O1 military rank 2024 pay chart – The O-1 Military Rank 2024 Pay Chart is a vital resource for understanding the compensation structure for newly commissioned officers in the United States Armed Forces. This chart provides a detailed breakdown of base pay, allowances, and benefits, offering valuable insights for both current and aspiring military personnel. It serves as a cornerstone for informed decision-making, ensuring that individuals can make well-informed choices about their career paths and financial planning.
This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of the O-1 pay chart, exploring its various components and the factors that influence compensation. We will analyze the pay structure for different branches of the military, examine the impact of location and duty assignments, and discuss the various special pay and allowances available. Furthermore, we will provide insights into career progression for O-1 officers, compare their compensation with other ranks, and explore the comprehensive benefits package offered to them.
Understanding the O-1 Rank
The O-1 rank is the lowest commissioned officer rank in the United States military. It’s often referred to as a “second lieutenant” in the Army, Air Force, and Space Force, or an “ensign” in the Navy and Coast Guard. This rank represents the initial step into a military leadership role, signifying a transition from enlisted personnel to a commissioned officer.
Responsibilities and Duties
O-1 officers are primarily responsible for leading small teams, often platoons or squads, in various military operations. They are expected to:
- Supervise and train junior enlisted personnel
- Execute orders from higher-ranking officers
- Maintain unit readiness and morale
- Plan and conduct tactical operations
- Develop and maintain effective communication with superiors and subordinates
Training and Qualifications
To become an O-1 officer, individuals must undergo rigorous training and meet specific qualifications:
- A bachelor’s degree is typically required, although some branches may accept an associate’s degree or equivalent experience.
- Successful completion of Officer Candidate School (OCS) or a service academy program.
- Passing physical fitness tests and medical evaluations.
- Demonstrating leadership qualities and strong academic performance.
Pay and Benefits
O-1 officers receive a base salary based on their time in service and location. Additionally, they are eligible for various benefits, including:
- Health insurance
- Retirement plan
- Housing allowance
- Educational opportunities
- Access to military commissaries and exchanges
O-1 Pay Chart Analysis: O1 Military Rank 2024 Pay Chart

This section delves into the specifics of the O-1 pay chart for 2024, highlighting the differences between branches and exploring any noticeable trends or changes compared to previous years.
O-1 Pay Chart for 2024
The O-1 pay chart for 2024 Artikels the base pay for newly commissioned officers across all branches of the US military. It’s essential to understand that this chart reflects base pay only, and doesn’t include additional benefits like housing allowance, food allowance, or special pay.
Discover how Educational Word Searches has transformed methods in this topic.
| Rank | Basic Pay (Monthly) |
|---|---|
| O-1 (Second Lieutenant/Ensign) | $3,824.00 |
Pay Differences Between Branches
While the base pay for O-1 officers is generally consistent across all branches, slight variations may exist due to specific branch-related allowances or special pay. For example, officers in certain branches like the Air Force or Navy might receive additional pay for flying duties.
Trends and Changes in O-1 Pay
O-1 pay has generally seen an upward trend over the past few years, reflecting adjustments for inflation and cost of living. However, the specific increase in pay each year varies based on factors like the federal budget and economic conditions. For instance, the 2024 pay increase for military personnel was determined based on the Consumer Price Index (CPI) and was around 4.6%.
This signifies that O-1 officers in 2024 receive a slightly higher base pay than their counterparts in previous years.
4. Factors Affecting O-1 Pay
Alright, so we’ve talked about the basics of O-1 pay, but there’s a lot more to it than just the base pay. The actual amount an O-1 receives can be influenced by several factors, like where they’re stationed, their specific job, and even special allowances. Let’s break it down.
4.1 Location and Duty Assignments
It’s not all about the money, but it definitely plays a role. Where you’re stationed and what you’re doing can impact your pay. Think of it like this: If you’re in a high-cost-of-living area, your pay might be adjusted to compensate for the higher expenses. The same goes for duty assignments. Some roles require specialized skills or are considered more demanding, which can translate to higher pay.
For example, an O-1 stationed in New York City might receive a higher pay grade compared to one stationed in a smaller town in Kansas. This is because the cost of living in New York City is significantly higher. Similarly, an O-1 serving in a combat zone might receive additional pay and allowances for the risks involved. It’s all about balancing the scales, making sure everyone’s compensated fairly for their contributions.
4.2 Special Pay and Allowances
Now, this is where things get interesting. There are special payments and allowances that can add to an O-1’s base pay, depending on their situation and responsibilities. These are like bonuses or extra perks for specific circumstances. It’s like a reward for going above and beyond, or for facing certain challenges.
| Special Pay/Allowance | Eligibility Criteria | Estimated Monetary Value |
|---|---|---|
| Hazardous Duty Pay | Serving in designated hazardous areas | $225 per month |
| Flight Pay | Pilots, flight engineers, and other aircrew members | Varies based on flight hours and type of aircraft |
| Family Separation Allowance | Military members separated from their families due to duty | Varies based on location and length of separation |
| Foreign Language Proficiency Pay | Proficiency in designated foreign languages | $100 – $350 per month |
These are just a few examples. There are many other special pay and allowances available, depending on the specific needs and circumstances of the O-1. It’s like a whole system of incentives to recognize different skills and contributions, ensuring everyone’s fairly compensated.
