualifications are also important for military service, as they demonstrate the applicant’s knowledge, skills, and ability to learn and adapt.
- Relevance to Job Requirements: The specific academic qualifications required for a particular military occupational specialty vary depending on the job’s requirements. For example, roles that involve technology or engineering may require a degree in a relevant field, while other roles may only require a high school diploma.
- Cut-off Scores: The Army typically sets minimum academic requirements for each military occupational specialty, such as a minimum GPA or a specific degree. These cut-off scores ensure that all candidates meet the minimum qualifications for the position.
- Weighting in Selection: The weight given to academic qualifications in the selection process varies depending on the specific role. For roles that require specialized knowledge or skills, academic qualifications may be given more weight. However, for roles that require more practical experience or skills, experience may be given more weight than academic qualifications.
Preparing for the Recruitment Process

The recruitment process for the military is rigorous and demanding. It requires physical fitness, academic prowess, and a strong mental attitude. To succeed, you need to prepare well in advance. This section will provide you with practical tips on how to prepare for the physical fitness tests, enhance your academic performance, and develop essential skills and qualities.
Physical Fitness Preparation
Preparing for the physical fitness tests is crucial for success in military recruitment. The tests assess your physical endurance, strength, and agility, which are essential for the demanding nature of military service. Here are some practical tips to enhance your physical fitness:
- Start Early and Gradually Increase Intensity: Don’t wait until the last minute to begin training. Start gradually and increase the intensity and duration of your workouts over time. This will help you avoid injuries and build a strong foundation.
- Focus on Key Fitness Components: The physical fitness tests typically assess cardiovascular endurance, muscular strength, and flexibility. Incorporate exercises that target these components into your training regimen. For example, running, push-ups, sit-ups, and stretching are essential.
- Seek Professional Guidance: Consider consulting a certified personal trainer or fitness professional to develop a personalized training plan tailored to your needs and goals. They can help you design a safe and effective program that addresses your specific weaknesses and strengths.
- Maintain Consistency: Consistency is key to achieving fitness goals. Aim for regular workouts, ideally 3-4 times a week. Don’t skip workouts, even if you feel tired or unmotivated.
- Proper Nutrition and Rest: Fuel your body with nutritious foods and get adequate sleep. This will help you recover from workouts and improve your overall performance.
Academic Performance Enhancement
Academic performance is another critical aspect of military recruitment. Many branches of the military require candidates to meet certain academic standards. Here are some strategies to improve your academic performance:
- Time Management: Effective time management is essential for balancing studies and other commitments. Create a study schedule and stick to it. Break down large tasks into smaller, manageable steps.
- Active Learning: Instead of passive memorization, engage in active learning techniques. This involves taking notes, asking questions, participating in discussions, and applying concepts to real-life situations.
- Seek Academic Support: Don’t hesitate to seek help from teachers, tutors, or classmates when you encounter difficulties. There are also online resources and study groups that can provide support and guidance.
- Practice Regularly: Regular practice is crucial for mastering academic concepts. Solve problems, complete assignments, and review notes consistently to reinforce your learning.
- Stay Motivated: Maintaining motivation is key to success. Set realistic goals, celebrate milestones, and remind yourself of your reasons for pursuing military recruitment.
Essential Skills and Qualities
Beyond physical fitness and academic performance, certain skills and qualities are essential for successful military recruitment. These traits contribute to your overall suitability and potential for success in military service:
- Leadership: The military emphasizes leadership skills. Demonstrate your ability to motivate, inspire, and guide others. Take on leadership roles in school, extracurricular activities, or community organizations.
- Teamwork: Military service is inherently a team effort. Show your ability to work effectively with others, communicate clearly, and contribute to the success of a group.
- Discipline and Self-Control: The military demands discipline and self-control. Show your ability to follow orders, adhere to rules, and maintain a professional demeanor.
- Problem-Solving and Decision-Making: Military personnel often face challenging situations that require quick thinking and effective decision-making. Develop your ability to analyze problems, weigh options, and make sound judgments.
