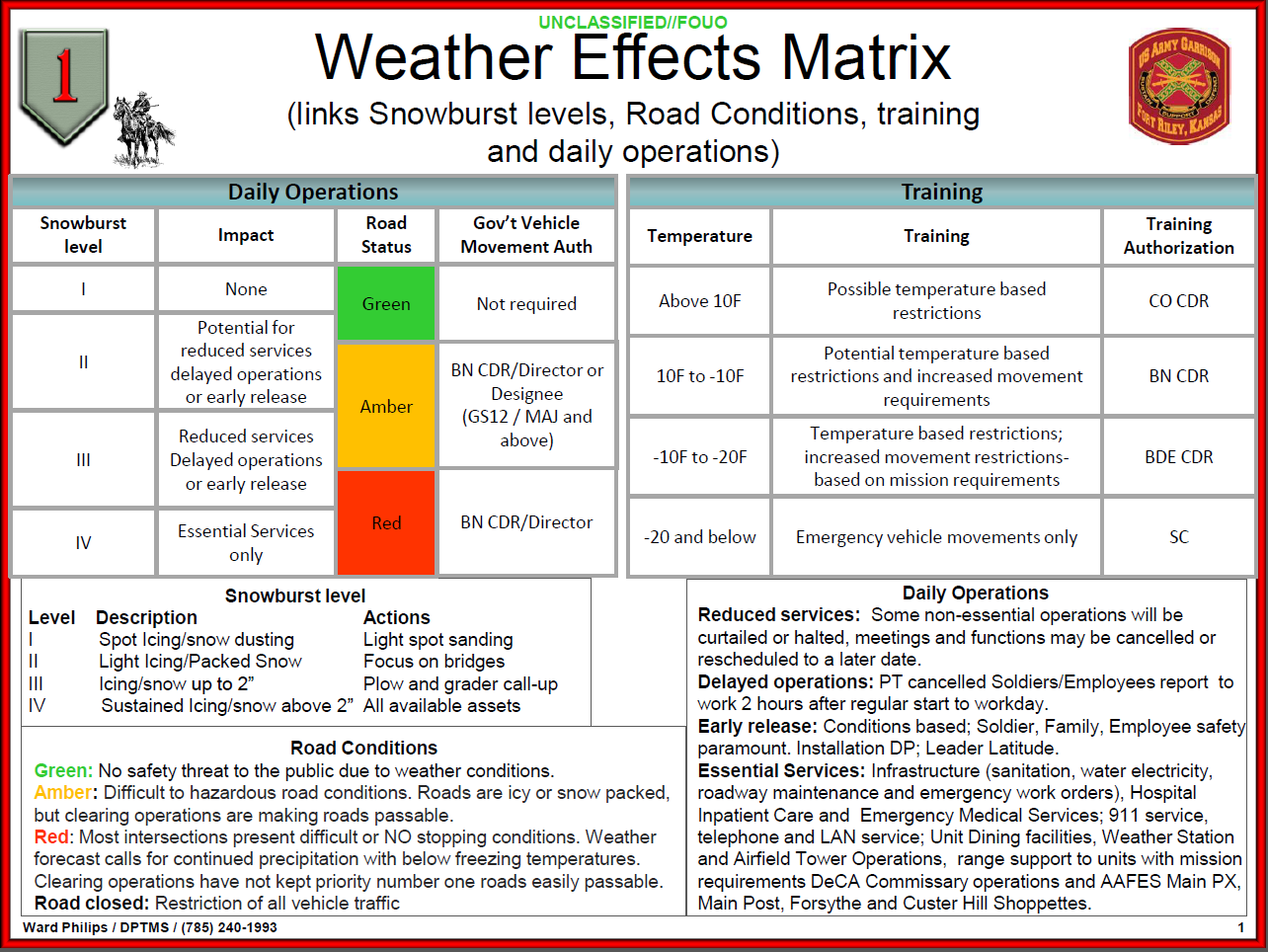
The Army APFU Weather Chart, a cryptic canvas of symbols and lines, holds the key to unlocking the battlefield’s capricious nature. It is a silent sentinel, whispering secrets of temperature, wind, and precipitation, guiding commanders in their strategic dance of maneuver and defense.
This chart, a masterpiece of meteorological shorthand, serves as a compass for military operations, translating the vagaries of the weather into actionable intelligence. It reveals the intricate interplay of atmospheric forces, allowing strategists to anticipate the impact of weather on troop movements, equipment deployment, and even the success of tactical maneuvers.