4.3 Potential Pay Raises or Adjustments in 2024
Now, let’s talk about the future. It’s impossible to predict exactly what will happen with O-1 pay in 2024, but there are some factors to consider. Inflation, for instance, can lead to pay adjustments to keep pace with the rising cost of living. The government’s budget also plays a role, as it dictates how much funding is available for military salaries.
And finally, legislative changes can impact pay, like the National Defense Authorization Act (NDAA) which sets the annual budget for the military.
For example, the 2023 NDAA included a 4.6% pay raise for all military personnel, including O-1s. While the exact amount of any pay raise in 2024 is unknown, it’s likely to be influenced by factors like inflation, budget constraints, and the overall economic climate. It’s a bit of a guessing game, but we’ll have to wait and see what happens.
Career Progression for O-1 Officers
Being an O-1 officer in the military is like being a fresh grad entering the workforce. You’re starting your career, learning the ropes, and proving yourself. This stage is all about gaining experience and laying the foundation for future success.
The typical career path for an O-1 officer involves a cycle of training, assignments, and opportunities for advancement. The initial focus is on mastering the fundamentals of military life, developing leadership skills, and gaining operational experience. As you progress, you’ll take on more responsibilities, leading smaller units and working your way up the ranks.
Opportunities for Promotion and Advancement
The opportunities for promotion within the O-1 rank are primarily based on performance and leadership potential. The military evaluates officers based on their performance in various areas, including:
- Leadership: Demonstrating effective leadership qualities in leading teams and achieving mission objectives.
- Technical Proficiency: Excelling in their specific military occupational specialty (MOS) and acquiring advanced skills.
- Physical Fitness: Maintaining a high level of physical fitness to meet the demands of military service.
- Education: Pursuing further education and professional development opportunities to enhance their knowledge and skills.
Promotion from O-1 to O-2 is typically based on a combination of performance evaluations, time in service, and recommendations from superiors.
Challenges and Rewards of Progressing as an O-1 Officer
The journey of an O-1 officer is filled with both challenges and rewards. Here are some key aspects:
- Challenges:
- High Expectations: As a newly commissioned officer, you’ll face high expectations from superiors and peers.
- Adapting to Military Life: Adjusting to the rigorous demands and structure of military life can be challenging.
- Balancing Work and Personal Life: Maintaining a balance between your military duties and personal life can be demanding.
- Rewards:
- Personal Growth: The military provides opportunities for personal growth, leadership development, and character building.
- Sense of Purpose: Serving your country and contributing to a greater cause can be deeply rewarding.
- Career Advancement: The military offers a clear career path with opportunities for promotion and advancement.
6. Comparison with Other Ranks
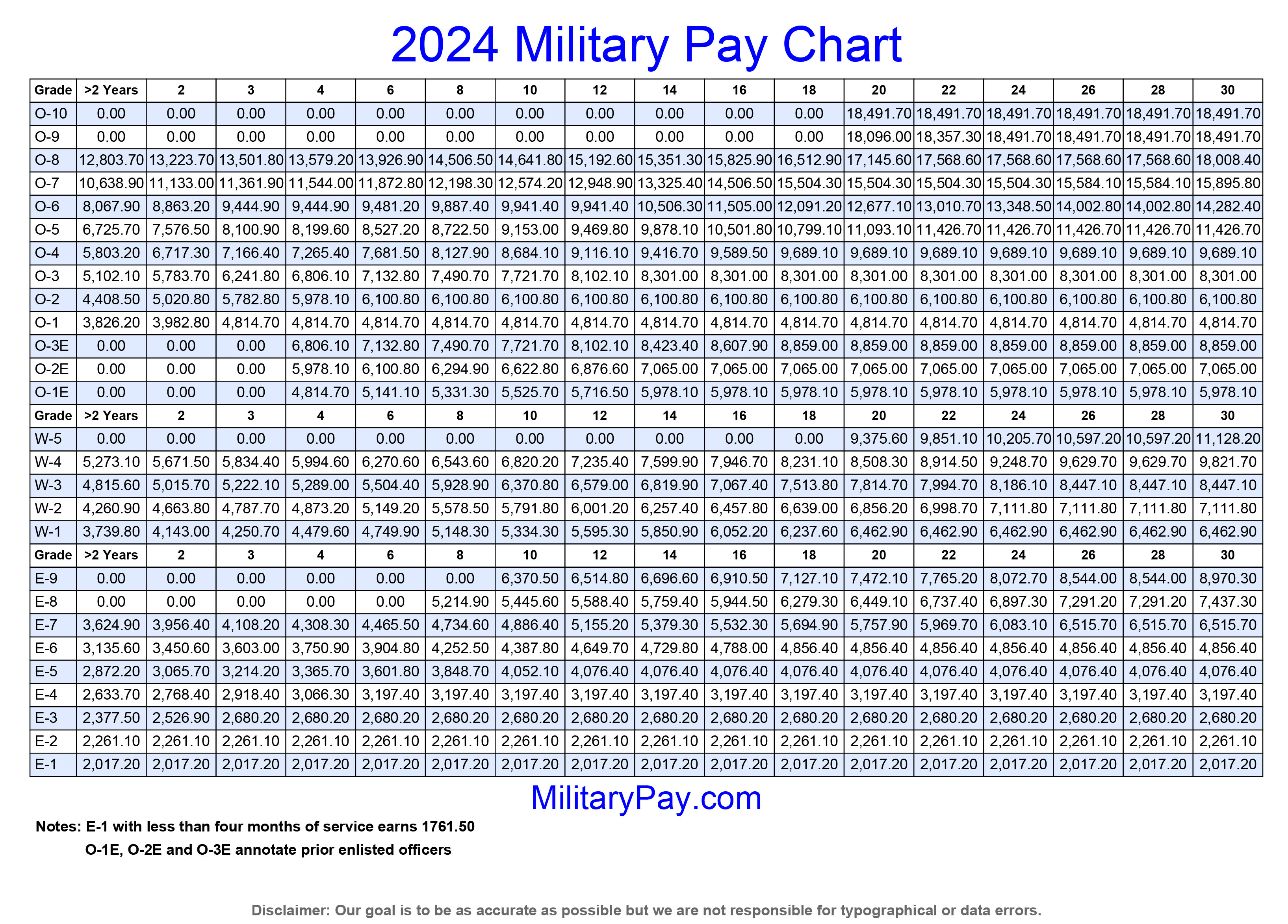