- Resilience and Adaptability: Military life can be unpredictable and demanding. Demonstrate your ability to adapt to change, overcome challenges, and maintain a positive attitude under pressure.
Historical Perspective
The evolution of cut-off scores in the military reflects changing societal needs, technological advancements, and the evolving nature of warfare. Understanding this historical context provides valuable insights into the present-day recruitment standards and their impact on the composition of the armed forces.
Evolution of Cut-Off Scores, Cut off scores army
The cut-off scores for military recruitment have fluctuated over time, influenced by various factors. In the early days of the military, physical fitness and basic skills were the primary selection criteria. As technology advanced, particularly in the 20th century, the emphasis shifted towards cognitive abilities and technical skills.
- Pre-World War II: During this era, physical fitness and basic literacy were the primary selection criteria. The military sought individuals who could endure the rigors of combat and understand basic orders.
- World War II and the Cold War: The technological advancements of World War II, such as the introduction of complex weapons systems, led to an increased demand for individuals with technical skills and higher cognitive abilities. This resulted in a rise in cut-off scores for aptitude tests and a greater emphasis on education.
- Post-Cold War Era: With the end of the Cold War, the military shifted its focus towards a smaller, more technologically advanced force. This led to a further increase in the emphasis on technical skills and education, resulting in higher cut-off scores for cognitive tests.
- Modern Era: In the modern era, the military continues to adapt to new technologies and evolving threats. This has resulted in a continued emphasis on cognitive abilities, technical skills, and the ability to adapt to changing environments.
Recruitment Criteria: Past vs. Present
The recruitment criteria of the past differed significantly from those of the present. While physical fitness has always been a crucial factor, the importance of cognitive abilities and technical skills has increased dramatically over time.
| Criteria | Past | Present |
|---|---|---|
| Physical Fitness | Emphasis on basic strength, endurance, and agility. | Emphasis on overall physical fitness, including cardiovascular health, strength, flexibility, and endurance. |
| Cognitive Abilities | Basic literacy and numeracy skills were sufficient. | Higher emphasis on cognitive abilities, including problem-solving, critical thinking, and decision-making skills. |
| Technical Skills | Limited emphasis on technical skills, except for specialized roles. | Increased emphasis on technical skills, such as computer proficiency, mechanical aptitude, and knowledge of advanced weaponry. |
| Education | High school diploma or equivalent was often sufficient. | Higher education levels are increasingly sought after, with many roles requiring a college degree or specialized training. |
Global Comparisons
The recruitment process and cut-off scores for military service vary significantly across different countries, influenced by a multitude of factors, including national security needs, cultural values, and economic conditions. Comparing and contrasting these variations provide valuable insights into the global landscape of military recruitment.
Recruitment Processes Across Different Countries
The recruitment process for military service varies significantly across different countries, reflecting diverse national security needs, cultural values, and economic circumstances. Here are some examples:
- United States: The US military utilizes a comprehensive recruitment process, including physical and mental aptitude tests, background checks, and medical examinations. The process emphasizes individual qualifications and offers various career paths and benefits.
- United Kingdom: The British Armed Forces follow a structured recruitment process, involving aptitude tests, physical fitness assessments, and interviews. The focus is on selecting individuals with strong leadership qualities and a commitment to service.
- Israel: Israel’s mandatory military service for all citizens, both men and women, is a unique aspect of its recruitment process. This system ensures a large pool of trained personnel and promotes national unity.
- India: The Indian Armed Forces utilize a rigorous recruitment process, including written examinations, physical fitness tests, and medical examinations. The process is highly competitive, reflecting the large population and the importance of military service in Indian society.
- China: China’s People’s Liberation Army (PLA) emphasizes political loyalty and ideological conformity during recruitment. The PLA focuses on selecting individuals who align with the party’s values and are committed to serving the nation.