Understanding the APFU Weather Chart

The APFU (Army Personnel and Family Use) weather chart is an essential tool for military operations, providing crucial information about weather conditions that can significantly impact mission success. It offers a comprehensive overview of various weather elements, allowing commanders and personnel to make informed decisions regarding operations, troop movements, and equipment deployment.
Key Components and Information
The APFU weather chart presents a detailed visual representation of weather conditions, encompassing key elements such as temperature, wind speed, precipitation, and cloud cover. These elements are presented using a combination of symbols, abbreviations, and numerical values.
Temperature
Temperature is depicted on the chart using a color scale, with different colors representing specific temperature ranges. For example, blue might indicate freezing temperatures, while red represents high temperatures. This color-coded system allows for quick and easy identification of temperature variations across different locations and time periods.
Wind Speed
Wind speed is represented using arrows, with the length of the arrow indicating the wind speed. The direction of the arrow shows the direction from which the wind is blowing. For example, an arrow pointing north indicates a wind blowing from the north.
The chart may also include numerical values for wind speed, typically measured in knots or meters per second.
Precipitation
Precipitation is indicated using various symbols, such as raindrops for rain, snowflakes for snow, and hail symbols for hail. The intensity of precipitation is often represented by the size or density of the symbol. For example, larger raindrops might indicate heavy rain, while smaller raindrops represent light rain.
Cloud Cover
Cloud cover is depicted using symbols that represent different cloud types and amounts. For instance, a solid circle might indicate overcast skies, while scattered circles represent scattered clouds. The chart may also include numerical values for cloud cover, typically expressed as eighths of the sky covered by clouds.
So, you’re trying to figure out the best time to hit the beach, right? The Army APFU weather chart is your go-to for that, especially if you’re planning a trip to the islands. But, if you’re looking for something a little more detailed, like the latest on military deployments, check out this army 600-8-22 guide.
It’s packed with info, and trust me, you’ll want to be in the know before you head out on your adventure. Once you’ve got the weather down, you’re good to go!
Symbols and Abbreviations
The APFU weather chart utilizes a standardized set of symbols and abbreviations to ensure clarity and consistency in communication. Understanding these symbols is crucial for interpreting the information presented on the chart.
Temperature Symbols
- °C: Celsius temperature
- °F: Fahrenheit temperature
Wind Speed Symbols
- KT: Knots (nautical miles per hour)
- M/S: Meters per second
Precipitation Symbols
- RA: Rain
- SN: Snow
- GR: Hail
- TS: Thunderstorms
Cloud Cover Symbols
- OVC: Overcast
- SCT: Scattered
- BKN: Broken
- CLR: Clear
Interpreting Weather Data
The APFU weather chart presents a wealth of information about current and forecasted weather conditions. Understanding how to interpret this data is crucial for making informed decisions about military operations.
Identifying Weather Patterns
The APFU weather chart provides a comprehensive view of weather patterns, allowing military personnel to identify potential threats and opportunities.
- Wind Speed and Direction:The chart displays wind speed and direction using arrows and numerical values. Strong winds can affect aircraft operations, artillery fire, and troop movements. Conversely, favorable wind conditions can enhance air operations and artillery accuracy.
- Precipitation:The chart indicates the likelihood and type of precipitation, such as rain, snow, or hail. Precipitation can impact visibility, road conditions, and the effectiveness of certain weapons systems.
- Temperature:The chart shows current and forecasted temperatures, which can influence troop comfort, equipment performance, and the risk of frostbite or heat exhaustion.
- Cloud Cover:The chart displays cloud cover using symbols, indicating the amount of cloud cover and its potential impact on visibility and air operations.
Impact on Military Operations
Weather data can be used to make informed decisions about various aspects of military operations.
- Troop Movements:Heavy rain or snow can make roads impassable, delaying troop movements and disrupting supply lines. Conversely, clear weather conditions allow for rapid troop deployment and maneuver.
- Equipment Deployment:Certain equipment, such as artillery and aircraft, are sensitive to weather conditions. The APFU weather chart helps determine the suitability of equipment deployment based on wind speed, precipitation, and temperature.
- Tactical Planning:Weather conditions can influence the effectiveness of different tactics. For example, a dense fog could hinder visibility and favor ambush tactics, while clear skies would be ideal for air strikes.