It’s time to compare the O-1 rank with other ranks in the military. We’ll look at pay, benefits, and the overall experience, so you can get a better understanding of what each rank offers.
6.1. Pay and Benefits Comparison
The pay and benefits of an O-1 officer are different from those of other ranks, so let’s break it down.
Base Pay
Here’s a table showing the base pay for officers of different ranks in 2024:| Rank | Base Pay (USD) ||—|—|| O-1 | 36,984 || O-2 | 44,130 || O-3 | 53,564 || O-4 | 66,786 || O-5 | 83,538 || O-6 | 101,646 || O-7 | 121,524 || O-8 | 144,282 || O-9 | 169,536 || O-10 | 198,014 |As you can see, base pay increases significantly as you climb the ranks.
Allowances
Allowances, like housing and food, can vary based on location and family size. Here’s a quick comparison:* Housing Allowance: Higher ranks often receive a larger housing allowance, especially if they have families.
Food Allowance
Officers typically receive a food allowance, but the amount may be based on rank and duty location.
Other Allowances
There are various other allowances for things like travel, uniform maintenance, and special duty assignments. These allowances can vary depending on the specific circumstances and the rank of the officer.
Benefits
Benefits for officers include:* Health Insurance: The military provides comprehensive health insurance for officers and their families.
Retirement Plan
Officers contribute to a retirement plan, and the government matches their contributions.
Other Benefits
Other benefits include life insurance, educational assistance, and access to military commissaries and exchanges. These benefits are generally available to all officers, regardless of rank.
6.2. Advantages and Disadvantages of Different Ranks
Let’s explore the advantages and disadvantages of different ranks in the military.
Leadership Responsibilities
* O-1: You’ll be a leader right away, but you’ll have a small team and limited decision-making authority.
Higher Ranks
As you move up, your leadership responsibilities grow. You’ll have more troops under your command and more complex decisions to make.
Career Progression
* O-1: This is the starting point, and you’ll be evaluated for promotion to O-2.
Higher Ranks
Promotion opportunities become more competitive as you climb the ranks. You’ll need strong performance and a good track record.
Work-Life Balance
* O-1: You’ll have more time for personal life, but you’ll still have to be available for duty.
Higher Ranks
As you advance, you’ll have more demanding responsibilities, which can impact your work-life balance. Duty hours, deployments, and family responsibilities become more complex.
6.3. Factors Influencing Rank Choice
Here are some factors that might influence an officer’s decision to pursue a specific rank:
Personal Goals and Aspirations
Some officers may aspire to high-ranking positions, while others may be content with a lower rank. Your career goals and ambitions will play a significant role in your rank choices.
Family Considerations
Family obligations and responsibilities can also influence an officer’s career choices. Some officers may prioritize family life, while others may choose to focus on their military career.
Risk Tolerance
The higher the rank, the more responsibility and risk you take on. Your willingness to accept these challenges will affect your rank aspirations.