Cut-off Scores and Selection Criteria
Cut-off scores and selection criteria for military recruitment vary significantly across different countries, reflecting diverse national security needs, cultural values, and economic circumstances. Here are some examples:
- United States: The US military uses standardized tests, such as the Armed Services Vocational Aptitude Battery (ASVAB), to assess candidates’ cognitive abilities. The ASVAB scores are used to determine eligibility for different military occupations.
- United Kingdom: The British Armed Forces utilize a combination of aptitude tests and physical fitness assessments to evaluate candidates. The focus is on selecting individuals with the necessary skills and physical capabilities to meet the demands of military service.
- Israel: Israel’s mandatory military service for all citizens requires individuals to meet specific physical and mental standards. The focus is on ensuring a high level of fitness and mental resilience among recruits.
- India: The Indian Armed Forces have stringent physical fitness standards and medical requirements for recruitment. The process emphasizes physical strength, endurance, and overall health.
- China: China’s People’s Liberation Army (PLA) has strict selection criteria, including political loyalty, physical fitness, and academic qualifications. The focus is on selecting individuals who are ideologically aligned and possess the necessary skills and knowledge to serve in the military.
Unique Challenges and Considerations
Military recruitment around the world faces various unique challenges and considerations, including:
- Demographic Trends: Declining birth rates and an aging population in many developed countries pose challenges to military recruitment. The shrinking pool of potential recruits necessitates innovative recruitment strategies and incentives.
- Economic Factors: In competitive labor markets, military recruitment faces competition from other industries offering higher salaries and better benefits. The military must offer attractive compensation packages and career opportunities to attract qualified individuals.
- Social Attitudes: Public perception of military service can influence recruitment. Negative media coverage or societal anxieties about war and conflict can deter potential recruits. The military needs to engage with the public and promote the value of military service.
- Cultural Factors: Cultural norms and values can impact military recruitment. In some cultures, military service may be considered a prestigious career path, while in others, it may be viewed as a last resort.
Impact of Cultural and Societal Factors
Cultural and societal factors significantly influence military recruitment standards. For example:
- Gender Roles: In some cultures, women may be discouraged from joining the military due to traditional gender roles. However, in other societies, women have equal opportunities for military service, and their contributions are highly valued.
- Educational Attainment: The level of education required for military service can vary across countries. In some countries, a high school diploma may be sufficient, while in others, a college degree may be required.
- Religious Beliefs: Religious beliefs can influence military recruitment. In some cultures, individuals may be prohibited from participating in armed conflict due to their religious beliefs.
The Future of Recruitment
The world of recruitment is rapidly evolving, driven by technological advancements, shifting demographics, and evolving workforce expectations. As we move forward, the way organizations attract, engage, and hire talent will be significantly impacted by these forces, leading to a more data-driven, personalized, and technology-enabled recruitment landscape.
Emerging Trends and Technological Advancements
Emerging technologies are poised to reshape the recruitment landscape, automating tasks, enhancing candidate experience, and enabling more efficient and effective talent acquisition.
- Blockchain: Blockchain technology can revolutionize the recruitment process by providing a secure and transparent platform for storing and verifying candidate credentials, eliminating the need for paper-based documentation and reducing the risk of fraud. Blockchain can also streamline the background check process, making it faster and more efficient. For example, a blockchain-based system could securely store and verify educational certificates, work history, and other relevant documents, ensuring their authenticity and reducing the time and effort required for manual verification.
- Virtual Reality (VR): VR technology offers a compelling way to create immersive recruitment experiences, allowing candidates to virtually tour company offices, meet with hiring managers, and experience the company culture firsthand. This can significantly enhance candidate engagement and provide a more realistic understanding of the work environment. VR can be used to create virtual job simulations, allowing candidates to demonstrate their skills in a realistic setting and providing employers with a more comprehensive assessment of their abilities.
For instance, a VR simulation could allow candidates to experience a typical day in the life of a software engineer, providing them with a hands-on understanding of the role and the company’s work environment.
