Army regulation 600 8 10 leaves and passes – Army Regulation 600-8-10: Leaves and Passes is a comprehensive guide outlining the rules and procedures for Army personnel seeking time away from duty. This regulation covers various leave types, pass options, and the processes involved in obtaining approval for these absences.
From the intricacies of leave accrual and usage to the procedures for emergency requests, AR 600-8-10 provides a detailed framework for managing time off within the military context.
Understanding this regulation is crucial for all Army personnel, as it governs their ability to take time away from duty for personal reasons, family obligations, or simply to rest and recharge. Whether it’s a vacation, a visit to family, or a medical appointment, AR 600-8-10 ensures that leave and pass requests are processed fairly and efficiently while maintaining the operational readiness of the Army.
Overview of Army Regulation 600-8-10
Army Regulation 600-8-10, “Leaves and Passes,” Artikels the procedures and guidelines for Army personnel seeking time off from their duties. This regulation ensures that Soldiers receive appropriate rest and recuperation while maintaining operational readiness and unit effectiveness.
Purpose and Scope
AR 600-8-10 establishes the framework for granting leaves and passes to Army personnel. It clarifies the different types of leave and passes available, the procedures for applying and obtaining approval, and the responsibilities of both Soldiers and commanders in managing leave and pass requests.
The regulation applies to all active duty Army personnel, including officers, enlisted Soldiers, and warrant officers.
Key Provisions Regarding Leaves and Passes
AR 600-8-10 lays out a comprehensive set of provisions regarding leaves and passes, encompassing various aspects such as:
- Types of Leave and Passes: The regulation details the different types of leave available, including ordinary leave, emergency leave, convalescent leave, and special leave. It also Artikels the various types of passes, such as weekend passes, day passes, and furloughs.
- Eligibility and Entitlement: AR 600-8-10 specifies the eligibility criteria for different types of leave and passes, including factors such as time in service, performance, and medical conditions. It also clarifies the entitlement to leave based on length of service and other factors.
Army Regulation 600-8-10 outlines the procedures for leave and passes for active-duty soldiers, encompassing various aspects like eligibility, types of leave, and processing procedures. These regulations are crucial for maintaining discipline and ensuring soldiers are adequately rested and prepared for duty.
Soldiers stationed at army barracks saugus massachusetts are subject to these regulations, just as soldiers stationed at any other military installation. Therefore, understanding and adhering to the guidelines laid out in AR 600-8-10 is paramount for all soldiers, regardless of their location or assignment.
- Leave and Pass Procedures: The regulation Artikels the steps involved in requesting and obtaining leave or a pass, including the required forms, the approval process, and the responsibilities of commanders and Soldiers in managing leave requests.
- Leave and Pass Administration: AR 600-8-10 addresses the administrative aspects of leaves and passes, including the documentation required, the tracking of leave and pass periods, and the procedures for reporting absences.
- Leave and Pass Restrictions: The regulation Artikels specific restrictions on leaves and passes, such as limitations on the amount of leave that can be taken at a time, the timing of leave requests, and the conditions under which leave can be revoked.
Types of Leave and Passes
AR 600-8-10 defines various types of leave and passes to cater to different needs and situations of Army personnel. These include:
Leave
- Ordinary Leave: This type of leave is granted for rest and recuperation, personal reasons, or to attend to family matters. Ordinary leave is typically granted for a period of up to 30 days at a time.
- Emergency Leave: This leave is granted for unforeseen circumstances, such as family emergencies, illness, or death in the family. Emergency leave can be granted for any period deemed necessary by the commander.
- Convalescent Leave: This leave is granted to Soldiers who are recovering from an illness or injury. Convalescent leave is typically granted for a period of up to 30 days at a time.
- Special Leave: This leave is granted for specific reasons, such as to attend a wedding, funeral, or to participate in a special event. Special leave is typically granted for a period of up to 15 days at a time.
Passes
- Weekend Passes: These passes are granted to Soldiers to spend time off-duty on weekends. Weekend passes are typically granted for a period of 48 hours or less.
- Day Passes: These passes are granted to Soldiers to spend time off-duty during the day. Day passes are typically granted for a period of 24 hours or less.
- Furloughs: These passes are granted to Soldiers for extended periods of time, typically for 30 days or more. Furloughs are usually granted for family emergencies, medical reasons, or to attend to personal matters.