7. Military Benefits for O-1 Officers
Serving as an O-1 officer in the military comes with a comprehensive benefits package designed to support you and your family throughout your service. These benefits are a significant part of the overall compensation you receive, providing financial security, healthcare, housing assistance, and other valuable perks.
Healthcare
The military offers exceptional healthcare benefits to O-1 officers, providing comprehensive coverage for a wide range of medical services. This includes:
- Comprehensive Coverage: Access to a wide array of medical services, including preventive care, routine checkups, and treatment for illnesses and injuries.
- Specialized Services: Access to specialized care, such as mental health services, dental care, and vision care, ensuring your overall well-being.
- Low Co-pays and Minimal Out-of-Pocket Expenses: Reduced financial burden for medical expenses, allowing you to focus on your health and service.
- Access to Military Hospitals and Network of Providers: Access to high-quality medical care at military hospitals and a network of civilian providers, ensuring convenient and reliable access to healthcare.
Housing
The military provides various housing options for O-1 officers, catering to different needs and preferences:
- Base Housing: Access to on-base housing, offering a secure and affordable living environment close to your duty station.
- Housing Allowance: Financial assistance for off-base housing, allowing you to choose a living arrangement that suits your family’s needs.
- Off-Base Housing Options: Flexibility to rent or purchase housing off-base, giving you greater control over your living situation.
- Subsidized Housing and Rent Assistance: Financial support to offset housing costs, making it more affordable to live in desirable locations.
Retirement
The military offers a robust retirement plan for O-1 officers, ensuring financial security after your service:
- Thrift Savings Plan (TSP): A government-sponsored retirement savings plan similar to a 401(k), allowing you to save for your future and receive matching contributions from the government.
- Retirement Pay: A pension based on your years of service and rank, providing a steady stream of income after you retire.
- Early Retirement Options: Eligibility for retirement after 20 years of service, allowing you to pursue other opportunities earlier in life.
- Survivor Benefits: Benefits for your spouse and dependents in the event of your death, ensuring their financial well-being.
8. Financial Planning for O-1 Officers
As an O-1 officer, you’re embarking on a new chapter in your career and financial life. It’s crucial to develop a solid financial plan to manage your income, expenses, and savings effectively. This guide will provide practical strategies and resources to help you navigate the financial aspects of your military journey.
Budgeting
A well-structured budget is the foundation of sound financial planning. It allows you to track your income and expenses, identify areas for improvement, and allocate funds for your financial goals.
- Income: Start by listing all your sources of income, including your military salary, allowances, and any other earnings.
- Fixed Expenses: These are costs that remain relatively constant each month, such as rent or mortgage payments, car payments, insurance premiums, and loan repayments.
- Variable Expenses: These are costs that fluctuate from month to month, including groceries, dining out, entertainment, and utilities.
- Savings Goals: Set specific savings goals, such as an emergency fund, retirement savings, or a down payment on a house.
Here’s a sample budget table to get you started:| Category | Estimated Monthly Cost | Notes ||—|—|—|| Housing | $1,500 | Rent or mortgage payment || Food | $500 | Groceries, dining out || Transportation | $300 | Car payment, gas, public transportation || Personal Needs | $200 | Clothing, entertainment, personal care || Savings | $200 | Emergency fund, retirement |
Saving Strategies
Saving is an essential part of financial security. It allows you to build a financial cushion for unexpected expenses, achieve your long-term goals, and enjoy financial peace of mind.
- Emergency Fund: Aim to have 3-6 months of living expenses in a high-yield savings account to cover unexpected events like job loss, medical emergencies, or car repairs.
- Retirement Savings: Utilize the Thrift Savings Plan (TSP) and maximize your contributions to receive matching funds. The TSP is a retirement savings plan specifically designed for military personnel.
- Specific Goals: Create separate savings accounts for specific goals, such as a down payment on a house, travel, or your children’s education.
Investment Options
Investing your savings can help you grow your wealth over time. There are various investment options available, each with its own risk and reward profile.
Traditional Investments: Stocks, bonds, and mutual funds offer potential for long-term growth and diversification.
Alternative Investments: Real estate, precious metals, and collectibles can provide diversification and potential for higher returns, but also carry higher risk.
Debt Management
Debt can significantly impact your financial well-being. Developing a plan to manage debt effectively is crucial for your financial health.
- Debt Payoff Plan: Create a plan to prioritize paying off your debts, focusing on either the smallest balance first (debt snowball method) or the highest interest rate first (debt avalanche method).
- Negotiate Interest Rates: Contact your creditors to see if you can negotiate lower interest rates on your loans.
- Utilize Credit Counseling: Consider seeking help from credit counseling agencies if you’re struggling with debt management.
Maximizing Financial Resources
There are numerous ways to maximize your financial resources and achieve your financial goals.
- Side Hustles: Explore freelance opportunities, online tutoring, or selling crafts to supplement your income.