- AI-Powered Chatbots: AI-powered chatbots can automate the initial stages of the recruitment process, providing instant responses to candidate inquiries, scheduling interviews, and collecting basic candidate information. This can free up recruiters to focus on more strategic tasks, such as candidate engagement and talent sourcing. AI chatbots can be programmed to provide personalized responses based on candidate profiles and preferences, creating a more engaging and efficient candidate experience.
They can also be used to screen candidates based on predefined criteria, automating the initial stages of the selection process and identifying the most promising candidates for further evaluation.
Artificial Intelligence and Automation Impact on Cut-Off Scores
AI-powered systems are increasingly being used in recruitment to automate tasks and improve efficiency. This includes the potential to impact the way cut-off scores are determined and applied.
- Automating Cut-Off Score Setting: AI algorithms can analyze historical data on candidate performance and job success to automatically set cut-off scores for different assessment tests and selection criteria. This can help to ensure consistency and fairness in the selection process, reducing the risk of human bias. For example, AI algorithms could analyze data on past candidates’ test scores and subsequent job performance to identify optimal cut-off scores for different roles, ensuring that candidates who are most likely to succeed are selected.
- Personalizing Cut-Off Scores: AI can be used to personalize cut-off scores based on individual candidate profiles, taking into account factors such as experience, education, and skills. This can help to create a more equitable and relevant selection process, allowing candidates with diverse backgrounds and experiences to be fairly assessed. For instance, AI could adjust cut-off scores for a specific technical test based on a candidate’s prior experience in the field, ensuring that candidates with less experience are not unfairly disadvantaged.
- Eliminating Bias in Cut-Off Score Determination: AI algorithms can be designed to eliminate bias from the cut-off score determination process, ensuring that all candidates are evaluated based on their merits and not on their gender, race, or other protected characteristics. AI can identify and mitigate biases that may exist in historical data, leading to a more objective and fair selection process. For example, AI could be used to analyze past hiring decisions and identify any potential biases in the application of cut-off scores, ensuring that future decisions are made in a fair and unbiased manner.
Future Direction of Military Recruitment and Standards
The military faces unique challenges in recruitment, needing to attract and retain talent in a highly competitive job market. The future direction of military recruitment will be shaped by a confluence of factors, including technological advancements, geopolitical shifts, and evolving social values.
- Technological Advancements: As military technology continues to advance, the skills and knowledge required for future military personnel will evolve. The military will need to adapt its recruitment strategies to attract individuals with the necessary technical expertise and the ability to learn and adapt to rapidly changing technologies. For instance, the increasing use of autonomous weapons systems, cyber warfare, and space operations will require the military to recruit individuals with expertise in artificial intelligence, cybersecurity, and space technology.
- Geopolitical Shifts: Global events and geopolitical tensions will continue to shape the military’s recruitment needs. The military will need to be prepared to respond to emerging threats and challenges, requiring a flexible and adaptable workforce. This may involve recruiting individuals with specific language skills, cultural awareness, and expertise in particular regions of the world. For example, the rise of cyber threats and the increasing importance of cyber warfare may necessitate the recruitment of individuals with expertise in cybersecurity, digital forensics, and network security.
- Demographic Changes: Changing demographics will also impact military recruitment. The military will need to attract and retain a diverse workforce that reflects the changing demographics of the population. This will require a focus on diversity and inclusion initiatives, ensuring that all individuals have equal opportunities to serve. For example, the military may need to implement outreach programs to attract individuals from underrepresented groups, such as women and minorities, to ensure that its workforce reflects the diversity of the population it serves.
Resources and Support

Embarking on a military career is a significant decision, and it’s crucial to have the right resources and support to guide you through the process. From understanding cut-off scores to accessing essential services, this section provides a comprehensive overview of the support available to aspiring recruits.
Cut-off Scores
Cut-off scores are minimum requirements for various military branches and roles. They reflect the minimum standards needed to successfully complete the training and perform the required duties. These scores are determined based on factors like physical fitness, academic performance, and aptitude tests.