Types of Leave
AR 600-8-10 Artikels various types of leave authorized for Soldiers, each serving a distinct purpose and requiring specific eligibility criteria. This section delves into the details of each leave type, providing a comprehensive understanding of their applications and processes.
Regular Leave
Regular leave is the most common type of leave granted to Soldiers. It allows them to take time off for personal reasons, such as vacation, visiting family, or attending personal appointments.
Eligibility Criteria
Soldiers are generally eligible for regular leave after completing their initial training and upon meeting the following criteria:
- Completion of the probationary period (typically 90 days) for new recruits.
- Completion of any required training or duty assignments.
- No outstanding disciplinary actions or pending investigations.
Procedures for Applying
Soldiers must submit a leave request through their chain of command, typically through a DA Form 31 (Leave and Pass Request). The request should specify the intended purpose of the leave, the requested dates, and any supporting documentation, such as travel itineraries or medical appointments.
Duration
The duration of regular leave is determined by the Soldier’s length of service and is subject to unit mission requirements. Generally, Soldiers are entitled to a minimum of 14 days of regular leave per year, with the maximum duration increasing with years of service.
Emergency Leave
Emergency leave is granted in situations where a Soldier needs to address an urgent family emergency, such as a serious illness, death, or natural disaster.
Eligibility Criteria
Emergency leave is granted when a Soldier’s immediate family member experiences a critical situation requiring their presence. This typically includes:
- Spouse or children.
- Parents, siblings, or grandparents.
- Other close relatives living in the same household.
Procedures for Applying
Soldiers requesting emergency leave must provide sufficient documentation to support their request, such as a medical certificate, death certificate, or news reports. The request is processed through the chain of command and may be expedited depending on the urgency of the situation.
Duration
The duration of emergency leave is typically limited to the time required to address the emergency. It can range from a few days to a few weeks, depending on the circumstances.
Special Leave
Special leave is granted for specific purposes, such as attending a wedding, funeral, or a court appearance.
Eligibility Criteria
Soldiers can apply for special leave for events that are not covered by regular leave, such as:
- Attending a wedding or funeral of a close family member.
- Appearing in court as a witness or defendant.
- Participating in a civic or community event.
- Undergoing medical treatment that cannot be performed during duty hours.
Procedures for Applying
Soldiers requesting special leave must provide supporting documentation, such as a wedding invitation, death certificate, or court summons. The request is processed through the chain of command and requires approval from the unit commander.
Duration
The duration of special leave is determined by the specific purpose of the leave and is subject to unit mission requirements. It is typically granted for a short period, ranging from a few days to a week.
Convalescent Leave
Convalescent leave is granted to Soldiers who require time to recover from an illness or injury.
Eligibility Criteria
Soldiers are eligible for convalescent leave if they are:
- Hospitalized or undergoing medical treatment.
- Recovering from a significant injury or illness.
- Unable to perform their military duties due to medical reasons.
Procedures for Applying
Soldiers requesting convalescent leave must provide medical documentation from a qualified medical professional. The request is processed through the chain of command and requires approval from the unit commander.
Duration
The duration of convalescent leave is determined by the severity of the illness or injury and the medical recommendations. It can range from a few days to several weeks, depending on the individual’s recovery progress.
Educational Leave
Educational leave is granted to Soldiers who are pursuing higher education.
Eligibility Criteria
Soldiers can apply for educational leave if they are:
- Enrolled in a recognized educational institution.
- Pursuing a degree or certification program.
- Meeting the requirements for educational leave as Artikeld in AR 600-8-10.
Procedures for Applying
Soldiers requesting educational leave must provide documentation from their educational institution, including course schedules and transcripts. The request is processed through the chain of command and requires approval from the unit commander.
Duration
The duration of educational leave is typically limited to the time required to complete the educational program. It can range from a few weeks to several months, depending on the course load and program duration.
Other Types of Leave
AR 600-8-10 also Artikels other types of leave, including:
- Pass:A short-term absence from duty, typically for a few hours or days, granted for personal reasons or to attend official events.
- Permissive TDY:Temporary duty assignments that are authorized for specific purposes, such as attending training courses or conferences.
- Home Leave:Granted to Soldiers stationed overseas to visit their families in their home country.