- Negotiate Salary: Research industry standards and prepare to negotiate a competitive salary during promotion reviews.
- Utilize Military Benefits: Take advantage of education benefits, housing allowances, and other military resources to reduce financial burdens.
Financial Planning Resources
Numerous reputable resources are available to provide financial guidance and support to military personnel.
- Military OneSource: Provides comprehensive financial planning resources, including budgeting tools, debt management advice, and investment guidance.
- Financial Counseling Network: Offers free and confidential financial counseling to military personnel and their families.
- National Endowment for Financial Education (NEFE): Provides educational resources and financial planning tools tailored for military families.
Resources for O-1 Officers
Starting your journey as an O-1 officer is exciting, but it’s also important to know where to find the right support and information. Think of it like navigating the bustling streets of Jakarta Selatan – you need a good map and a few trusted guides!
When investigating detailed guidance, check out pt ola tv apk download now.
Official Military Resources
Navigating the military world can feel like a maze, but luckily, there are official resources to help you find your way. These resources provide information on everything from pay and benefits to career development and even mental health support.
- Defense Finance and Accounting Service (DFAS): This is your go-to for all things pay and benefits. They’re the ones who handle your salary, allowances, and other financial matters. You can find their website at https://www.dfas.mil/ and their contact information is available on their website.
- Military OneSource: This comprehensive resource offers support on a wide range of topics, including finances, family matters, education, and even legal assistance. You can access their website at https://www.militaryonesource.mil/ . They also have a toll-free number you can call: 1-800-342-9647.
- Your Branch’s Service Academy: Each branch of the military has its own service academy, which offers resources and support specifically tailored to their officers. For example, if you’re in the Army, you can reach out to the United States Military Academy at West Point. You can find contact information for each branch’s academy online.
Financial Planning Resources
Managing your finances as a young officer can be a bit overwhelming, but there are resources available to help you get on the right track. It’s like learning to budget in a bustling city like Jakarta Selatan – you need a solid plan to avoid getting lost in the expenses.
- Military Financial Advisors: These professionals are specifically trained to understand the financial needs of military personnel. They can help you with budgeting, saving, investing, and even planning for retirement. You can find a military financial advisor through the Military OneSource website or by contacting your local base financial office.
- The Personal Finance Society: This organization offers resources and education on a wide range of financial topics, including budgeting, debt management, and investing. You can access their website at https://www.thepfs.org/ .
Career Development Resources
As an O-1 officer, you’re just starting your career, and it’s important to have a plan for your future. These resources can help you map out your career path and develop the skills you need to succeed.
- Your Branch’s Professional Development Programs: Each branch of the military has its own professional development programs specifically designed for officers. These programs can help you advance your skills, build your leadership abilities, and prepare for future leadership roles.
- Military Leadership Courses: There are numerous military leadership courses available, both online and in person, that can help you develop your leadership skills and prepare for future challenges.