Examples of Weather Data Usage
- Desert Storm:During the Gulf War, US military planners used weather data to predict sandstorms, which could have disrupted air operations. By adjusting flight plans and timing, they minimized the impact of these weather events.
- Hurricane Katrina:The US Coast Guard used weather data to predict the path and intensity of Hurricane Katrina, allowing for the timely evacuation of coastal areas and the deployment of rescue teams.
Weather Factors Affecting Military Operations
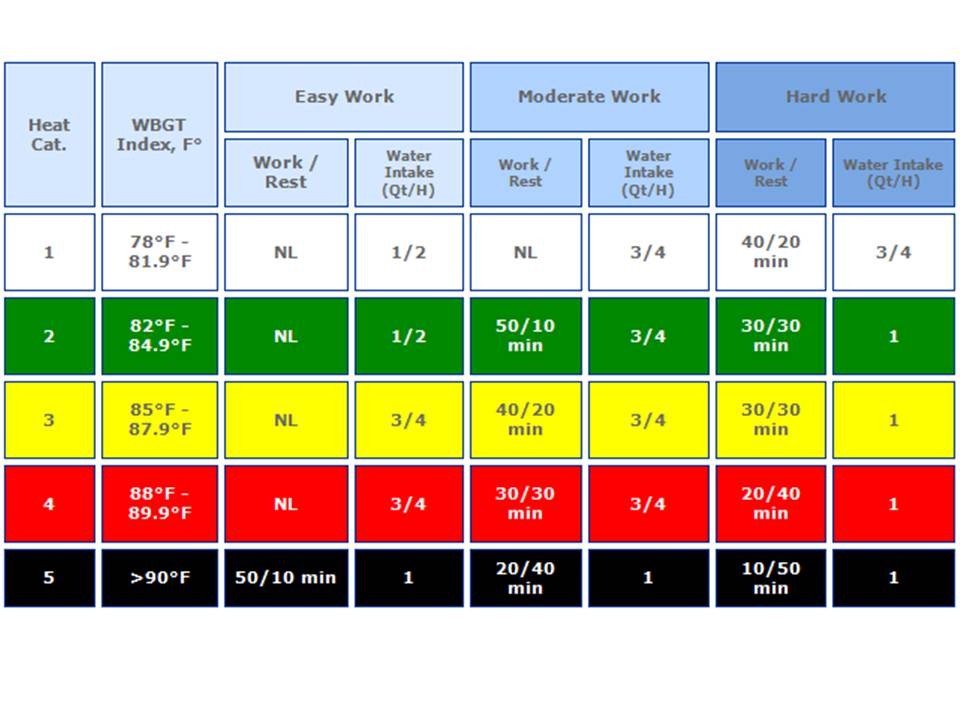
Weather plays a crucial role in military operations, impacting mission success, troop safety, and overall operational effectiveness. Understanding the influence of weather factors is vital for military planners and commanders to make informed decisions and mitigate potential risks.
Impact of Weather Factors on Military Operations
Weather conditions can significantly influence the success or failure of military operations. Understanding the impact of various weather factors is essential for planning, executing, and adapting to changing circumstances. Here’s a breakdown of how specific weather factors affect military operations:
| Weather Factor | Impact on Operations | Example | Mitigation Strategies |
|---|---|---|---|
| Temperature Extremes | Extreme temperatures can affect troop performance, equipment functionality, and overall mission success.
| During the 1991 Gulf War, US troops experienced extreme heat, leading to dehydration and heat exhaustion. |
|
| Wind Gusts | Strong wind gusts can disrupt air operations, affect ground mobility, and compromise communication systems.
| During the 2005 Hurricane Katrina disaster, high winds severely hampered rescue and relief efforts. |
|
| Precipitation | Precipitation can significantly impact visibility, ground mobility, and logistical operations.
| During the 1944 Battle of the Bulge, heavy snow and fog significantly hindered Allied operations. |
|
| Visibility | Limited visibility can significantly impact air and ground operations, increasing the risk of accidents and hindering target acquisition.
| During the 1982 Falklands War, dense fog hampered British air operations, resulting in several aircraft losses. |
|
Using the APFU Weather Chart in Planning: Army Apfu Weather Chart
The APFU weather chart is a valuable tool for military planners, providing crucial information about weather conditions that can significantly impact operations. By understanding and integrating the chart into planning processes, military units can effectively assess weather risks, develop contingency plans, and make informed decisions about mission timing, route selection, and equipment preparation.