Procedures for Applying for Leave

Applying for leave is a standard process for Soldiers. The process ensures that leave requests are processed efficiently and that Soldiers are granted leave in a timely manner. It also helps to ensure that units are adequately staffed during leave periods.
Submitting a Leave Request
The process for submitting a leave request begins with the Soldier completing the appropriate form. The form details the requested leave period, the type of leave, and the Soldier’s intended destination. The Soldier then submits the request to their unit leadership for approval.
- Soldiers must submit a DA Form 31, Application for Leave, Pass, or Permit, to their unit leadership.
- The DA Form 31 requires the Soldier to provide information about their leave request, including the type of leave, the dates of leave, the reason for leave, and the Soldier’s intended destination.
- The Soldier’s unit leadership will review the leave request and ensure that it meets all applicable regulations.
- If the leave request is approved, the unit leadership will forward the request to the appropriate approving authority.
Unit Leadership’s Role in Leave Approval
Unit leadership plays a crucial role in the leave approval process. They ensure that the Soldier’s leave request meets the unit’s operational needs and that the Soldier’s absence will not negatively impact the unit’s mission. They also verify the Soldier’s eligibility for leave and ensure that the Soldier has met all the requirements for leave.
- Unit leadership will review the Soldier’s leave request to determine if it is appropriate and if the Soldier meets all the requirements for leave.
- They will also consider the unit’s operational needs and ensure that the Soldier’s absence will not negatively impact the unit’s mission.
- If the unit leadership approves the leave request, they will forward the request to the appropriate approving authority.
Approving Authority
The approving authority for leave requests varies depending on the type of leave and the Soldier’s rank. For example, the unit commander can approve leave for Soldiers below the rank of sergeant, while the battalion commander can approve leave for Soldiers above the rank of sergeant.
- The approving authority will review the leave request and ensure that it meets all applicable regulations.
- They will also consider the unit’s operational needs and ensure that the Soldier’s absence will not negatively impact the unit’s mission.
- If the approving authority approves the leave request, they will sign the DA Form 31 and return it to the Soldier.
Leave Accrual and Usage
Leave accrual and usage are critical aspects of Army personnel management, ensuring soldiers have time for rest, personal matters, and family commitments while maintaining operational readiness. Understanding the regulations governing leave accrual and usage is crucial for both soldiers and their supervisors.
Leave Accrual
Leave accrual for Army personnel is calculated based on their length of service. Soldiers earn 2.5 days of leave per month for the first 10 years of service. After 10 years, they accrue 3.0 days per month. Leave accrual is calculated on a monthly basis, regardless of whether a soldier is on leave or performing duty.
Leave accrual is calculated on a monthly basis, regardless of whether a soldier is on leave or performing duty.
Leave Usage
Leave usage is subject to various regulations to ensure fair and equitable access to leave while maintaining operational readiness.
Leave Restrictions
- Maximum Leave Balance:The maximum leave balance a soldier can accrue is 60 days. Any leave exceeding this limit is forfeited.
- Leave Limits:The amount of leave a soldier can take at one time depends on their leave balance and the operational requirements of their unit. For example, a soldier with a leave balance of 30 days can take up to 30 days of leave at one time.
However, commanders can restrict leave based on unit mission requirements.
- Emergency Leave:Emergency leave can be granted for urgent personal or family matters, regardless of the soldier’s leave balance. However, emergency leave must be approved by the soldier’s commander.
Consequences of Exceeding Leave Limits or Abusing Leave Privileges, Army regulation 600 8 10 leaves and passes
Exceeding leave limits or abusing leave privileges can result in disciplinary action, including:
- Article 15:A non-judicial punishment for minor offenses. This can include loss of privileges, extra duty, and reduction in rank.
- Court-Martial:A judicial process for more serious offenses. This can result in a variety of punishments, including imprisonment, dishonorable discharge, and loss of pay.
- Administrative Action:This can include reprimands, letters of counseling, and other administrative actions.
Passes: Army Regulation 600 8 10 Leaves And Passes
Passes are temporary authorizations granted to Soldiers for a specific purpose and duration. They are distinct from leave, which is authorized absence from duty for personal reasons. Passes are generally used for short-term absences, often for a few hours or days, and are typically granted for specific purposes, such as visiting family, attending appointments, or conducting personal business.