- Physical Fitness: Physical fitness is a crucial aspect of military service. Each branch has its own set of physical fitness standards, and candidates must achieve a certain score on the Armed Services Vocational Aptitude Battery (ASVAB) to qualify.
- Academic Performance: Educational qualifications are essential for most military roles. The minimum education requirements vary depending on the branch and specific role.
- Aptitude Tests: The ASVAB is a standardized test used to assess a candidate’s aptitude in various areas, including verbal, mathematical, and spatial reasoning. The scores on the ASVAB help determine eligibility for specific military occupations.
To find the specific cut-off scores for different branches and roles, you can consult the official websites of each branch:
- Army: https://www.goarmy.com/careers-and-jobs.html
- Navy: https://www.navy.com/careers/jobs.html
- Air Force: https://www.airforce.com/careers/jobs.html
- Marines: https://www.marines.com/careers/jobs.html
- Coast Guard: https://www.gocoastguard.com/careers/jobs.html
Support Services
The military recruitment process offers comprehensive support services to help individuals navigate the journey successfully. These services are designed to address various needs and concerns, ensuring a smooth transition into military life.
- Counseling and Guidance: Career counselors and advisors are available to provide personalized guidance throughout the recruitment process. They can help individuals understand their interests, identify suitable roles, and develop a plan to achieve their goals.
- Financial Assistance: The military offers various financial assistance options to help potential recruits overcome financial barriers. These include scholarships, grants, and tuition assistance programs.
- Physical Training and Preparation: The military recognizes the importance of physical fitness and provides resources and programs to help individuals prepare for the physical demands of military service.
- Mental Health Support: The military understands that the recruitment process can be stressful and provides access to mental health professionals and programs to address any concerns or anxieties.
Application Guide
The application process for military service involves a series of steps designed to ensure that individuals meet the necessary requirements and are prepared for the challenges of military life.
- Initial Contact: The first step is to contact a recruiter or visit a recruitment office. Recruiters can provide information about different branches, roles, and the application process.
- Eligibility Requirements: To be eligible for military service, individuals must meet certain criteria, including age, education, and physical fitness.
- Medical Screening: A comprehensive medical examination is conducted to assess the candidate’s overall health and fitness for military service.
- Background Checks: Security checks and background investigations are conducted to ensure the candidate’s suitability for military service.
- Training and Deployment: Once accepted, recruits undergo rigorous training programs to prepare them for their specific roles. After training, individuals may be deployed to various locations around the world.
- Application Deadlines and Timelines: Application deadlines and timelines vary depending on the branch and role. It’s important to contact a recruiter for specific information.
FAQ Compilation
What are the specific cut-off scores for each branch of the military?
Cut-off scores vary depending on the specific branch of the military, the role, and the current needs of the military. It’s best to contact a recruiter or visit the official website of the branch you’re interested in for the most up-to-date information.
How can I prepare for the physical fitness tests?
Start by familiarizing yourself with the specific tests required for the branch and role you’re interested in. Develop a training plan that focuses on building strength, endurance, and flexibility. Seek guidance from a certified personal trainer or fitness professional if needed.
Are there any resources available to help me with the application process?
Yes, each branch of the military has recruitment offices and websites that offer support services and guidance throughout the application process. You can also contact a recruiter or visit a recruitment office to get personalized assistance.
What are the ethical considerations related to cut-off scores?
The use of cut-off scores raises ethical considerations related to fairness, bias, and inclusivity. It’s crucial to ensure that cut-off scores are based on objective criteria and that they do not unfairly exclude qualified individuals from consideration.

Whitney Morris is a renowned author with a passion for military history and strategic analysis. Born in Jakarta, Indonesia, Defense developed a deep fascination for warfare and national defense from a young age. His unwavering interest in military strategy, combined with his natural storytelling ability, has earned him a reputation as an engaging and insightful writer in the field.