- Mentors: Find a mentor within your branch who can provide guidance and support as you navigate your career. A mentor can be a senior officer who has been in your shoes and can offer valuable insights and advice.
Impact of Military Budget
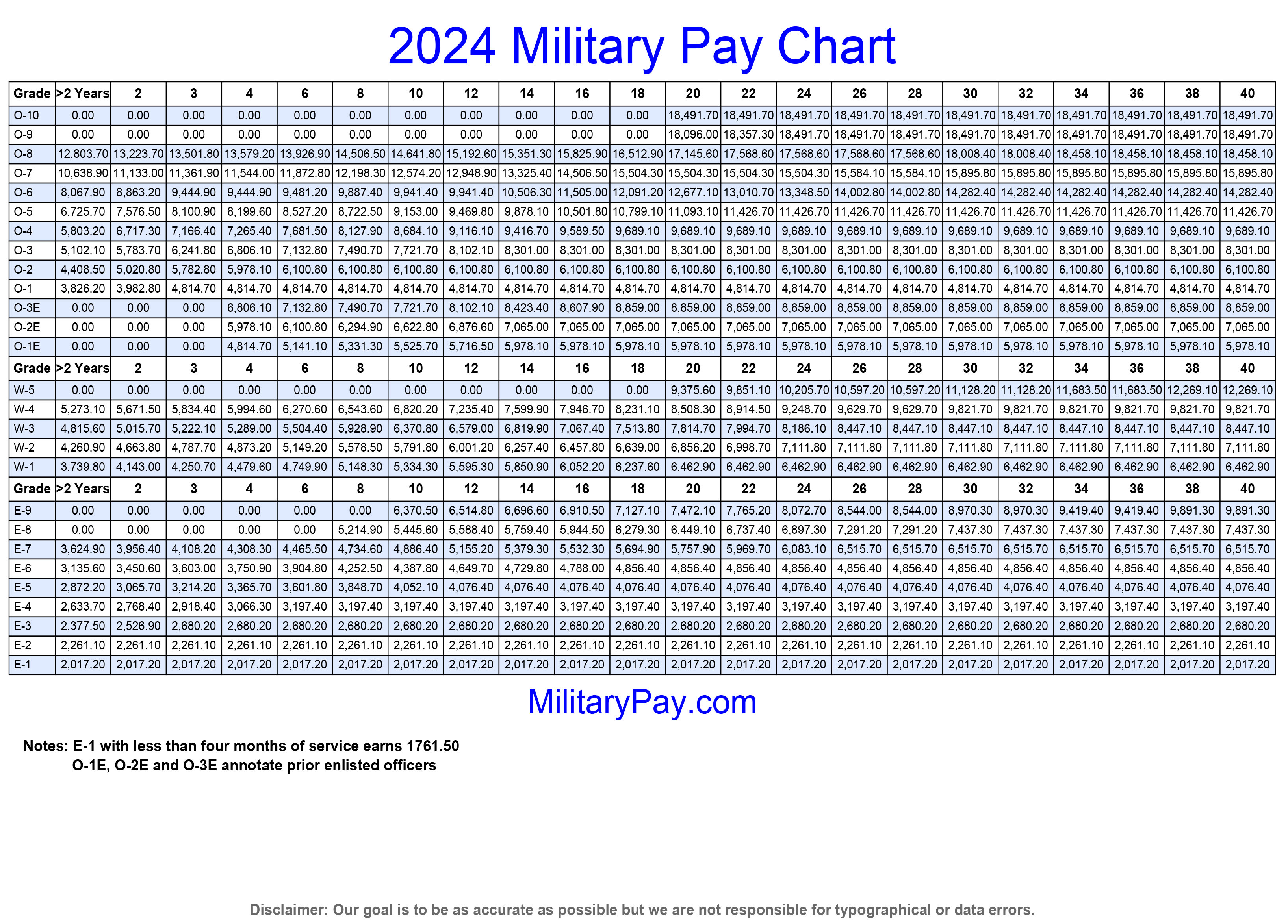
The military budget plays a significant role in shaping the compensation and benefits received by O-1 officers. Fluctuations in funding can directly impact their overall pay, benefits, and career progression. Understanding the potential impact of budget changes is crucial for O-1 officers to make informed decisions about their military careers.
Impact of Budget Cuts
Budget cuts can have a substantial impact on O-1 pay and benefits. Here’s how:* Reduced Base Pay: Budget cuts may lead to a reduction in base pay for O-1 officers, affecting their overall income.
Limited Benefits
Budget constraints may limit the availability of benefits like housing allowances, healthcare, and educational opportunities.
Delayed Promotions
Budget cuts can affect the rate of promotions, potentially delaying career advancement for O-1 officers.
Reduced Training and Development
Funding reductions can impact the availability of training and development opportunities, limiting career growth and skill development.
Impact of Budget Increases
Budget increases can have a positive impact on O-1 pay and benefits. Here’s how:* Increased Base Pay: Budget increases can lead to higher base pay for O-1 officers, improving their financial stability.
Enhanced Benefits
Increased funding can lead to expanded benefits packages, including improved healthcare coverage, housing allowances, and educational opportunities.
Faster Promotions
Budget increases can support a faster promotion rate, accelerating career advancement for O-1 officers.
Improved Training and Development
Increased funding can provide more opportunities for training and development, enhancing skills and career prospects.
Potential Policy Shifts
Policy shifts related to military pay and benefits can also be influenced by budget changes. For example, budget cuts might lead to:* Increased Co-pays for Healthcare: To manage costs, the government may increase co-pays for healthcare services, affecting the affordability of medical care for O-1 officers.
Reduced Housing Allowances
Budget constraints might lead to a reduction in housing allowances, impacting the ability of O-1 officers to afford adequate housing.
Changes to Retirement Benefits
Budget cuts could lead to changes in retirement benefits, potentially affecting the financial security of O-1 officers in their later years.
11. Historical Context of Military Pay
Military pay, the compensation given to soldiers for their service, has a long and fascinating history, reflecting the evolution of warfare, societal values, and economic conditions. Understanding this historical context is crucial for appreciating the complexities of modern military compensation and its role in attracting and retaining skilled personnel. This section provides an overview of the development of military pay from ancient times to the present, highlighting key trends and factors that have shaped its evolution.
Early Military Pay (Pre-20th Century)
Military pay in ancient civilizations was primarily based on subsistence allowances and the spoils of war. In ancient Egypt, for example, soldiers received rations, clothing, and land grants in exchange for their service. The Roman Empire developed a more formalized system, with soldiers receiving regular salaries, known as “stipendium,” which varied based on rank and length of service.
- During the Middle Ages, the feudal system dominated military organization. Knights and other warriors were primarily rewarded with land grants, known as “fiefs,” in exchange for their loyalty and military service.
- As professional armies emerged in the late Middle Ages and early modern period, cash payments became increasingly common. This shift was driven by the need for a more reliable and consistent source of income for soldiers, as well as the growing importance of professional military skills.