Types of Passes
Passes are categorized based on their purpose and duration.
- Regular Pass:A Regular Pass is the most common type of pass, granted for various reasons, including visiting family, attending social events, or conducting personal business. It is typically granted for a duration of up to 72 hours, but the specific duration is determined by the approving authority.
- Emergency Pass:An Emergency Pass is granted for urgent situations requiring a Soldier’s immediate absence from duty. These situations may include family emergencies, medical appointments, or other unforeseen circumstances. Emergency passes are typically granted for a shorter duration than Regular Passes, depending on the urgency of the situation.
- Weekend Pass:A Weekend Pass is granted to Soldiers for the purpose of spending time off-duty during weekends. This type of pass is typically granted for a duration of 48 hours, starting on Friday evening and ending on Sunday evening.
- Special Pass:A Special Pass is granted for specific purposes that do not fall under the categories of Regular, Emergency, or Weekend Passes. This could include attending a training course, participating in a competition, or performing other official duties that require a Soldier’s absence from their assigned unit.
Eligibility Criteria and Procedures
The eligibility criteria and procedures for applying for passes vary depending on the type of pass and the Soldier’s unit. However, generally, all Soldiers are eligible to apply for passes, subject to the approval of their unit commander or designated authority.
- Regular Pass:To apply for a Regular Pass, a Soldier typically submits a request to their unit commander or designated authority. The request should include the purpose of the pass, the requested duration, and the Soldier’s intended destination. The approving authority will review the request and determine if the pass is warranted and if the Soldier’s absence will not negatively impact unit operations.
- Emergency Pass:To apply for an Emergency Pass, a Soldier must provide documentation or evidence supporting the urgency of the situation. This could include a doctor’s note, a family member’s statement, or other relevant documentation. The approving authority will review the request and determine if the pass is justified based on the provided documentation.
- Weekend Pass:The eligibility criteria and procedures for applying for a Weekend Pass are generally the same as for a Regular Pass. However, the approving authority may consider factors such as unit operational requirements and the Soldier’s duty schedule when determining whether to grant a Weekend Pass.
- Special Pass:To apply for a Special Pass, a Soldier must submit a request that clearly Artikels the purpose of the pass, the duration required, and any relevant supporting documentation. The approving authority will review the request and determine if the pass is warranted and if the Soldier’s absence will not negatively impact unit operations.
Restrictions and Limitations
There are certain restrictions and limitations associated with passes, depending on the type of pass and the Soldier’s unit. These restrictions may include:
- Geographical Limitations:Some passes may be restricted to specific geographical areas. For example, a Soldier may be granted a pass to visit their family in a nearby city, but not to travel to a different state.
- Duration Limitations:The duration of a pass is typically limited to a specific timeframe, depending on the type of pass and the approving authority.
- Operational Requirements:If a Soldier’s absence from duty would negatively impact unit operations, the approving authority may deny the pass request.
- Security Restrictions:Some passes may be restricted due to security concerns. For example, a Soldier may not be granted a pass to travel to a foreign country if their clearance level is insufficient.
Emergency Leave and Passes

Emergency leave and passes are granted to Soldiers facing urgent personal or family situations requiring immediate attention. These situations necessitate immediate action to address a critical personal need, prevent undue hardship, or ensure the well-being of the Soldier or their family.
Procedures for Requesting Emergency Leave or Passes
To request emergency leave or a pass, Soldiers must follow specific procedures Artikeld in AR 600-8-10.
- The Soldier must submit a written request to their unit commander, detailing the nature of the emergency and the need for immediate leave or a pass. This request should be clear, concise, and supported by relevant documentation.
- The unit commander reviews the request and determines if the situation qualifies for emergency leave or a pass. They may require additional documentation or information to verify the urgency of the situation.
- If the commander approves the request, they will issue the necessary orders or authorization for the Soldier to proceed on emergency leave or a pass. The commander will also notify higher headquarters of the emergency leave or pass granted.
Criteria for Granting Emergency Leave or Passes
The criteria for granting emergency leave or passes are based on the severity of the situation and the potential impact on the Soldier and their family. The following factors are considered:
- The nature of the emergency: The emergency must be a genuine and urgent situation requiring immediate action.