Integrating the APFU Weather Chart into Military Planning
The APFU weather chart should be a core component of military planning processes. This involves:
- Early Integration:Incorporate the APFU weather chart into the initial stages of mission planning, alongside other factors such as terrain analysis and enemy capabilities.
- Regular Updates:Monitor weather forecasts and updates regularly throughout the planning process, ensuring the chart reflects the most current and accurate information.
- Collaboration:Facilitate collaboration between planners, weather specialists, and operational units to ensure a comprehensive understanding of weather conditions and their potential impact on the mission.
Assessing Weather Risks and Developing Contingency Plans
The APFU weather chart provides critical data to assess weather risks and develop contingency plans. Here’s how:
- Identifying Potential Hazards:Analyze the chart to identify potential weather hazards such as high winds, heavy precipitation, fog, or extreme temperatures. This allows planners to anticipate potential challenges and develop appropriate responses.
- Evaluating Impact on Operations:Assess how weather conditions could affect specific aspects of the mission, including troop movement, aircraft operations, communications, and logistics. This helps planners develop realistic and adaptable plans.
- Developing Contingency Plans:Based on the assessed weather risks, develop contingency plans for various scenarios. This might involve alternative routes, delaying operations, adjusting equipment, or modifying tactics to mitigate the impact of adverse weather.
Utilizing the Chart to Inform Decisions, Army apfu weather chart
The APFU weather chart is a powerful tool for informing key decisions regarding mission timing, route selection, and equipment preparation:
- Mission Timing:Use the chart to determine the most favorable weather conditions for specific mission objectives. For example, a night operation might be more advantageous in clear skies with low visibility for the enemy.
- Route Selection:Analyze the chart to select routes that minimize exposure to adverse weather conditions. For instance, avoiding high-altitude areas during periods of heavy snowfall or choosing routes with less exposure to strong winds.
- Equipment Preparation:Utilize the chart to identify necessary equipment modifications or adjustments based on anticipated weather conditions. This could involve preparing for extreme cold, using waterproof gear, or ensuring communication systems are weather-resistant.
Weather Forecasting and Prediction

Accurate weather forecasting is crucial for military operations, as it allows commanders to anticipate potential challenges and plan accordingly. Weather conditions can significantly impact the success of missions, from troop movements to air operations.
Meteorological Models and Satellite Imagery
Meteorological models are complex mathematical equations that simulate atmospheric processes. They use data from various sources, including weather stations, radar, and satellites, to predict future weather conditions. Satellite imagery provides real-time snapshots of cloud cover, precipitation, and other weather phenomena, offering valuable insights for weather forecasting.
Accuracy and Limitations of Weather Forecasts
Weather forecasts are not always perfect. Their accuracy depends on factors such as the complexity of the weather system, the quality of input data, and the limitations of the forecasting models. While forecasts can be quite accurate for short-term predictions, they become less reliable as the forecast horizon extends.
The accuracy of weather forecasts is typically higher for short-term predictions (e.g., 12-24 hours) and decreases as the forecast horizon extends.
Continuous Weather Monitoring and Updates
Military operations often require constant awareness of changing weather conditions. Continuous weather monitoring involves the use of automated weather stations, radar systems, and satellite imagery to provide real-time updates on weather patterns. This information is crucial for making informed decisions regarding mission planning, troop movements, and logistical operations.
Continuous weather monitoring and updates are essential for military operations, as they provide a dynamic understanding of evolving weather conditions.
Essential Questionnaire
What does APFU stand for?
APFU stands for “Army Personnel and Family Weather Unit.”
Is the APFU Weather Chart used in all branches of the military?
While the APFU Weather Chart is primarily used by the Army, similar weather charts and tools are used by other branches of the military as well.
How often is the APFU Weather Chart updated?
The frequency of updates depends on the specific unit and mission, but it is generally updated at least daily, and often more frequently in dynamic weather situations.
Where can I find more information about the APFU Weather Chart?
You can find additional resources and training materials on the Army’s official website and through various military publications.

Whitney Morris is a renowned author with a passion for military history and strategic analysis. Born in Jakarta, Indonesia, Defense developed a deep fascination for warfare and national defense from a young age. His unwavering interest in military strategy, combined with his natural storytelling ability, has earned him a reputation as an engaging and insightful writer in the field.