The 20th Century and Beyond
The 20th century witnessed a significant transformation in military compensation, driven by the demands of two world wars and the subsequent rise of the modern welfare state. World War I and World War II saw a dramatic expansion of military forces, leading to a need for standardized pay scales and comprehensive benefits to attract and retain large numbers of soldiers.
- The introduction of modern benefits, such as retirement plans, healthcare, and education assistance, became increasingly common in the post-war era. These benefits were designed to enhance the attractiveness of military service and to ensure that soldiers had access to essential services and support.
- Military pay and benefits have also been influenced by factors such as inflation, economic conditions, and geopolitical events. During periods of high inflation, military pay scales have often been adjusted to maintain the purchasing power of soldiers. Similarly, economic downturns can lead to increased demand for military service, potentially resulting in higher pay and benefits.
Contemporary Military Pay
Today, military pay scales and benefits vary significantly across different branches of the military, reflecting the unique demands and requirements of each service. However, all branches offer competitive salaries, comprehensive benefits packages, and opportunities for career advancement.
- Military pay is structured based on rank, time in service, and other factors, such as deployment and special skills. Soldiers are also eligible for a range of benefits, including healthcare, housing allowances, retirement plans, and education assistance.
- Military compensation plays a crucial role in attracting and retaining qualified personnel. In a competitive labor market, the military must offer competitive salaries and benefits to attract and retain talented individuals.
- Despite the efforts to provide competitive compensation, there are ongoing debates and challenges related to military pay. Some argue that military pay is not keeping pace with inflation or with salaries in the private sector. Others raise concerns about the cost of military compensation and the need for greater efficiency and accountability.
| Era | Key Features | Notable Changes |
|---|---|---|
| Ancient Civilizations | Subsistence allowances, spoils of war | Introduction of standardized pay scales |
| Medieval Europe | Feudal system, land grants | Transition to cash payments, emergence of professional armies |
| 19th Century | Regular salaries, pay based on rank | Increased emphasis on benefits, introduction of retirement plans |
| 20th Century | Standardized pay scales, comprehensive benefits | Expansion of benefits, adjustments to inflation |
| 21st Century | Competitive salaries, comprehensive benefits | Focus on attracting and retaining talent, addressing cost concerns |
12. International Comparisons
Comparing the pay and benefits of O-1 officers in the United States with other countries provides valuable insights into the global landscape of military compensation. This analysis helps understand the factors influencing these differences and their implications for recruitment and retention in various military forces.
12.1 Pay and Benefits Comparison
This section compares the pay and benefits of O-1 officers in the United States with those in the United Kingdom, Germany, and India. These countries represent diverse military structures and economic contexts, offering a comprehensive comparison. Data for this analysis is sourced from government websites, international organizations like the OECD and World Bank, and reputable research institutions.
| Country | Salary (USD) | Housing Allowance | Healthcare Benefits | Retirement Plan | Other Benefits |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| United States | $42,000 – $50,000 | Varies based on location and family size | Comprehensive healthcare for service members and families | Defined benefit pension plan | Educational benefits, life insurance, disability benefits |
| United Kingdom | £30,000 – £38,000 | Provided for service members in official accommodation | National Health Service (NHS) coverage | Defined contribution pension plan | Travel allowance, childcare assistance |
| Germany | €40,000 – €48,000 | Housing allowance provided based on rank and family size | Universal healthcare coverage | Defined contribution pension plan | Education subsidies, travel benefits |
| India | ₹500,000 – ₹600,000 | Housing provided in military quarters | Military-run healthcare system | Defined benefit pension plan | Canteen facilities, subsidized food, travel benefits |
12.2 Factors Influencing Compensation Differences
Several factors contribute to the variations in military compensation across nations. These include economic, political, social, and military structural factors.
- Economic Factors:
- GDP per capita: Countries with higher GDP per capita tend to offer higher military compensation to attract and retain skilled personnel.
- National Debt: High national debt can strain government budgets, potentially limiting resources for military compensation.
- Economic Growth: Strong economic growth can support higher military spending, leading to improved compensation packages.
- Political Factors:
- Military Spending Priorities: Countries with significant security threats or global military ambitions often allocate more resources to defense, impacting compensation levels.
- Political Stability: Stable political environments tend to foster predictable and sustainable military compensation policies.
- Public Opinion: Public support for military service can influence government decisions regarding compensation levels.
- Social Factors:
- Social Welfare Systems: Countries with comprehensive social welfare systems may offer less generous military benefits, as some needs are already met through social programs.
- Cost of Living: Higher cost of living in certain regions can necessitate higher military compensation to ensure a reasonable standard of living.
- Cultural Perceptions of Military Service: Societies with a strong tradition of military service may offer higher compensation to reflect the value placed on military contributions.
- Military Structure:
- Size and Structure of the Armed Forces: Larger and more complex military forces may require higher compensation to attract and retain personnel across various specialties.