- The impact on the Soldier and their family: The emergency must pose a significant risk to the Soldier’s well-being or the well-being of their family.
- The Soldier’s ability to return to duty: The Soldier must be able to return to duty within a reasonable timeframe after the emergency is addressed.
- The unit’s operational requirements: The unit’s mission and operational requirements must be considered when granting emergency leave or passes.
Documentation Required to Support an Emergency Leave or Pass Request
To support their request, Soldiers must provide appropriate documentation to verify the emergency. The required documentation may vary depending on the nature of the emergency. Common examples include:
- Medical documentation: If the emergency involves a medical situation, the Soldier must provide medical documentation from a qualified healthcare provider. This documentation should include the diagnosis, prognosis, and recommended treatment plan.
- Legal documentation: If the emergency involves a legal matter, the Soldier must provide legal documentation from a qualified attorney or court official. This documentation should include the nature of the legal matter, the status of the case, and any court orders or deadlines.
- Family documentation: If the emergency involves a family member, the Soldier must provide documentation verifying the family relationship and the nature of the emergency. This documentation may include birth certificates, marriage certificates, or death certificates.
Leave and Pass Administration
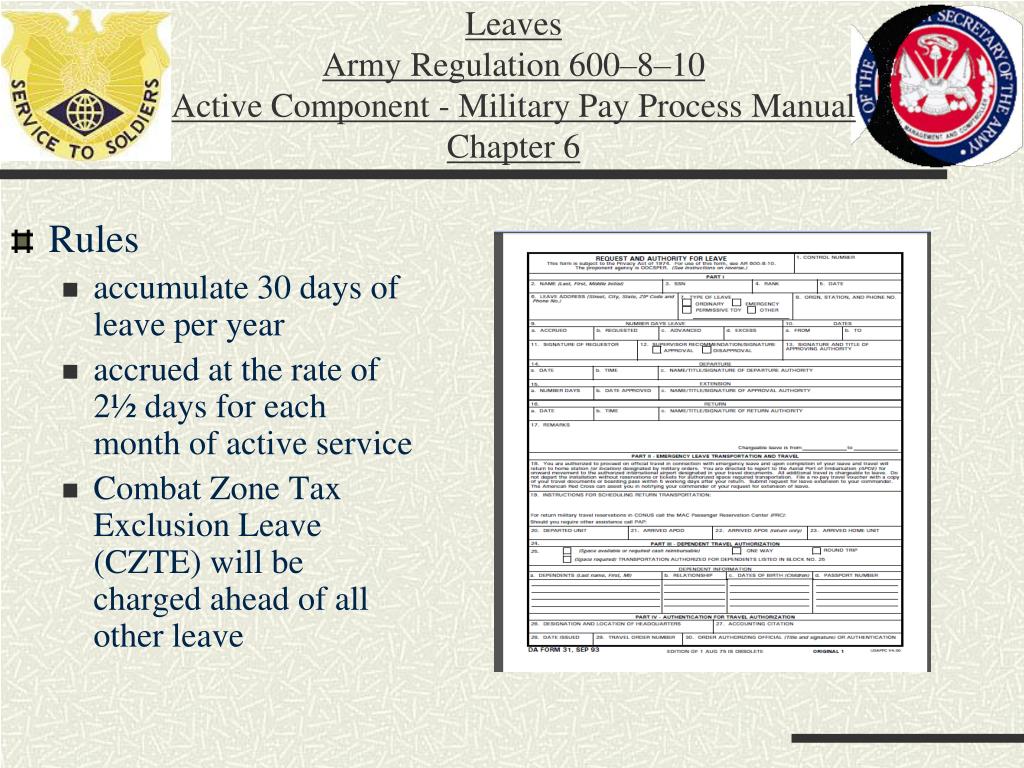
The efficient administration of leave and passes is crucial for maintaining unit readiness and ensuring Soldiers have the opportunity to rest and recharge. This section Artikels the responsibilities of unit leaders and other personnel involved in leave and pass administration, details the procedures for tracking leave and pass requests, and explains the role of the Army’s leave and pass system in managing these requests.
Responsibilities of Unit Leaders and Personnel
Unit leaders and other personnel play critical roles in the administration of leave and passes. They are responsible for ensuring that leave and pass requests are processed promptly and accurately, and that Soldiers are informed of their leave and pass entitlements.