- Deployment Frequency: Frequent deployments can impact compensation levels, as countries may offer additional incentives or allowances for those serving in high-risk or demanding environments.
- Career Paths: Well-defined career paths and opportunities for advancement can influence compensation, as service members are motivated by potential for future growth.
12.3 Implications for Recruitment and Retention
International comparisons of military compensation have significant implications for recruitment and retention. Understanding these implications is crucial for military leaders to develop effective strategies to attract and retain qualified personnel.
- Attractiveness of Military Service: Comparisons of pay and benefits can influence the attractiveness of military service in different countries. Higher compensation packages can make military service more appealing, especially in countries where alternative career options are readily available. Conversely, lower compensation levels may lead to challenges in attracting and retaining skilled personnel, particularly in competitive labor markets.
- Strategies for Recruitment and Retention: Countries can implement various strategies to improve recruitment and retention in light of international comparisons. These strategies include:
- Salary Adjustments: Increasing base salaries to match or exceed compensation levels in comparable countries can enhance competitiveness.
- Enhanced Benefits Packages: Offering more comprehensive benefits, such as improved healthcare, retirement plans, and educational opportunities, can attract and retain personnel.
- Career Development Programs: Investing in robust career development programs can provide service members with opportunities for growth and advancement, boosting morale and retention.
- Improved Work-Life Balance: Implementing policies that support work-life balance, such as flexible work arrangements and childcare assistance, can make military service more attractive to individuals with family commitments.
- Public Relations Campaigns: Promoting the value of military service and highlighting the benefits of a military career can increase public support and encourage recruitment.
- Potential Risks and Challenges: Relying heavily on international comparisons can present certain risks and challenges. These include:
- Unrealistic Expectations: Setting compensation levels based solely on international comparisons without considering domestic economic and social factors can lead to unsustainable financial burdens.
- Competition for Resources: Focusing on increasing military compensation may divert resources from other critical areas, such as training, equipment, and infrastructure.
- Impact on Military Culture: Excessive emphasis on compensation can potentially erode the values of service and commitment that are essential for military effectiveness.
Ethical Considerations
The ethical considerations surrounding military pay and benefits are complex and multifaceted. While the military serves a vital role in protecting national security, the compensation and benefits provided to service members raise important questions about fairness, equity, and the balance between service and reward.
The Relationship Between Compensation and Responsibility
The principle of fair compensation for military service is rooted in the idea that those who risk their lives and make significant sacrifices for the nation deserve appropriate recognition and support. However, determining what constitutes “fair” compensation is a subject of ongoing debate. Some argue that military pay should be competitive with comparable civilian jobs, considering the risks and demands of military service.
Others contend that the inherent value of service to the nation transcends financial considerations and that the benefits package, including healthcare, education, and retirement, should be prioritized. This debate highlights the tension between the financial aspects of military service and the intangible values of patriotism, duty, and sacrifice.
Potential Impact of Pay Disparities on Morale and Service Commitment, O1 military rank 2024 pay chart
Pay disparities within the military can create tensions and affect morale. If service members perceive that their pay is not commensurate with their responsibilities or that there are significant discrepancies between different ranks or specialties, it can lead to feelings of dissatisfaction, resentment, and a decline in service commitment. For example, if a junior enlisted member with a high level of training and experience feels underpaid compared to a civilian counterpart with similar skills, they might be less inclined to re-enlist or remain in the military.
Essential FAQs
What is the difference between base pay and allowances?
Base pay is the fixed amount of money an O-1 officer receives based on their rank and years of service. Allowances are additional payments provided to cover specific expenses, such as housing, food, or clothing.
How can I access the official 2024 military pay charts?
The official 2024 military pay charts are available on the Defense Finance and Accounting Service (DFAS) website. You can also access this information through the Department of Defense (DoD) website.
What are the eligibility requirements for special pay and allowances?
Eligibility for special pay and allowances varies depending on the type of pay or allowance. Factors such as years of service, deployment status, location, and specific duty assignments may influence eligibility. Refer to official military regulations for detailed eligibility criteria.
What are some common challenges faced by O-1 officers?
O-1 officers often face challenges related to balancing leadership responsibilities with personal life, managing financial obligations, and navigating the complexities of military bureaucracy. They may also experience difficulties in obtaining promotions and navigating career progression.
What resources are available for O-1 officers seeking financial planning advice?
Military OneSource, the Financial Counseling Network, and the National Endowment for Financial Education (NEFE) provide comprehensive financial planning resources tailored for military personnel. These organizations offer budgeting tools, debt management advice, and investment guidance.

Whitney Morris is a renowned author with a passion for military history and strategic analysis. Born in Jakarta, Indonesia, Defense developed a deep fascination for warfare and national defense from a young age. His unwavering interest in military strategy, combined with his natural storytelling ability, has earned him a reputation as an engaging and insightful writer in the field.