- Unit Commanders: Unit commanders are responsible for approving or disapproving leave and pass requests. They must ensure that the requests are in accordance with applicable regulations and that the unit’s mission will not be compromised by the Soldier’s absence.
- First Line Supervisors: First line supervisors are responsible for ensuring that Soldiers understand their leave and pass entitlements, and for providing guidance on the process for requesting leave and passes. They also play a role in ensuring that Soldiers are properly briefed on their responsibilities while on leave or pass.
- Personnel Clerks: Personnel clerks are responsible for processing leave and pass requests, maintaining leave and pass records, and ensuring that Soldiers’ leave and pass balances are accurate. They also provide guidance to Soldiers on leave and pass procedures.
Procedures for Tracking Leave and Pass Requests
The Army has established a system for tracking leave and pass requests to ensure that they are processed efficiently and accurately.
- Leave and Pass Requests: Soldiers must submit a leave and pass request through their chain of command. The request should include the dates of the leave or pass, the reason for the leave or pass, and any other relevant information.
- Leave and Pass Approval: The Soldier’s unit commander or designated representative is responsible for approving or disapproving the leave or pass request. The approval or disapproval should be documented in the Soldier’s personnel records.
- Leave and Pass Tracking: The Army uses a variety of systems to track leave and pass requests. These systems include the Army’s Integrated Personnel and Pay System (IPPS-A), which tracks leave and pass balances, and the Army’s Leave and Pass System (ALPS), which is used to manage leave and pass requests.
Role of the Army’s Leave and Pass System
The Army’s leave and pass system is designed to manage leave and pass requests and ensure that Soldiers have the opportunity to rest and recharge. The system also ensures that the unit’s mission is not compromised by the absence of Soldiers on leave or pass.
- Leave Accrual: The Army’s leave and pass system tracks the accrual of leave for Soldiers. Leave accrual is based on the Soldier’s rank and length of service.
- Leave Usage: The system also tracks the usage of leave by Soldiers. This information is used to ensure that Soldiers are not exceeding their leave balances.
- Pass Requests: The system also manages requests for passes. Passes are short-term absences from duty for personal reasons.
Impact of Leave and Passes on Military Operations

Leave and passes, while essential for the well-being of service members, can have a significant impact on unit readiness and operational effectiveness. Striking a balance between the need for rest and recuperation and the demands of military service is crucial for maintaining a capable and resilient force.
Balancing Rest and Recuperation with Operational Demands
The Army recognizes the importance of providing service members with adequate time for rest and recuperation. Leave and passes allow soldiers to recharge, reconnect with family and friends, and address personal matters, which are essential for maintaining morale, mental health, and overall well-being.
However, the absence of personnel due to leave can impact unit readiness and operational effectiveness, particularly during periods of high operational tempo or deployments.
- Impact on Training and Readiness:The absence of personnel during training exercises can disrupt the flow of training and reduce the effectiveness of unit cohesion and proficiency. This can lead to a decrease in overall unit readiness and preparedness for operational deployments.
- Impact on Operational Deployment:During operational deployments, the availability of personnel is critical for mission success. Leave and passes can create gaps in manpower, potentially impacting mission execution and compromising the safety of deployed personnel.
Leave and Pass Policies in Response to Operational Needs
The Army has implemented various policies and procedures to manage leave and passes, taking into account the specific needs of military operations. These policies aim to balance the need for rest and recuperation with the demands of military service.
- Leave Restrictions:During periods of high operational tempo or deployments, leave restrictions may be imposed to ensure sufficient personnel are available for mission execution. These restrictions can include limiting the duration of leave, prohibiting certain types of leave, or requiring prior approval for leave requests.
- Pass Restrictions:Pass restrictions may be implemented to limit the movement of personnel outside of designated areas, particularly during periods of heightened security or operational risk. These restrictions can help to maintain unit cohesion and ensure the safety of personnel.
- Flexible Leave and Pass Policies:In recognition of the unique needs of different units and operational environments, the Army has implemented flexible leave and pass policies. These policies allow commanders to tailor leave and pass procedures to meet the specific needs of their units and operations.
For example, commanders may authorize staggered leave periods to ensure a consistent level of manpower throughout the year.
Examples of Leave and Pass Policy Adjustments
- During a deployment to a combat zone, the commander may impose stricter leave restrictions to ensure the availability of personnel for critical missions. This may involve limiting leave to a few days per month or requiring personnel to obtain special approval for any leave request.
- During a training exercise, the commander may authorize a limited number of personnel to take leave to ensure that the exercise can proceed without significant disruption. This may involve prioritizing leave requests for personnel with family emergencies or other pressing personal needs.
- In a garrison environment, the commander may implement a flexible leave policy that allows personnel to take leave at times that are most convenient for them. This may involve allowing personnel to take leave on weekends or holidays or to stagger leave periods to ensure that the unit is always fully staffed.
Historical Context of Leave and Pass Policies
The evolution of leave and pass policies in the United States Army reflects a dynamic interplay between military necessity, societal norms, and the changing nature of warfare. From the early days of the nation to the modern era, these policies have adapted to meet the evolving needs of the military and the well-being of its personnel.
Early Leave and Pass Practices
The early American Army, modeled after the British system, had rudimentary leave and pass policies. Early regulations focused primarily on preventing desertion and ensuring the availability of troops for campaigns. Leave was typically granted for short periods and was often contingent upon the availability of replacements.
Passes were primarily used for short-term absences for personal reasons, such as visiting family or conducting business.
The Civil War Era
The Civil War witnessed a significant increase in the size of the Army and a corresponding need for more formalized leave and pass policies. The Union Army, in particular, implemented more structured regulations to address the logistical challenges of managing a large and dispersed force.
The introduction of furloughs, which allowed soldiers to return home for extended periods, was a significant development. Furloughs were intended to boost morale and recruitment, recognizing the importance of family ties and the need for rest and recuperation.
The concept of “home leave” as a right and a privilege emerged during this period.
The 20th Century and Beyond
The 20th century saw further evolution in leave and pass policies, driven by factors such as the rise of professional armies, the increasing complexity of military operations, and the changing social landscape. The development of the “leave system” as we know it today, with its emphasis on accrued leave and the right to vacation time, occurred during this period.
Key developments include:
- The establishment of a standardized leave accrual system:This ensured that soldiers earned leave time based on their length of service and provided them with predictable periods of time away from duty.
- The recognition of leave as a valuable tool for maintaining morale and readiness:Studies demonstrated the positive impact of leave on soldier well-being, reducing stress and improving performance.
- The introduction of “emergency leave” and ” compassionate leave” provisions:These allowed soldiers to respond to family emergencies or personal crises, reflecting a greater understanding of the importance of family and personal responsibilities.
Rationale for Current Leave and Pass Policies
Current Army leave and pass policies are grounded in several key rationales:
- Maintaining troop morale and readiness:Leave provides soldiers with the opportunity to rest, recharge, and reconnect with family and friends, which contributes to their overall well-being and ability to perform their duties effectively.
- Supporting family and personal responsibilities:Leave allows soldiers to attend to personal and family matters, fostering a sense of balance between military service and personal life.
- Enhancing recruitment and retention:Attractive leave policies are a key factor in attracting and retaining qualified personnel, particularly in a competitive job market.
- Promoting a positive military culture:Leave policies that are fair, transparent, and supportive of soldiers’ needs contribute to a positive and professional military environment.
Detailed FAQs
What happens if I exceed my leave limits?
Exceeding leave limits can have serious consequences, including disciplinary action, potential loss of pay, and even a reduction in rank. It’s essential to carefully track your leave accrual and usage to avoid exceeding your authorized limits.
Can I use leave for personal travel outside the United States?
Yes, you can use leave for personal travel outside the United States, but you must notify your unit and obtain any necessary travel authorizations. Additionally, you may need to comply with specific travel restrictions or regulations depending on your destination.
How long does it typically take for a leave request to be approved?
The processing time for leave requests can vary depending on the unit and the time of year. However, it’s generally advisable to submit your request well in advance of your desired departure date to allow for sufficient processing time.
Can I apply for leave online?
Many units utilize online systems for submitting and tracking leave requests. You should check with your unit leadership for specific procedures and access to online systems.

Emma Nehls is a military writer and historian with a passion for exploring the intricacies of warfare and the human experience within the military. With extensive knowledge and a deep understanding of military strategy, tactics, and historical contexts, Nehls brings a unique perspective to his writings.